-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(11): 1628-1634
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231311.08
Received: Oct. 11, 2023; Accepted: Oct. 27, 2023; Published: Nov. 2, 2023

Features of the Course of Cardiovascular Pathology and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with COVID-19
Najmutdinova D. K. , Xudoyberganova Sh. Sh.
Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The relationship between COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus is complicated andbidirectional. On the one hand, diabetes mellitusis conside redone of the most important risk factors for a severe course of COVID-19. Several factors that are often present in diabetes mellitus are likely to contribute to this risk, such as older age, a proinflammatory and hypercoagulable state, hyperglycemia and underlying comorbidities (hypertension, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease and obesity). On the other hand, a severe COVID-19 infection, and its treatment with steroids, can have a specific negative impact on diabetes itself, leading to worsening of hyperglycemia through increased insulin resistance and reduced b-cell secretory function. Worsening hyperglycemia can, in turn, adversely affect the course of COVID-19. Although more knowledge gradually surfaces as the pandemic progresses, challenges in understanding the interrelationship between COVID-19 and diabetes remain.
Keywords: Diabetes, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, Coronavirus, Severity, Mortality, Comorbidities, Treatment
Cite this paper: Najmutdinova D. K. , Xudoyberganova Sh. Sh. , Features of the Course of Cardiovascular Pathology and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients with COVID-19, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 11, 2023, pp. 1628-1634. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231311.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus is a complex chronic disease characterized by glucose dysregulation caused by an absolute or relative insulin deficiency. It includes various different types, with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) as the most prevalent subtypes. T1D is characterized by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic b-cells, while T2D results from a combination of b-cell secretory defect and insulin resistance [1]. The global burden of diabetes is high, with an overall prevalence of 9.3% and 463 million people suffering from the disease worldwide [2]. It is often accompanied by various comorbidities and long-term complications, including obesity, hypertension, vasculopathy, a proinflammatory and hypercoagulable state and cardiovascular disease (CVD) [3-5].In December 2019, the first cases of atypical pneumonia with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were identified. A rapid global spread of the virus led the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a pandemic on March 11th, 2020. Clinical presentation of COVID-19 is diverse and can vary from asymptomatic infection and mild upper respiratory tract symptoms to respiratory failure needing intensive care and death.This review aims to provide an overview and assessment of the bidirectional relationship between COVID-19 and diabetes. On the one hand, diabetes and its associated comorbidities increase the risk of a more severe course of COVID-19 and increased mortality [6]. Patients with diabetes are known to have an increased risk of infections, which is partly attributed to hyperglycemia causing immune dysfunction, among other effects [11-15]. On the other hand, severe SARS-CoV-2 infection and its associated hyperinflammation contribute to hyperglycemia through an indirect negative effect on insulin target tissues and a potential direct negative effect on pancreatic b-cells [16]. The resulting hyperglycemia can, in turn, worsen the prognosis of COVID-19 [17-20]. In this review, we will first discuss the primary risk of COVID-19 infection in patients with diabetes, then the risk of a severe course of COVID-19 with diabetes, followed by the potential additional risk of the most relevant comorbidities and other concomitant factors, and finally the role of glycemic control and the effect of the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself. All studies that were considered relevant for this review were found using PubMed and by cross-referencing.
2. Risk of Infection with COVID-19
- Patients with diabetes are known to have an increased risk of infections, in particular skin infections, genito-urinary tract infections and (bacterial) respiratory tract infections [14]. Hyperglycemia, including the resulting glycosuria,also increases the virulence of certain pathogens [11]. In addition to an increased risk of infection, patients with diabetes also have a higher rate of infection-related hospitalizations as well as infection-related mortality. These risks are present in both T1D and T2D. (15). Importantly, it is well-known that the risk of infections is further increased with poorer glycemic control [12-14].For SARS-CoV-2, clinical reports from all around the world found diabetes mellitus to be one of the most common comorbidities present in patients with COVID-19. In the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, this finding, along with the known increased infection risk for other infections, led to the assumption that patients with diabetes are at increased primary risk of COVID-19 infection. However, most of these reports describe patients in a hospitalized or even intensive care unit (ICU)setting,i.e.patients with a more severe course of the disease.In the first largest consecutive case series from the United States of America (USA), describing 5,700 patients with COVID- 19 admitted to 12 hospitals in the New York area, diabetes mellitus was the third most common comorbidity with 33.8% of patients suffering from the disease, after hypertension (56.6%) and obesity (41.7%) [19]. This series, however, included both patients admitted to the general ward as well as to the ICU and does not distinguish between the two. A meta-analysis of six Chinese studies including 1,527 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 clearly demonstrated the difference between prevalence of diabetes in severe versus non-severe cases, describing a prevalence of diabetes of 11.7% in ICU cases, but 4.0% in non-ICU cases [20]. In another study from China, prevalence of diabetes in 1,590 patients with COVID-19 was 8.2%, rising to 34.6% in patients with a severe course of the disease [16]. In line with this finding, a report of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention on 44,672 COVID-19 cases which also included non-hospitalized patients, showed a lower prevalence of diabetes (5.3%) [20]. Similarly, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported an overall prevalence of diabetes in patients with COVID-19 of 10.9%, with a prevalence of 6.4% in non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients [18]. In a meta-analysis on 33 studies with a total of 16,003 patients, which included 30 studies from China, two from the USA and one from France, the pooled prevalence of diabetes in patients with COVID-19 was 9.8%. Finally, in Italy, a single-center study on 146 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 demonstrated a prevalence of diabetes of 8.9% [10]. With an estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the general population of 10.5% in the USA [11], 11.2% in China [12], 7.6% in France [13], and 8.3% in Italy [14], respectively, the prevalence of diabetes in patients infected with COVID-19 was not higher than in the general population.In summary, based on these studies, the primary risk of infection with COVID-19 does appear to be increased in patients with diabetes mellitus.
3. Risk of a Severe Course of COVID-19
- During previous pandemics, numerous studies have shown that patients with diabetes are a key vulnerable group for a severe course of infections. During the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic, hospitalization of individuals with diabetes was up to six times higher as compared to individuals without diabetes, risk of admission to the intensive care unit was four times higher [17], and risk of death two times higher [18].In China, a nationwide study reported a higher prevalence of diabetes among patients with severe COVID-19 as compared to patients with non-severe disease (16.2% vs 5.7%) [15]. The China Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported a diabetes prevalence of 5.3% among all 44,672 COVID-19 cases, but 19.7% among non-survivors, with a case fatality rate of 2.3% vs 7.3%, respectively. In the USA, among 5,279 patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in a prospective cohort study in New York City, prevalence of diabetes was higher in patients admitted to the hospital than patients not admitted (34.7 vs 9.7%) [7]. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported diabetes prevalence rising with increasing severity of COVID-19, from 6.4% in non-hospitalized patients to 24.2% in hospitalized patients and 32.4% in ICU patients. The most recent report of the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (National Health Institute) in Italy, describing 85,418 patients who died from COVID-19, reported a prevalence of T2D of 29.3%. Although diabetes is an independent risk factor for disease severity [9], of course, patients with diabetes often have other comorbidities or concurrent factors that could add to their increased risk of severe COVID-19.
4. Role of Cardiovascular Risk Factors, (Micro) Vascular Complications and Pharmacologic Treatment
- Several mechanisms have been suggested as an underlying additional explanation for the more severe course of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes. This chapter aims to provide an overview of prognostic factors associated with severity of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes. It focuses on the most relevant factors in the context of diabetes and COVID-19 such as demographic features, cardiovascular risk factors, (micro) vascular complications and pharmacologic treatments. Other comorbidities associated with diabetes mellitus are beyond the scope of this review [5]. In assessing the risk of an individual for a more severe course of COVID-19, it is important to consider these prognostic features, summarized in the top half of Figure 1.
5. Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease
- Among the most commonly described comorbidities present in patients with COVID-19 are hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD), with hypertension being the most common in numerous reports from around the world [6-8]. Hypertension and CVD are also among the most commonly associated comorbidities with diabetes [3,4]. Considering this strong association, and the fact that both hypertension and CVD have been identified as strong independent risk factors for severity of COVID-19 in the general population, it can be safely assumed that they are important concomitant factors adding to the risk of severe COVID-19 in patients with diabetes. Several studies have confirmed this.
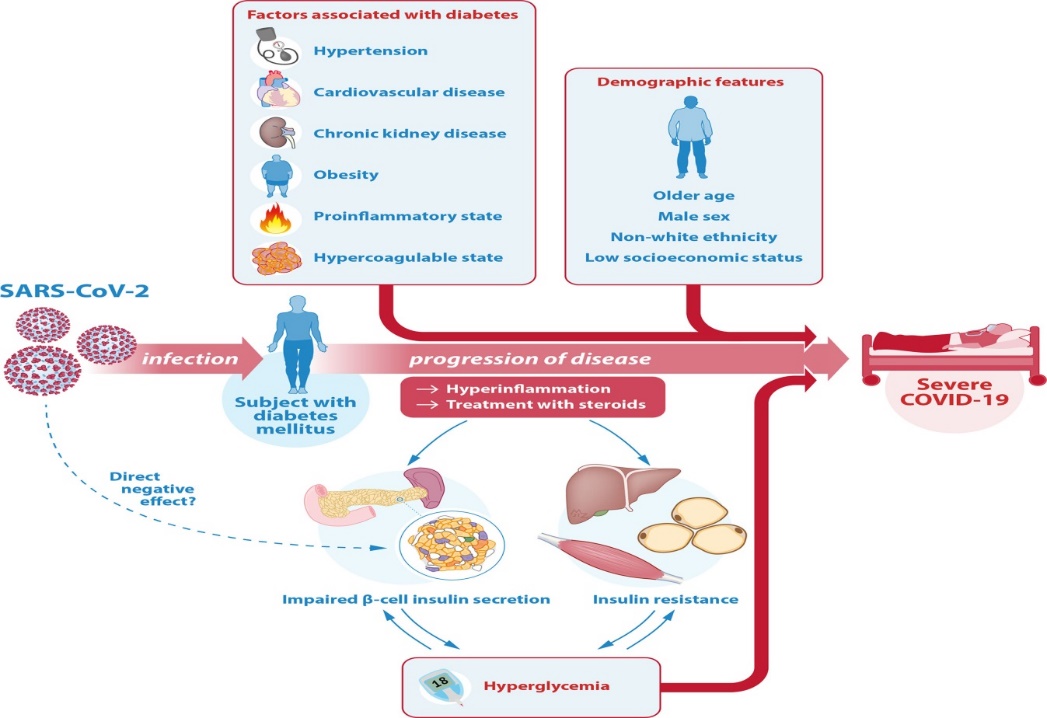 | Figure 1. Illustration of the interrelationship between SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19 and diabetes |
6. Inflammation
- In COVID-19, the most common post-mortem findings include profound inflammation of several tissues [17]. Patients with severe COVID-19, in particular patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, have amarked rise in inflammatory markers such as C- reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer, ferritin and interleukin 6 (IL-6) [8]. An extreme formof hyperinflammation associated with severe COVID-19 is found in some patients who experience a cytokine storm, an uncontrolled state of hyperinflammation resulting in widespread tissue damage, multi-organ failure and death. In several studies, high blood concentrations of inflammatory markers, cytokines and chemokines have been associated with COVID-19 severity and mortality [7,8]. Diabetes is associated with a proinflammatory state, which may contribute to the risk of a more severe course of COVID-19 and a higher risk of experiencing a cytokine storm. The proinflammatory cytokines and toxic metabolites that are present in a cytokine storm are already chronically elevated in individuals with diabetes as part of thelow-gradechronicinflammation. Although understanding the underlying pathogenesis of low-grade inflammation leading to a more rapid progression of COVID-19 and the associated cytokine stormis still subject of research, one of the most important pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the higher risk in patients with diabetes is thought to involve the proinflammatory NF-kappa-B pathway, which is chronically activated in patients with diabetes. Additionally, the low-grade chronic inflammation present in individuals with diabetes is associated with exaggerated macrophage, monocyte and T-cell recruitment, and with decreased regulatory T-cell function, which promotes further inflammation in a continuous feedback cycle. Indeed, in several clinical studies in patients with diabetes and COVID-19, worse inflammatoryprofiles with high erinflammatory markers such as CRP, D-dimer, IL-6 and ferritin were identified compared to patients without diabetes [17,19]. Patients with diabetes were also at a higher risk of excessive uncontrolled inflammation responses. Additionally, elevated CRP and D-dimer levels, as well as higher IL-6, TNF-a and ferritin levels were found in non-survivors as compared to survivors with diabetes. A high CRP was independently associated with increased risk of mortality (OR 1.87) for patients with diabetes hospitalized with COVID-19. Among patients with diabetes, the group most vulnerable to hyperinflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19 consists of the individuals with poor glycemic control, since hyperglycemia stimulates the synthesis and release of cytokines [19].CoagulationCOVID-19 has been widely associated with thromboembolic events such as pulmonary embolism, deep-vein thrombosis (DVT), ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction, which represent a predominant cause of death in patients with severe COVID-19. Similar to the proinflammatory state, diabetes is also associated with a hypercoagulable state. Patients with diabetes in general have an increased risk of thromboembolic events, which, in the case of COVID-19, can add to a high risk of death. Hypercoagulation in COVID-19 is thought to occur due to the profound inflammatory response and cytokine storm observed in some patients. Because patients with diabetes have a more pronounced inflammatory response (see paragraph Inflammation), they may be at greater risk to suffer from thromboembolic events in the case of COVID-19. Another important contributor in patients with diabetes may be hyperglycemia, which was previously shown to further exaggerate coagulation, as well as hyperinsulinemia, which inhibits fibrinolytic activity [16]. In two studies, longer prothrombin times and higher D-dimer concentrations were found in COVID-19 non-survivors as compared to survivors in hospitalized Chinese patients with diabetes. However, this was not the case in the French nationwide cohort study in which D-dimer levels were not a significant predictor of 7-day mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalized with COVID-19 [17]. Apart from these studies describing biochemical outcome parameters such as D-dimer levels, no clinical studies have yet been performed on the prevalence of thromboembolic events in patients with diabetes as compared to patients without diabetes. It could be hypothesized that patients with COVID-19 and diabetes are at higher risk of thromboembolic events, especially when other risk factors such as older age, obesity, inflammation and immobilization due to hospital admission are present.
 | Table 1 |
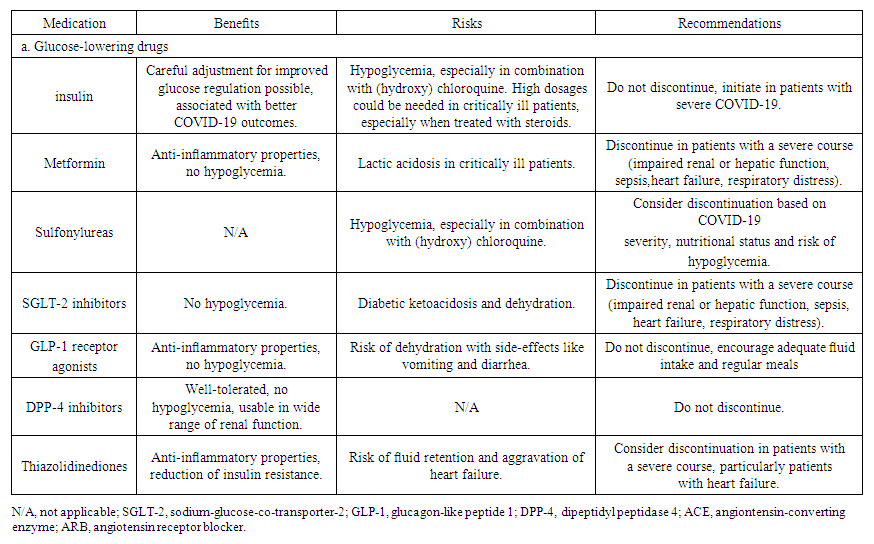
7. Medication
- In addition to diabetes mellitus and the conditions that are associated with the disease, the treatments of these conditions might also increase the risk of a more complicated course of COVID-19, as well as account for drug interactions with treatments given for COVID-19. This gives rise to some specific considerations in patients with diabetes and/or associated comorbidities who are infected with SARS-CoV-2. The benefits, risks and recommendations for each of the treatments are summarized in.Some studies reported that insulin use in patients with diabetes was associated with a greater COVID-19 related morbidity and mortality [21]. Even though in two of these studies adjustment for confounders using multivariable regression models was performed [21], worse outcomes in patients on insulin therapy could be related to confounding by indication, rather than pointing to a harmful effect of insulin. Patients on insulin therapy are more likely to have a more severe and a longer duration of diabetes. In addition, glucose dysregulation, and thus increased use of insulin, occurs with more severe COVID-19 (see paragraph Direct and Indirect Effects of SARS-CoV-2). Indeed, better glycemic control is associated with better COVID-19-related outcomes (see paragraph Glycemic Control). In one study, treatment with insulin was associated with achievement of glycemic targets and improvement of COVID-19-related outcomes in patients hospitalized with the disease. The French nationwide cohort study also did not find any significant association between insulin use and increased mortality [21]. Moreover, the Italian case-control study on patients with T2D hospitalized with COVID-19 and T2D controls without COVID-19 even demonstrated a lower prevalence of basal insulin use in those hospitalized (OR 0.18), after adjustment for cardiovascular, pulmonary and kidney disease.Patients with COVID-19 that were treated with metformin have been reported to have better outcomes including reduced mortality and lower levels of inflammation in studies using univariable, as well as adjusted multivariable analyses [22]. However, because of the anti-inflammatory, cell-protective and important glucose regulatory effects of metformin without risk of hypoglycemia, it has been suggested to maintain metformin treatment in all patients hospitalized with COVID-19, provided they have not developed kidney or liver failure.With contradictory evidence, it is still unclear whether sulfonylureas are associated with increased morbidity or mortality in patients with COVID-19. In the Scottish nationwide population-based study, the authors have found an increased risk of severe COVID-19 in patients using sulfonylureas (OR 1.310) after adjustment for age, sex, diabetes duration and type of diabetes [21].Sodium-glucose-co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors do not carry a risk of hypoglycemia and have not been associated with increased risk of severe COVID-19 in multivariable adjusted analyses [21]. However, they are associated with a risk of diabetic ketoacidosis during illness. To reduce the risk of metabolic decompensation, expert recommendations state to discontinue SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with severe COVID-19.Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists exert anti- inflammatory properties, which is known to have beneficial effecton low-grade inflammation associated with atherosclerosis. Furthermore, GLP-1 receptor agonists have renoprotective effects. Considering the well-known beneficial effect of both GLP-1 receptor agonists as well as SGLT-2 inhibitors on prevention of cardiovascular and kidney disease, both risk factors for a severe course of COVID-19, these drugs may be of preventive importance.DPP-4 inhibitors are generally well-tolerated, have no risk of hypoglycemia and can be used for a wide range of kidney function, it is recommended that they are continued in patients with COVID-19.Thiazolidinediones exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and significantly reduce insulin resistance. Therefore, it has been speculated that thiazolidinediones could ameliorate prognosis of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes. However, this has not yet been confirmed by clinical studies [21].
8. Discussion
- Patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are at greater risk for a severe course of COVID-19 and mortality. This poorer prognosis is likely additionally linked to the comorbidities and other risk factors that are often concomitantly present with diabetes mellitus, but also to glycemic control. The interrelation between diabetes and COVID-19 is complicated and bidirectional, with COVID-19 causing hyperglycemia on the one hand, but hyperglycemia causing worse outcome of COVID-19 on the other hand. Diabetes itself, as well as the comorbidities often associated with diabetes additionally contribute to this risk of a severe outcome of COVID-19. This relationship is illustrated in Рисунок 1. Although diabetes itself appears to be an independent risk factor for severe COVID-19, the most important factors that co-contribute to an increased risk of COVID-19 severity and mortality in patients with diabetes include older age, hypertension, CVD, CKD, obesity, a proinflammatory and hypercoagulable state, and glucose dysregulation. All of these factors should be acknowledged when assessing the risk of a more severe course of COVID-19 in patients with diabetes.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML