-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(11): 1660-1662
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231311.14
Received: Oct. 12, 2023; Accepted: Nov. 3, 2023; Published: Nov. 8, 2023

Comparative Analysis of General and Biochemical Analysis of Blood, Coagulogram Indicators and Collagen IV in Urine in Patients Diagnosed with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis Due to Chronic Hepatitis B and C
Bakhtiyar Dauletbaev Kochkorovich, Zafar Niyazov Muqimovich, Zulfiya Valieva Sayfitdinovna
Department of Propaedeutic and Internal Medicine, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Cirrhosis of the liver is considered a diffuse process and is characterized by the transformation of its normal structure into fibrous tissue and the formation of regeneration nodules. Every year, 5-7% of patients with liver cirrhosis of various etiologies go to the stage of decompensation. In the scientific research work, 124 of the 350 patients treated at the clinic of the Andijan State Medical Institute, who were diagnosed with advanced liver cirrhosis based on hepatitis V and C, 124 with clinical signs of type II hepatorenal syndrome were observed. The values of collagen IV in urine were 242.33 ± 3.85 μg in liver cirrhosis developed on the basis of viral hepatitis V, and 259.48 ± 3.55 μg in its S form, they were reliably different from each other (R<0.001), and the group after indicators was higher in liver cirrhosis confirmed. This indicates that the fibrosis processes are more rapid in liver cirrhosis developed on the basis of viral hepatitis C.
Keywords: Liver cirrhosis, Biochemical analysis, Collagen IV in urine
Cite this paper: Bakhtiyar Dauletbaev Kochkorovich, Zafar Niyazov Muqimovich, Zulfiya Valieva Sayfitdinovna, Comparative Analysis of General and Biochemical Analysis of Blood, Coagulogram Indicators and Collagen IV in Urine in Patients Diagnosed with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis Due to Chronic Hepatitis B and C, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 11, 2023, pp. 1660-1662. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231311.14.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Liver disease is one of the six leading causes of death among 35-60-year-olds in economically developed countries. 14-30 people per 100,000 inhabitants. Worldwide, 1.4 million people die each year from cirrhosis of the liver (JCs) and its complications. One of the most dangerous complications is hepatorenal syndrome (GRS), which leads to death in most cases. [4,5] Hepatorenal syndrome is a serious complication of the kidney in patients with liver failure due to acute or chronic liver disease, in addition to which other causes of kidney disease leading to kidney failure are not observed. In hepatorenal syndrome, the kidney almost does not change morphologically, the amount of mesangial cells is reduced.There are some observations in the world dedicated to the study of GRS. According to them, approximately 18% of patients with JTs develop GRS in the first years of the disease, reaching 39% by the fifth year. GRS was diagnosed in 17% of patients hospitalized for ascites, and in-hospital mortality in this group exceeded 50%. The development of GRS has been confirmed in patients with a compensated form of liver failure in the presence of predisposing factors such as bacterial infection or sepsis, high-volume paracentesis, gastrointestinal bleeding, nephrotoxic drugs or intensive use of diuretics [9].Clinical symptoms of GRS are growth, azotemia, edema syndrome, ascites, increased urine osmolarity, and hyponatremia. Understanding the collected clinical data, new diagnostic criteria for GRS were developed at the 2005 conference in San Francisco, and recommended by a special group within the International Ascites Club [1]. Medical workers of our republic are faced with a number of tasks, including early detection and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal system, liver and kidneys, and further coordination and adaptation to the requirements of international standards, and positive work is being carried out in this direction. Tasks such as "... increasing the efficiency, quality and popularity of medical care provided to the population in our country, as well as introducing high-tech methods of early diagnosis and treatment of diseases, creating a patronage service, supporting a healthy lifestyle and preventing diseases..." defined. They allow early diagnosis of various diseases and complications caused by them among the population, their prevention and improvement of patients' quality of life [3].
2. Materials and Methods of Research
- In the scientific research work, 124 of the 350 patients treated at the clinic of the Andijan State Medical Institute, who were diagnosed with advanced liver cirrhosis based on hepatitis V and C, 124 with clinical signs of type II hepatorenal syndrome were observed. The following criteria of hepatorenal syndrome, recommended by the "international ascites" club in 1994 and revised and partially modified in 2007, were used to separate them into a separate group.• Liver cirrhosis with ascites;• Serum creatinine level of 133 mmol/l and higher;• Absence of shock symptoms;• The presence of hypovolemia (if no positive changes in kidney function are observed after the cancellation of diuretics for two days and after administration of 1 g of albumin per 1 kg of body weight);• Not taking nephrotoxic drugs at the same time and in the recent past;• Absence of kidney parenchymatous diseases (proteinuria is less than 0.5 g per night, microhematuria is not detected, there are no signs of kidney damage on ultrasound examination).Patients who were diagnosed with hepatorenal syndrome and included in the study were divided into two groups. The first group consisted of 60 patients with liver cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis V, 28 of them were men (46.7%) and 32 women (53.3%), the average age was 46.44±1.38. The second group had liver cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C. It consisted of 64 patients. 3 patients died of esophageal variceal bleeding and 1 of hepatocarcinoma and were not included in the follow-up group. Of the remaining 60 patients, 25 were men (41.6%) and 35 were women (58.4%), the average age was 48.82±1.6. 45% of them were patients with genotype 1, 15% with genotype 2, and 13% with genotype 3. Genotypes were not determined in the remaining cases.Class A according to Child Pugh, class V in 46% and class C in 24% of the observed patients were recorded in 30% of the patients. Based on the goals and tasks set before us, all patients underwent excellent clinical and laboratory-instrumental examinations at the clinic of the Andijan State Medical Institute and were observed in an outpatient setting for 3 months.Eplerenone, spironolactone, glutathione and L-ornithine L-aspartate, which have a hepato-nephroprotective effect, were prescribed to all patients with clinical and laboratory symptoms of hepatorenal syndrome. Based on the instructions, albumin preparations in the amount of 1 mg per 1 kg of body weight were administered intravenously several times. sent.Follow-up criteria: patients diagnosed with advanced liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis V and C.Criteria for exclusion from the study: liver fibrosis developed as a result of chronic heart failure, all diseases leading to nephropathy (autoimmune and systemic diseases, kidney diseases, amyloidosis and related diseases, etc.).All scheduled general and special laboratory-instrumental examinations were performed in the patients under observation, in the first three days of hospitalization before the start of treatment and after 3 months. Patients diagnosed with hepatorenal syndrome received glutathione and L-ornithine L-aspartate, which have nephroprotective and antifibrosis effects, along with the standard treatment used in liver cirrhosis and its complications. Glutathione was given to patients intravenously at a dose of 1.2 g for 10 days, depending on the severity of the disease. then injected intramuscularly at a dose of 0.6 g for a week. L-ornithine L-aspartate was also administered intravenously to patients at a dose of 5 g for 10 days according to the severity of the disease.
3. Results and Discussions
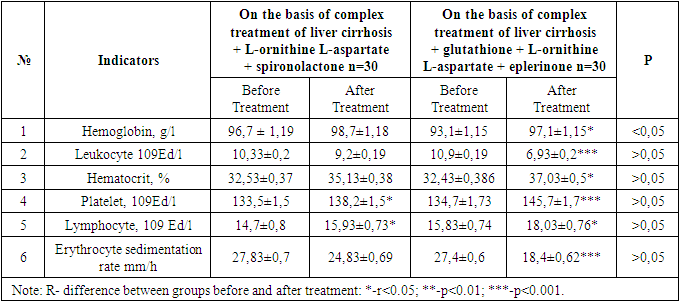
- The results of comparative analysis of patients before and after treatment are presented. Both groups of patients were divided into two subgroups of 30 patients in order to evaluate the effectiveness of complex treatment procedures with different contents. The first subgroups were prescribed spironolactone + L-ornithine L-aspartate on the basis of the complex treatment of liver cirrhosis, and eplerenone + L-ornithine L-aspartate + glutathione drugs were prescribed to the second subgroups on the basis of the complex treatment of liver cirrhosis. Also, the second group of patients were prescribed antiviral drugs in monad doses, taking into account indications and contraindications and taking into account their genotypes. Table 1 shows the results of general blood analysis obtained after complex treatment procedures with various components in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis V.
|
4. Conclusions
- The values of collagen IV in urine were 242.33 ± 3.85 μg in liver cirrhosis developed on the basis of viral hepatitis V, and 259.48 ± 3.55 μg in its S form, they were reliably different from each other (R<0.001), and the group after indicators was higher in liver cirrhosis confirmed. This indicates that the fibrosis processes are more rapid in liver cirrhosis developed on the basis of viral hepatitis C.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML