Tillaeva Ziyoda, Shaykhova Guli
Department of Hygiene of Children, Adolescents and Nutrition of Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Tillaeva Ziyoda, Department of Hygiene of Children, Adolescents and Nutrition of Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
An environment that provides good physical and psycho-emotional development helps to favorably develop the child population and shape health. Children in preschool educational institutions spend a significant part of their waking hours, which requires a favorable environment in it. Today, according to hygienic standards, the territory of kindergartens should be safe and contribute to the harmonious development of the child. This requirement is especially relevant in connection with unfavorable indicators of the health of children already at the stage of preschool childhood.
Keywords:
Preschool educational institution, Children, Territory, Architecture, Project
Cite this paper: Tillaeva Ziyoda, Shaykhova Guli, Hygienic Justification and Comparison of the Territory of Public and Private Preschool Educational Institutions, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 11, 2023, pp. 1697-1702. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231311.23.
1. Introduction
Preschool age is a period of perception of knowledge, abilities, skills, those foundations of development that are formed throughout the entire period of a person’s life, as well as the formation of health [1]. Today's modern world requires in preschool buildings a bright architectural and artistic image, comfort, elegance, which will cause a positive visual reaction in preschool children, by attracting attention, interest, creative thinking and imagination [6]. In recent years, one can notice many changes in the field of architectural space for preschool education, which forces us to make optimal decisions on the formation of the structural and environmental organization of the architecture of preschool educational institutions. Outdated and incorrectly designed architectural and planning projects for the territory of preschool educational institutions do not always allow children to fully express their energy, which leads to frequent fatigue and a weakened immune system. The child strives for active action, communication, self-expression and vivid impressions; children play, breathe fresh air, and feel more free. And this reason becomes paramount to meet the needs of children. Unfortunately, when designing walking areas, not all the potential that the sites could have is realized [4]. This article examines the territory’s standards according to SanPin No. 0355-18 “On the content, structure and organization of the operating mode of preschool educational institutions in the Republic of Uzbekistan” [5]. Studying the hygienic standards of the architectural space of public and private preschool institutions will help identify shortcomings and develop a new architectural and planning project for the territories of the preschool educational institution.
2. Purpose of the Research
Justification and comparison of public and private preschool institutions to ensure learning and healthy development for kindergarten students.
3. Materials and Methods
The research materials were data from the territory of the State preschool educational institution No. 459 of the Yangi Khayot district and the private preschool educational institution “Astera” of the Sergeli district, Tashkent city, as well as SanPin No. 0355-18.
4. Results and Discussion
When studying the territories of preschool educational institutions of the State and private type, special attention was paid to the street network, the location of residential buildings, the direction of the main pedestrian paths, the general system of green architecture, as well as the legal use of the sector when locating group rooms and playgrounds, as well as natural resources, which are located on the site and nearby [5].There are State and variable forms of preschool educational institutions. A state preschool educational institution is an organization funded and managed by the state that provides preschool educational services for the development of preschool children [2].Variable forms of preschool institutions are variations of educational preschool institutions, which are state or municipal structural units of the preschool education system. Variable forms of preschool institutions carry out educational activities and implement general educational programs of preschool education [3].We studied (Table 1) State preschool educational institution (SPEI) No. 459 and private preschool educational institution “Astera” in the city of Tashkent.Table 1. Indicators of State preschool educational institution No. 459 and private kindergarten “Astera”
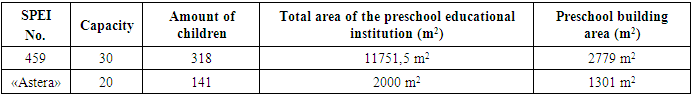 |
| |
|
The SPEI is located in the Yangi Hayet district, located on the intra-block territory of a residential microdistrict, remote from city streets, and has a separate area of 11,751.5 m2. Outside the territory there are no sanitary protection zones of enterprises, sanitary gaps from garages, parking lots, highways, railway transport facilities, subways, take-off and landing routes of air transport. The building area is 2779 m2, the capacity of each group cell is 30 children. At the moment, SPEI No. 459 has 318 students, 12 groups. (Table 1).The private preschool educational institution "Astera" located in the "Sergeli" district of the city of Tashkent, is also located on the intra-block territory of a residential microdistrict, remote from city streets, and has a separate area of 2000 m2. The building area is 1301 m2, the capacity of each group cell is 20 children. Currently there are about 141 children in the kindergarten. Outside the territory there are no sanitary protection zones of enterprises, sanitary gaps from garages, parking lots, highways, railway transport facilities, subways, take-off and landing routes of air transport. The studied data meets sanitary requirements.The state preschool educational institution (Table 2,3,4,5) has two main buildings (buildings), which consists of two floors each. The territory of the State Educational Institution is fenced with a fence 2.20 m high. The radius of pedestrian accessibility is 3200 m. In addition to the main building, the territory includes playgrounds (gazebos), a general physical education area, there is also a splash pool and a utility area where a catering unit, a laundry room, and a vegetable pantry are located, electrical panel and waste collection area with containers. The distance of intra-block waste sites is 50 m from the border of the preschool educational institution.Table 2. The area of land allocated for each object within the territory of a public and private preschool educational institution
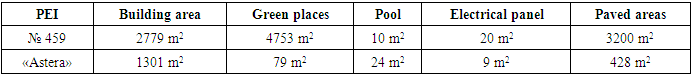 |
| |
|
Table 3. Sanitary and hygienic justification for the radius of pedestrian accessibility, the distance of garbage sites and the height of the fence
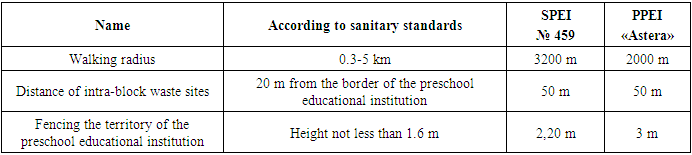 |
| |
|
Table 4. Number of objects and their area (m2) within the territory SPEI No. 459
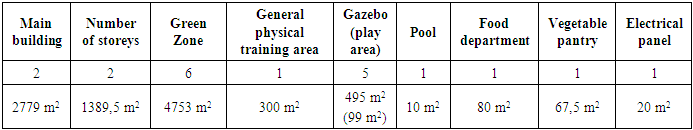 |
| |
|
Table 5. Number of objects and their area (m2) within the territory PPEI"Astera"
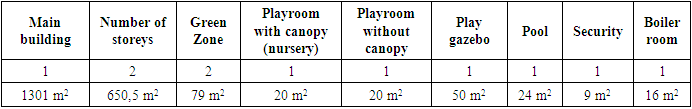 |
| |
|
The private preschool educational institution consists of one building with two floors, the territory is fenced with a fence 3 m high, the radius of pedestrian accessibility is 2000 m. On the territory of the preschool educational institution there are two small playgrounds, the first of them with a canopy, intended for toddlers, the second interactive playground without The canopy is intended for preschool children; in addition to the playgrounds, there is one large playhouse, a small building for security and a boiler room. There is also a splash pool (collapsible) and a waste collection area located in the backyard of the building. The catering unit, laundry room and food pantry are located inside the building. The distance of intra-block waste sites is 50 m from the border of the preschool educational institution.In addition, we studied the areas of the main elements of the preschool educational institution (Fig. 1,2), where you can see the percentage ratio of buildings, green areas and ground coverage with asphalt or paving stones. On the territory, the green area of the SPEI is 42%, the area of all buildings is 30% and the asphalt areas are 28% of the entire territory. In SPEI, all studied indicators comply with sanitary standards. (Figure 1).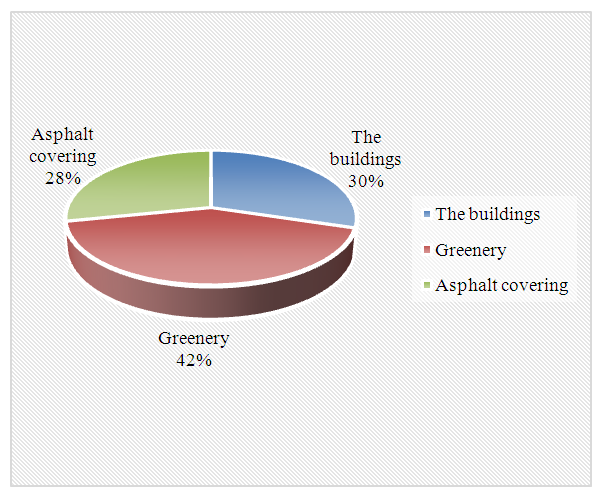 | Figure 1. The area of the main elements of the State preschool educational institution No. 459 |
On the territory of the PPEI, the green part is 4%, the area of buildings is 69% and the area covered with paving stones is 27% of the entire territory. It should be noted that in private educational institutions the percentage of landscaping is 26% lower, since greenery in preschool educational institutions must be at least 30%. The building takes up most of the area, and the area is insufficient for children to be active outdoors (Figure 2).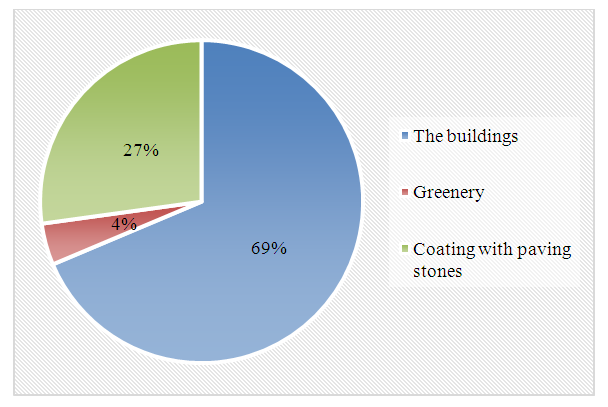 | Figure 2. The area of the main elements of the private preschool institution “Astera” |
The next stage of the work was the study of landscaping inside and outside the territory of the State and private preschool educational institutions (Table 6). Group playgrounds in the State Educational Institution are fenced with shrubs, have a green protective strip of trees and shrubs around the perimeter of the site, approximately 1.5 m, a green protective strip on the street side is 4 m. The distance of internal trees from the building is 8 m, shrubs are 5 m. Coverage of the physical education area compacted with soil. Landscaping inside and outside the territory of the SPEI complies with sanitary standards.Table 6. Hygienic justification for landscaping and plantings inside and outside the territory of State and private preschool educational institutions
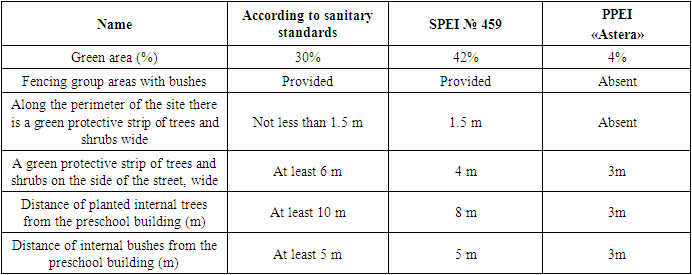 |
| |
|
In PPEI, group sites are not fenced with bushes and do not have a green protective strip along the perimeter of the site. On the street side, the green protective strip is 3 m, the distance of planted trees and shrubs inside the territory from the building is 3 m. The group areas are covered with paving stones, there is no physical training area. Landscaping inside and outside the territory of the PPEI does not meet sanitary standards.When studying the stripes between the elements of the site (Table 7), it was revealed that in the SPEI all the strips between the elements of the site that provide sanitary breaks comply with sanitary requirements, but in the PPEI they are absent.Table 7. Hygienic justification and comparison of strips between elements of the site, providing sanitary breaks
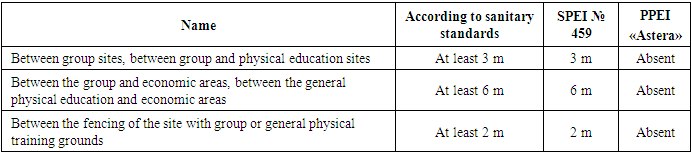 |
| |
|
In SPEI (Table 8), asphalt pavement is not used throughout the entire territory; there are cracks. The play area includes group playgrounds, individual for each group, as well as a general physical education area. The group sites are connected by a 1.5 m wide ring path around the perimeter of the site. The exit from the group areas to the group cells complies with sanitary standards; the group areas have an isolated and shaded part. The shade canopies of the gazebos are 40 m2, the floors in the areas are wooden, 20 cm high from the ground, the shade canopies are fenced on three sides. Each gazebo is divided into two parts in the center, each side is intended for separate groups of 30 children. Each gazebo has shady canopies, block structures, shelves for toys and equipment, and is equipped taking into account age characteristics. The equipment at the site is outdated and does not meet sanitary standards, which makes it more traumatic. The physical training ground is 300 m2, the surface of the ground is hard, it is not equipped for outdoor games, there are no areas with gymnastic equipment and sports equipment, and there is also no running track or jumping pit. The sports ground does not meet sanitary standards.Table 8. Hygienic justification for group sites of preschool educational institutions
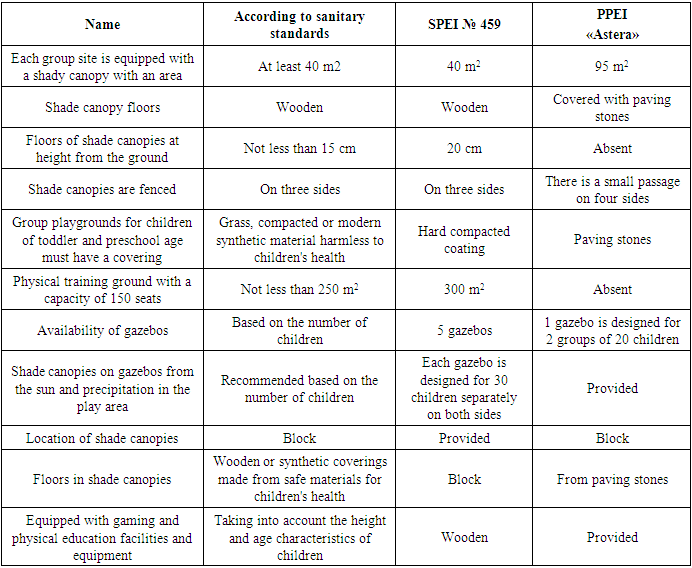 |
| |
|
The territory of the PPEI is covered with paving stones, there are two small playgrounds and one large gazebo with shady block canopies. Playgrounds for toddlers do not have a grass covering, and playgrounds for preschool age are not compacted with soil; the surface of the playgrounds and gazebos is made of hard paving stones - this coating is more traumatic for children of toddlers and preschool age. All group playgrounds are equipped with age-appropriate equipment. The group sites are not connected by circular paths, the exit from the group sites is closer to the group cells, there is both an isolated part and a shaded part in the sites. There is no physical education area at the PPEI, and physical education classes are not held in the yard. Playgrounds do not meet sanitary standards.On the territory of the SPEI there is a splashing pool (Table 9), with an area of 10 m2, variable depth is 0.25 m, access to the splashing pool through a foot bath with running water is not provided, there is a step with a handrail. The pool water is not filtered because the filtration system is outdated.Table 9. Hygienic justification for preschool swimming pools
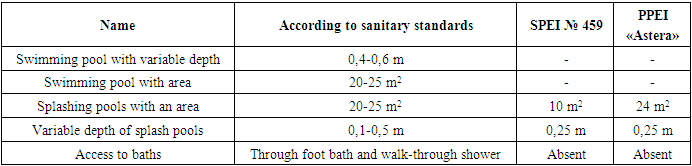 |
| |
|
In the PPEI there is a splash pool (collapsible) with an area of 24 m2, variable depth is 0.25 m, there is no access to baths. The pools in both preschool educational institutions do not meet the hygienic requirements for the design, operation and water quality of swimming pools.The economic zone in the State Preschool Educational Institution (Table 10) is located on the border of the land plot away from group and physical education areas, is fenced with green space, has independent entrance from the street, convenient connection with the catering unit and laundry room. Also in the utility area there is a vegetable storage area, places for drying clothes, beating out carpets and a waste collection area. At the waste collection site there are marked containers with a lid, the ground of the waste site is covered with a hard surface of 1.0 m in all directions. The location of the containers from the preschool educational institution is 30 m. There is also a drainage of water and storm water inside the preschool educational institution, in addition to external electric lighting, there are no areas with sand.Table 10. Hygienic justification for the economic zone in a preschool educational institution
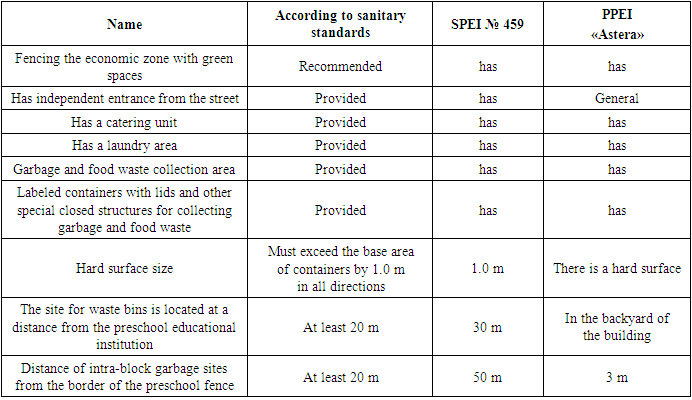 |
| |
|
The utility area in the PPEI is located inside the building on the first floor. There is a laundry room, catering unit, and food pantry. The entrance to the utility area is common; the waste collection area is located in the backyard of the building and is equipped with containers with a lid. There is a dryer on the side of the building. The location of the garbage container in the backyard of the private child care institution does not cause any inconvenience, since there are no windows where the containers are located, there is no provision for drainage of water and storm water, and there is external electric lighting. There are no sandboxes. The indicators of the economic zone in both preschool educational institutions comply with sanitary standards. In both preschool educational institutions, the distance of intra-block waste sites from the border of the preschool educational institution is 50 m.
5. Conclusions
1. In the SPEI, the general physical education area does not meet sanitary standards, since it is not equipped for outdoor games, there are no areas with gymnastic equipment and sports equipment, and there is also no running track and jumping pit. There is no physical education area at the Children's Educational Institution, and physical education classes are not conducted.2. In SPEI, the land is covered with asphalt, 28%, landscaping 42%. In PPEI the land is covered with paving stones 27%, landscaping is 26% lower.3. The economic zone in the State Preschool Educational Institution is located away from group and physical education areas, is fenced with green space, has independent entrance from the street, convenient connection with the catering unit and laundry room. The utility zone in the PPEI is located inside the building. The entrance to the economic zone is general and does not meet hygienic standards.4. There are no sandboxes in both preschool educational institutions.
References
| [1] | Arabadzhi M. N., Belyanskaya S. V. Health saving for early development of children. – 2023. – pp. 14-18. |
| [2] | Veretennikova V. B., Shikhova O. F., Shikhov Yu. A. Taxonomy of educational goals of teachers and parents of preschoolers in the context of the requirements of the federal state educational standard. – 2016. – No. 7 (136). – pp. 88-104. |
| [3] | Kuznetsova G.N., Pedagogical conditions for organizing the social development of young children in a short-term group in a preschool educational institution. – 2011. – No. 38 (255). – pp. 119-125. |
| [4] | Lamekhova N.V. Architectural and spatial aspects of the interaction of the kindergarten building with the site. – 2019. – pp. 245-248. |
| [5] | SanPiN RUz No. 0355-18 “Sanitary and hygienic requirements for the content, structure and organization of the operating mode of preschool educational institutions in the Republic of Uzbekistan.” – 2018. |
| [6] | Stepanova M.I. Modern architecture of kindergartens: new hygienic principles. – 2017. – pp. 225-227. |




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML








