-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(12): 1855-1859
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.07
Received: Nov. 3, 2023; Accepted: Nov. 22, 2023; Published: Dec. 2, 2023

An Improved Method for Improving Microcirculation in the Lower Extremities in Patients with Diabetic Angiopathy
Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Republic of Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Republic of Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Introduction. The problem of the occurrence and treatment of purulent-necrotic complications in patients with diabetic foot syndrome (DFS) is far from being solved and, despite the successes of modern medicine, contains a large number of unresolved issues of both theoretical and practical na-ture. In the treatment of diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities, the main attention is paid to the restoration of blood flow and insufficient attention is paid to the elimination of microcirculatory disorders. The purpose of the study. To increase the effectiveness of treatment of patients with dia-betic angiopathy of the lower extremities by improving microcirculation in the periphery of the low-er extremities. Materials and methods of research. The paper analyzes the results of a comprehensive ex-amination and treatment of 322 patients with diabetic foot syndrome (SDS) who were on inpatient treatment in the department of purulent surgery of the Bukhara Regional Multidisciplinary Medical Center in the period from 2017 to 2023. Among the patients, there was a predominance of 221 men (68.6%), 101 women (31.4%). The average age of the patients was 62.5±13.2 years. The duration of diabetes mellitus was 15.13 ± 5.64 g. Results and their discussion. The study of indicators of local cutaneous blood flow was carried out using Doppler flowmetry, which was performed in 126 (91.9%) patients of the main group, and 165 (89.2%) patients of the comparison group. Flowmetry was performed before and af-ter treatment. At rest, basal blood flow (PMIs) was determined and the response to an occlusion test was evaluated. When evaluating the results of the occlusal test, the microcirculation reserve index (RM) was used, calculated as the ratio of the maximum post-occlusal microcirculation index (pmmax.) to the PMisx index. before occlusion. Tmax was also evaluated. – the time required to achieve PMMAX. Patients of both groups before treatment showed a significant decrease in the val-ue of PM when measuring basal blood flow on the foot: 0.72 ± 0.24 pf. units – in the main group and 0.75±0.62 pf. units – in the comparison group. The LDF-grams taken on the ischemic foot were mo-nophasic and low-amplitude. A characteristic feature was the absence of a change in the PM value in response to an occlusive test. Conclusions. The effect of electromagnet-ic radiation by the Barva-Flex photonic matrix emitter significantly increases basal blood flow and increases the reserve capabilities of the microcirculatory bed.
Keywords: Diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities, Electromagnetic radiation, BarvaFlex
Cite this paper: Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich, An Improved Method for Improving Microcirculation in the Lower Extremities in Patients with Diabetic Angiopathy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 12, 2023, pp. 1855-1859. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231312.07.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The problem of the occurrence and treatment of purulent-necrotic complications in patients with diabetic foot syndrome (DFS) is far from being solved and, despite the successes of modern medicine, contains a large number of unresolved issues of both theoretical and practical nature. In the treatment of diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities, the main attention is paid to the restoration of blood flow and insufficient attention is paid to the elimination of microcirculatory disorders [8,10,11,13]. The existing methods of conservative and physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are often ineffective and are of an auxiliary nature. The state of nutritive blood flow and the dynamics of interstitial oxygen tension in conditions of critical ischemia have been poorly studied [2,9,12]. There are many unresolved questions about the role of a systemic inflammatory reaction and its effect on the course of ischemia of the limb [4,7,14]. There is practically no data on the effect on the microcirculatory bed of leukocyte-thrombocyte conglomerates formed in conditions of systemic inflammation, and existing works are fragmentary, contradictory and interpreted ambiguously [1,5]. The peculiarities of the local inflammatory reaction, as well as the course of wound infection in conditions of tissue ischemia, are insufficiently covered. To date, no clear algorithm has been developed for the treatment of purulent-necrotic complications in patients with diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities [3,6]. Given the unresolved nature of these problems, the goals and objectives of studying the local influence of electromagnetic radiation on the course of the wound process are predetermined.
2. The Purpose of the Study
- To increase the effectiveness of treatment of patients with diabetic angiopathy of the lower extremities by improving microcirculation in the periphery of the lower extremities.
3. Materials and Methods of Research
- The paper analyzes the results of a comprehensive examination and treatment of 322 patients with diabetic foot syndrome (SDS) who were on inpatient treatment in the department of purulent surgery of the Bukhara Regional Multidisciplinary Medical Center in the period from 2017 to 2023. Among the patients, there was a predominance of 221 men (68.6%), 101 women (31.4%). The average age of the patients was 62.5±13.2 years. The duration of diabetes mellitus was 15.13 ± 5.64 g.E. Wagner's classification (1979) was used to determine the degree of lesion of the foot tissues. Patients underwent ultrasound Dopplerography and color duplex mapping of the vessels of the lower extremities, radiography of the foot. The state of carbohydrate metabolism was monitored in the laboratory. Wound healing was assessed according to laser do-pler flowmetry.All patients were divided into two groups: the main group and the comparison group. The main group consisted of 137 (42.5%) patients, and the comparison group of 185 (57.4%) patients. Both groups were comparable in gender, age, and degree of trophic changes. Patients of both groups received traditional treatment: daily correction of glucose levels with constant laboratory monitoring, metabolic drugs (alpha-lipoic acid preparations, B vitamins), disaggregants, angiotropic drugs, dressings with adhesive dressings, antibacterial therapy was adjusted taking into account the isolated microflora and its sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs.Patients of the main group, in addition to standard conservative therapy, were exposed to the popliteal pits by electromagnetic radiation with a photonic matrix emitter "Barvaflex" (Fig. 1). A patent for the invention was obtained for this method by the Intellectual Property Agency of the Republic of Uzbekistan (IAP 07441).
 | Figure 1. Korobov photonic matrix emitter "Barva-Flex/SIK" |
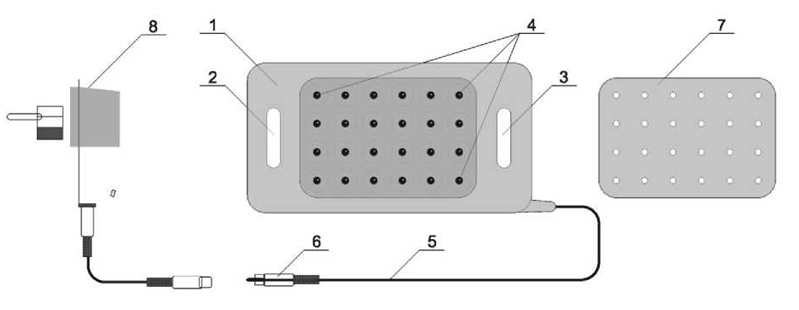 | Figure 2. Scheme of photonic and magnetic matrices "Barva-Flex" (description in the text) |
4. Results and Their Discussion
- The study of indicators of local cutaneous blood flow was carried out using Doppler flowmetry, which was performed in 126 (91.9%) patients of the main group, and 165 (89.2%) patients of the comparison group. Flowmetry was performed before and after treatment. At rest, basal blood flow (PMIs) was determined and the response to an occlusion test was evaluated. When evaluating the results of the occlusal test, the microcirculation reserve index (RM) was used, calculated as the ratio of the maximum post-occlusal microcirculation index (pmmax.) to the PMisx index. before occlusion. Tmax was also evaluated. – the time required to achieve PMMAX. Patients of both groups before treatment showed a significant decrease in the value of PM when measuring basal blood flow on the foot: 0.72 ± 0.24 pf. units – in the main group and 0.75±0.62 pf. units – in the comparison group. The LDF-grams taken on the ischemic foot were monophasic and low-amplitude. A characteristic feature was the absence of a change in the PM value in response to an occlusive test. Decomposition of LDF-grams into their component harmonics using wavelet analysis showed the absence of amplitudes of microcirculatory rhythms. The occlusion test revealed a significant decrease in PM in both groups (86.3±13.6% – in the main group and 79.4±21.5% – in the comparison group, with a norm of 246.7± 28.3%), an elongation of Tmax.Up to 182.6±34.5 and 176.8±27.3 s, respectively. The performed direct revascularization led to short-term venous hypertension, the phenomena of which significantly decreased in patients exposed to electromagnetic radiation by a photonic matrix emitter "Barvaflex". Analysis of LDF-grams after treatment indicated an improvement in tissue blood flow in patients of both groups, but its severity differed (Fig. 3).
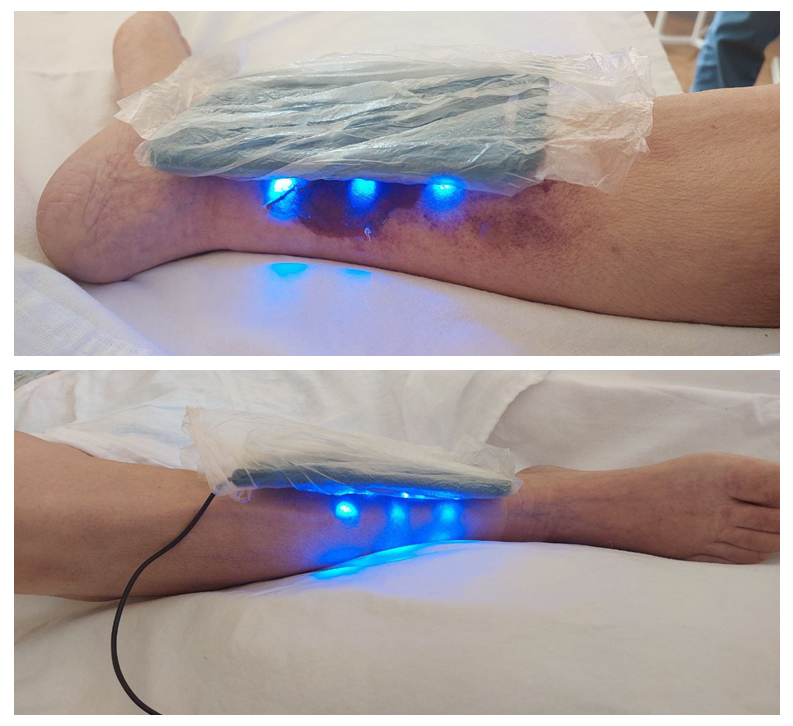 | Figure 3. Application of a patient with a neuroischemic form of SDS by electromagnetic radiation with a photonic matrix emitter "Barva-Flex" |
|
5. Conclusions
- A method for the treatment of diabetic angiopathy, including physical impact on the affected area, physical impact is electromagnetic radiation by a photonic matrix emitter "Barva-Flex" with 24 LED emitters, with wavelengths in the range of 600-570 nm, in pulse mode (total pulse power of 120 watts per pulse), which is carried out in contact, on the area of popliteal pits, medial surface of the ankle joints, calf muscles, pain points in the foot area for 2-3 minutes per field, up to 20 minutes per procedure, for a course of 10-12 daily procedures. The effect of electromagnetic radiation by the Barva-Flex photonic matrix emitter significantly increases basal blood flow and increases the reserve capabilities of the microcirculatory bed.Information about the source of support in the form of grants, equipment, and drugs. The authors did not receive financial support from manufacturers of medicines and medical equipment.Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML