-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(12): 1863-1866
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.09
Received: Nov. 7, 2023; Accepted: Nov. 28, 2023; Published: Dec. 6, 2023

The Effect of Various Forms of the Drug Litholit-A on the Motor and Behavioral Activity of Experimental Animals
A. A. Gaybullaev, S. S. Kariev, Sh. M. Khalilov
Department of Urology and Andrology, Center of the Development of Professional Qualifications of Medical Workers, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Aim of the research was to study the effect of hydrolate from the medicinal collection on the physiological development and motor-behavioral activity of experimental animals. Introduction. Urolithiasis occurs in 5% of the adult population of the world and continues to grow steadily. The frequency of the disease relapses without secondary prevention reaches 80%. In spite of the expansion of the effective synthetic drugs range, herbal diuretics occupy a significant place in the treatment and prevention of this pathology. Material and methods. The research was conducted on 30 mongrel male rats, aged 8 weeks. The experimental animals were randomly divided into three groups of 10 each. The duration of the experiment was 30 days. To determine the specific activity of the Litholit-A herbal preparation, experiments were carried out according to the methodological manual in accordance with modern recommendations. Results. The medicinal herbal collection and an alcoholic tincture from the medicinal plants of the flora of Uzbekistan was produced for the treatment of urolithiasis (primary and secondary prophylactic of urinary stone formation). Both forms of the drug showed encouraging results for the metaphylaxis of stone formation in the model of calcium urolithiasis. A comparative analysis of the effect of various forms of the developed phytopreparation on the motor and behavioral activity of rats was carried out. The results presented the absence of undesirable effects in all forms of the drug. Conclusion. A new form of the original domestic drug Litholit-A with a 30-day administration of the drug does not significantly affect the overall development and growth of animals. Hydrolate, unlike alcohol extract, does not have an exciting effect on the psychoemotional state, but enhances the function of the gastrointestinal tract. The absence of undesirable effects of hydrolate from the collection indicates the possibility of its long-term use as a diuretic in the complex of preventive and metaphylactic measures at urolithiasis.
Keywords: Herbal diuretics, Phytopreparations, Hydrolate, Experiment
Cite this paper: A. A. Gaybullaev, S. S. Kariev, Sh. M. Khalilov, The Effect of Various Forms of the Drug Litholit-A on the Motor and Behavioral Activity of Experimental Animals, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 12, 2023, pp. 1863-1866. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.09.
1. Introduction
- Urolithiasis occurs in 5% of the adult population of the world and continues to grow steadily. The frequency of the disease relapses without secondary prevention reaches 80% [1-4]. The leading causes of stone formation are functional and metabolic disorders, the correction of which requires long-term treatment. In spite of the expansion of the effective synthetic drugs range, herbal diuretics occupy a significant place in the treatment and prevention of this pathology [5-6].Various forms of phytopreparations such as infusions, tinctures, extracts, and combined remedies are used in practical medicine. Their efficiency usually manifests itself with prolonged use. In this regard, a distinctive feature is the rarity of undesirable effects with prolonged administration [6-7].In the process of studying the anti-lithogenic properties of representatives of the local flora, a diuretic medicinal gather from plants of the local flora was developed at the Department of Urology and Andrology of the Center for the Development of Professional Qualifications of Medical Workers. It consists of Flores millefolii, roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra and leaves of Helichrusum arenarium Samarkand [8]. An alcoholic extract was also purposefully created from this medicinal gather for the treatment of calcium urolithiasis. The diuretic properties of both the infusion and the alcoholic extract from the medicinal gather were confirmed in an experiment on mice and rats. The anti-inflammatory and anti-lithogenic abilities of the extract were revealed on the model of urolithiasis in rats (a significant decrease in the amount of deposits of calcium oxalate in the tubules of nephrons was observed). It was found that in addition to enhancing diuresis, the new preparation improved the condition of the epithelium and had nephroprotective abilities [6]. However, the presence of alcohol in the extract, in our opinion, is undesirable, which was the reason for the creation of a non-alcoholic form - hydrolate (Litholit-A). It was obtained by hydrodistillation: plants were lowered into water, brought to a boil and the resulting condensate was collected. The features of the technological process of preparing hydrolates were an indication for studying the properties and abilities of a new form of the preparation.Aim of the research was to study the effect of hydrolate (Litholit-A) from the medicinal gather on the physiological development and motor-behavioral activity of experimental animals.
2. Material and Methods
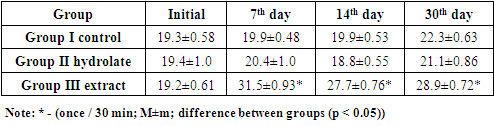
- The research was conducted on 30 male rats, aged 8 weeks. The experimental animals were acclimatized to a room temperature of 22°C with 12 hours of illumination and 12 hours of darkness cycles under vivarium conditions. All rats received standard nutrition throughout the course of the study and had free access to drinking water. Then they were randomly divided into three groups of 10 each: Group I - rats were administered 1.5 ml of distilled water per os 3 times a day; Group II - rats were administered 1.5 ml of hydrolate solution (Litholit-A) from the medicinal gather per os 3 times a day;Group III - rats were administered 1.5 ml of 40% alcohol extract from the medicinal gather. The duration of the experiment was 30 days. To determine the specific activity of the Litholit-A, experiments were carried out according to the methodological manual in accordance with special recommendations [9].The physiological development and motor-behavioral activity of experimental animals were evaluated. The weight and height of the rats were measured before and at the end of the study. The tests "Open field" and "Beam-walking test" were performed to estimate the indicators of motor-behavioral activity, as well as a study of the grooming average frequency. Testing was carried out before the start of taking the drugs, on the 7th and 14th days, and at the end of the study on the 30th day.Ethical expertise. The study was conducted in accordance with the rules adopted by the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals (Strasbourg, 1986).
3. Results
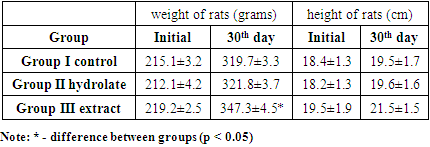
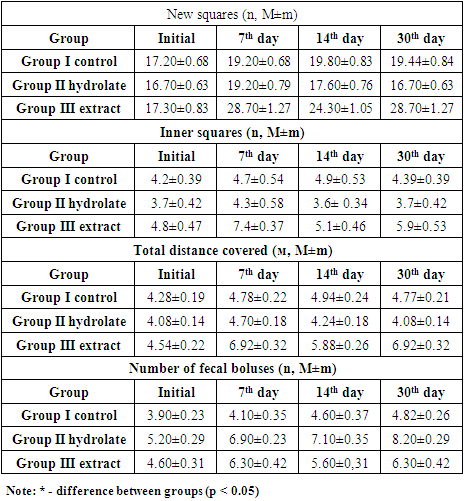
- Evaluation of the drugs effect on the physiological development of rats was studied on the basis of the weight and growth dynamics. These indicators in all groups were increased as they grew older and had no significant difference with the generally accepted criteria for normal development [10]. The difference in weight gain was observed in rats of Group III. Perhaps this is due to metabolic changes in experimental animals because of the presence of alcohol in the extract. Nevertheless, the lack of differences with the literature data indicate the safety of long-term use of the studied drugs in relation to the physiology of experimental animals (Tab. 1).
|
|
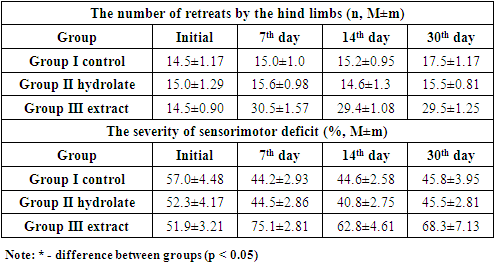
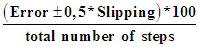 When tested on the "Narrowing path" installation, the number of hind limbs in rats of Group III already on the 7th day of the experiment significantly exceeded the same indicator in Group I (control) and Group II (30.5±1.57 vs. 15.0±1.0 and 15.6±0.98, respectively; p<0.01) with the same test execution time (Tab. 3).
When tested on the "Narrowing path" installation, the number of hind limbs in rats of Group III already on the 7th day of the experiment significantly exceeded the same indicator in Group I (control) and Group II (30.5±1.57 vs. 15.0±1.0 and 15.6±0.98, respectively; p<0.01) with the same test execution time (Tab. 3).
|
|
4. Conclusions
- A new form of the original domestic medicine Litholit-A with a 30-day administration, does not significantly affect the overall development and growth of animals. Hydrolate, unlike alcohol extract, does not have an exciting effect on the psychoemotional state, but enhances the function of the gastrointestinal tract. The absence of undesirable effects of hydrolate from the collection indicates the possibility of its long-term use as a diuretic in the complex of preventive and metaphylaxis measures at urolithiasis.The authors declare no conflict of interest. This study does not include the involvement of any budgetary, grant or other funds. The article is published for the first time and is part of a scientific work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML