Firdavs N. Nuraliev
Research Institute of Sanitation, Hygiene and Occupational Diseases of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Firdavs N. Nuraliev , Research Institute of Sanitation, Hygiene and Occupational Diseases of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The purpose of the research was study of the complex impact of working conditions factors on workers’ body resistance factors. It has been established that an increase in leukocytes indicates the formation of inflammation in the body of workers, and a decrease in the total number of lymphocytes indicates a decrease in the activity of the immune system, which leads to secondary immunodeficiency. A study of the main immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG, IgE) in the blood serum of spinning workers showed an imbalance between the parameters of these immunoglobulins. No significant differences were found between the immunoglobulin parameters of the control (sewing and weaving workshops) and the main (processing, scattering, carding, spinning workshops) groups. It was revealed that nonspecific factors of body resistance are not specific and are not sensitive to the influence of production factors, and also do not have diagnostic and prognostic value in determining pre-pathological and pathological conditions of the body of spinning workers.
Keywords:
Immunoglobulin, Cotton, Flax, Wool, Silk, Immunological studies, Textile industry
Cite this paper: Firdavs N. Nuraliev , Research Results on the Study of Cellular and Humoral Factors of Resistance in the Body of Spinning Workers, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 10, 2023, pp. 1366-1373. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231310.02.
1. Introduction
The textile industry is one of the leading industries in the world [9]. Textile workers are exposed to a range of chemicals, including dyes, solvents, optical brighteners, finishing agents and numerous types of natural and synthetic fiber dusts, which affect their health [4,13].One of the main productions of the textile industry is spinning. This production is a set of technological processes necessary for the production of continuous thread (yarn) used for the manufacture of textile products: fabrics, knitwear, curtains, nets, cords, threads, ropes and others.The primary barrier to any environmental exposure is the skin and mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, especially in people working under conditions of complex, combined, combined influence of adverse production factors on the body [5]. It is known that in textile production the main source of microbial air pollution is the product processed in this workshop: cotton, flax, wool, silk, kenaf, etc. This pollution begins from the first process in the technological chain, i.e. from loosening the product in the preparation workshop of the spinning production.Nonspecific immunological changes are an integral part of the body’s general primary reaction to the action of harmful production factors. Mass immunological studies make it possible to establish the presence and severity of adaptive reactions of one of the body’s regulatory systems - the immune system [2,10].Assessment of various variants of the immune response makes it possible to create an “immunological image” of the body’s state under the influence of factors in the working environment, including in the absence of occupational diseases [6,7,12].The purpose of the research was to study the complex impact of working conditions factors on the body resistance factors of spinning workers.
2. Material and Research Methods
In our studies, hematological (n = 137) and immunological (n = 60) studies were carried out to assess the state of resistance factors in the body of spinning production workers. The total number of leukocytes, the relative and absolute number of lymphocytes, cells of the monocyte-macrophage system (macrophages-monocytes, microphages-eosinophils, basophils), the relative and absolute number of neutrophils were studied. All these cells belong to cellular resistance factors. In addition, humoral resistance factors of the body were studied - immunoglobulins of classes A, M, G, E, C 3 component of complement, lactoferrin.Cellular resistance factors have been identified in human peripheral blood, and humoral factors in blood serum.The study of peripheral blood parameters of workers was carried out during a medical examination. For this purpose, blood was drawn in an amount of 5.0 ml; studies were carried out on a hemolytic analyzer “BC -3000” manufactured in China. The study was carried out in the scientific and practical laboratory of the Bukhara State Medical Institute named after Abu Ali ibn Sina.The study of immunological parameters was studied by studying the blood serum of workers that were isolated from their peripheral blood. Before use, blood serum in an amount of 2-3 ml was stored in the freezer at sub-zero temperatures. The studies were carried out using the ELISA method using test systems from the company “Vector-Best” (Novosibirsk, Russian Federation). The study was carried out at the Institute of Human Immunology and Genomics of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
3. Research Results
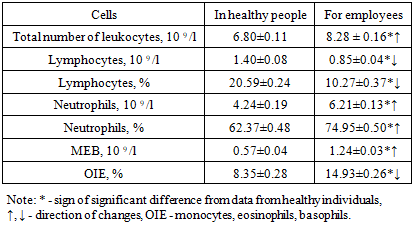
It is known that the human immune system performs a protective function for the body by responding to external and internal antigens, which can lead to pre-pathological and pathological conditions of the body [1]. Together, they perform the same function - protecting the body from external and internal influences. Antigens can be various substances that have restraining properties; they must have foreignness, immunogenicity, antigenicity and sufficient molecular weight (at least 5-10 KDa).The functioning of the immune system is negatively affected by various factors, from different types of microorganisms to chemical and physical factors. Specific activities of the immune system lead to the development of a pathological process. This fact is also important for various industries, where the body of workers is negatively affected by various industrial hazards [5,6].In this regard, together with the study and assessment of morbidity among workers in various industries, it is necessary to assess the state of the immune system or resistance factors of the body.For a comparative analysis of the results obtained, the studied workers were divided into groups by workshop: general group - included here in their surveyed (n = 137), workers of the sewing, weaving workshops (comparison groups), workers of the processing workshop, scattering, carding, spinning workshops (main groups). The results obtained were comparable to the parameters of healthy individuals of the same age who did not work in the industrial sector.The results of the study of cellular resistance factors of the general group are given in table. 1.Table 1. Indicators of cellular resistance factors in the general group of workers engaged in production, n = 137
 |
| |
|
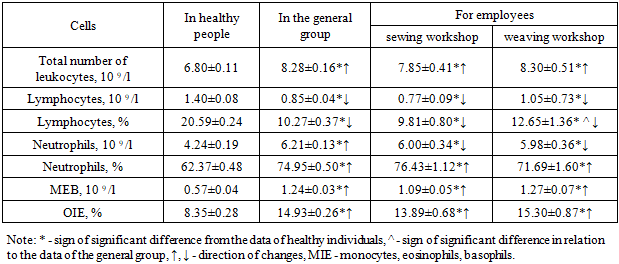
As can be seen from table. 1. the total number of leukocytes in workers was 1.22 times significantly higher in relation to healthy individuals (P <0.05), but in contrast to them, the main cells of the immune system - lymphocytes were significantly reduced in relation to healthy individuals - absolute parameters by 1.65, and relative by 2.0 times (P <0.001).A different picture was observed when comparing these workers and healthy ones for other granulocytes - neutrophils were increased in workers. This increase was 1.46 and 1.20 times, respectively (P < 0.05).Almost the same results were found for macrophages (monocytes) and microphages (eosinophils, basophils), where both relative and absolute parameters were significantly higher than those of healthy individuals - 2.18 and 1.79 times, respectively (P <0.001).The analysis shows that a decrease in some parameters of the relative and absolute values of these cells is accompanied by an increase in the number of others. This fact indicates that all cells of the body’s resistance factors are interconnected and complement each other’s functions.At the next stage of the research, the parameters of the general and control groups (workers of the sewing and weaving workshops) were comparatively studied. The research results are given in table. 2.Table 2. Indicators of cellular resistance factors in the general and control resistance groups employed in production
 |
| |
|
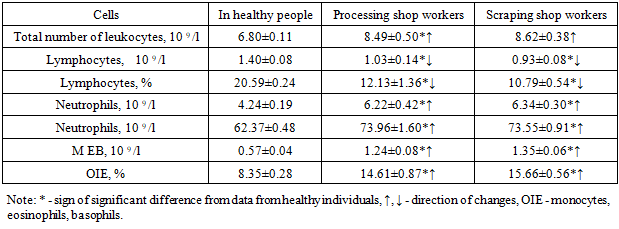
The results obtained show that the current changes in the relative and absolute indicators of the main cells of the body's resistance factors were preserved, that is, they were the same as the indicators of the general group, although the intensity of changes in some cells differed from the data of the healthy and general group.Significant differences were observed for all studied indicators in workers in relation to healthy ones (P <0.05). This was especially true for the relative and absolute values of lymphocytes, which were statistically significantly reduced in relation to healthy data (P <0.001) and the absolute and relative values of monocytes, eosinophils, basophils (macro- and microphages) – P <0.05.In some cases (relative numbers of lymphocytes and neutrophils), there was a significant difference in the data of the control group (weaving shop workers) in relation to the general group, but the values were insignificant, and therefore, we did not note this as a certain pattern.Next, an analysis of the obtained data for the main groups was carried out in comparison with the data of healthy individuals. The results are shown in table. 3.Table 3. Parameters of cellular resistance factors in the main groups in a comparative aspect
 |
| |
|
The results obtained show that in workers of the processing shop and the scutching shop, the total number of lymphocytes was increased by 1.25 and 1.27 times, respectively, in relation to data from healthy individuals (P < 0.05). Parameters were also elevated, only with varying intensities, and the absolute number of neutrophils was observed - respectively, 1.47 and 1.50 times more than the indicators of healthy people (P <0.001), as well as the relative number of these parameters increased by 1.17 and 1.18 times (P <0.05). This upward trend was noted in the relative and absolute numbers of monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils - 1.75 and 1.88 times (P <0.001) and 2.18 and 2.37 times (P <0.001), respectively.Unlike granulocytes, macro- and microphages, the main cells of the immune system were reduced in relation to healthy individuals by 1.36 and 1.51 times (absolute values), and by 1.70 and 1.91 times (relative values) - P <0.001.Analysis of the cellular composition of specific and nonspecific factors shows that a prepathological condition develops in the body, which is not clinically apparent, but is noted at the cellular level. The prognosis of the prepathological state of the body is unfavorable, since if the causes of the formation of the prepathological state are not eliminated, the process turns into a pathological process. In this regard, we recommend the parameters of the relative and absolute numbers of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils as diagnostic and prognostic criteria for the formation of prepathological and pathological conditions among spinning workers.At the next stage of research, similar laboratory parameters were analyzed among workers of the carding and spinning shops of this spinning enterprise. The results are shown in table. 4.Table 4. Comparative indicators of cellular resistance factors in workers of carding and spinning shops
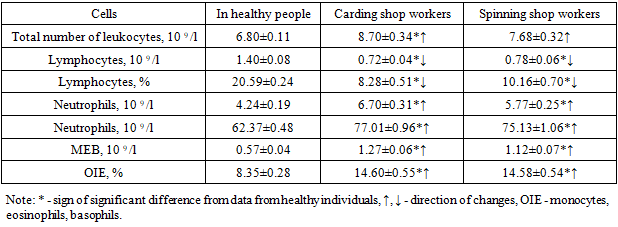 |
| |
|
It was found that among the workers of the carding and spinning shops, the relative and absolute amount of the studied cellular composition had the same trend as the previous parameters of the workers. The patterns obtained in previous studies also applied to these workers.To complete the perception of the obtained data, we present comparative parameters of the fold differences in the indicators of cellular resistance factors in spinning production workers from the parameters of healthy individuals (Table 5).Table 5. Multiplicity of differences in the indicators of cellular resistance factors in workers from the parameters of healthy individuals, how many times
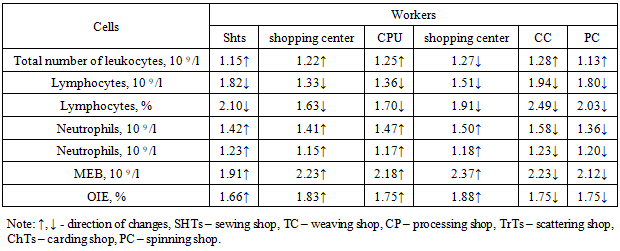 |
| |
|
From the table Figure 5 shows the tendency and intensity of changes in the relative and absolute parameters of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils. It was found that all parameters were significantly different from those of healthy individuals (P <0.05). The smallest differences concerned the total number of leukocytes, the relative and absolute number of neutrophils (P <0.05), and the greatest differences concerned the relative number of lymphocytes and the absolute number of monocytes, eosinophils, basophils (P <0.001).It should be taken into account that when assessing the state of the body's resistance factors, the most informative is the relative number of cells, and the absolute parameters directly depend on the total number of leukocytes, which change under the influence of any external and internal factors.When studying the cellular factors of body resistance in spinning production workers, in comparison with standard indicators, the following features were identified:firstly, all the studied parameters (total number of leukocytes, relative and absolute numbers of lymphocytes, neutrophils (granulocytes), monocytes, eosinophils, basophils (macro- and microphages)) were significantly different from the data of healthy individuals in spinning workers (P <0. 05- P <0.001);secondly, all workers showed a significant decrease in the main cells of the immune system - lymphocytes and a significant increase in the main cells of nonspecific protective factors - neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils and the total number of leukocytes (P <0.05- P <0.001);thirdly, all parameters had the same trend of changes with different intensity of differences among themselves;fourthly, the relative and absolute cell content of body resistance factors were cellular precursors of the prepathological state of the body of spinning workers;fifthly, a decrease in the content of lymphocytes led to an increase in the level of neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, since according to the “principle”, a decrease in one indicator of the immune system leads to an increase in another parameter of this system, that is, the cells complement each other’s function;sixth, the blood content of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils in spinning workers are recommended as diagnostic criteria for determining the prepathological state of the workers’ body and prognostic criteria for predicting the transition of the prepathological state to a pathological state;seventh, the studied parameters of cellular resistance factors of the body (total number of leukocytes, relative and absolute parameters of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils) are recommended to be determined during periodic medical examinations of spinning production workers as an addition to other clinical and laboratory indicators.The results obtained for determining different classes of immunoglobulins in the blood serum of the subjects are shown in Table. 6.Table 6. Content of immunoglobulins in the blood of spinning production workers, n =60
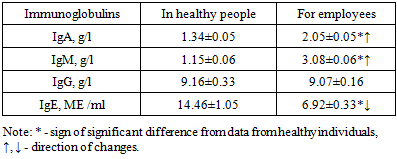 |
| |
|
It is known that IgA is the first line of defense of the body against pathogens, their metabolic products and other antigens. It provides local immunity. In our studies, IgA parameters in workers (general group) were 1.53 times higher than in healthy individuals (P <0.05).IgM provides the primary immune response and is the first of the immunoglobulins to react to the entry of an antigen into their body. A large amount of this immunoglobulin in the blood serum is observed in the first 5 days after exposure to the antigen. In our studies, the amount of IgM in workers was 3.08±0.06 g/l, which is 2.68 times more than in healthy individuals (P <0.001).IgG makes up 75% of all immunoglobulins in the human body, is synthesized after IgM and reaches its largest amount on the 28th day after exposure to the antigen. But, in our studies, the IgG content practically did not differ between healthy people and workers.It has been established that IgE is a precursor to allergic conditions; when an allergic condition is detected, the amount of IgE in the blood serum increases significantly. In our studies, the IgE content was at the normal level. This indicates that those examined had virtually no allergic background. This means that the industrial hazards of spinning production do not lead to allergic conditions.Next, we studied the content of immunoglobulins in the blood serum of workers in the control and main groups.The research results are given in table. 7.Table 7. The content of serum immunoglobulins in workers of the control and main groups of spinning production
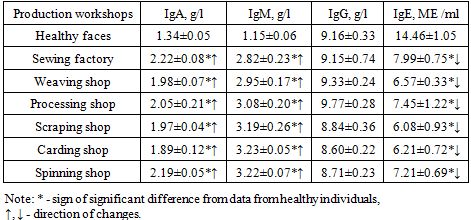 |
| |
|
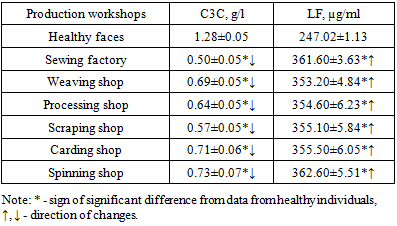
As can be seen from Table 7, significant changes were observed in the content of IgA in the blood serum of workers of all examined workshops - control (sewing workshop, weaving workshop) and main (processing workshop, scattering, carding, spinning workshops) groups (P <0.001 ).The increase was 1.66 and 1.48 times in the control groups and from 1.41 times to 1.63 times in the main groups (P < 0.001). In addition, changes of the same intensity, only towards a decrease, were observed when studying IgE (P <0.001). All parameters of the control and main groups were significantly lower by 1.81-2.20 times and 1.94-2.38 times, respectively (P <0.001), but it should be noted that all parameters were at the level of reference values (from 0 to 10 IU /ml).Significant differences between these workers and healthy individuals were also noted in the content of IgM in the blood serum (P <0.001), where all parameters of the studied population were increased in relation to the data of healthy individuals (1.15 ± 0.06 g/l). In the examined control groups, the values were 2.45 times (up to 2.82±0.23 g/l) and 2.57 times (2.95±0.17 g/l) higher than the average value of healthy people (P <0.001). The same trend of changes was found among workers of the main groups - accordingly, 2.68 times more for workers in the processing shop (3.08±0.20 g/l), 2.77 times more for workers in the scutching shop (3.19±0.26 g/l), 2.81 times more for carding shop workers (3.23±0.05 g/l) and 2.80 times more for spinning shop workers (3.22±0.07 g/l) k) - P <0.001. It should be noted that in terms of IgG content, no significant differences were found between the compared groups and the data from healthy individuals (P >0.05), all parameters were at the level of parameters of healthy individuals.Thus, the study of the main immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG, IgE) in the blood serum of spinning workers showed an imbalance between the parameters of these immunoglobulins. If IgA and IgM were significantly increased in relation to healthy individuals (P <0.001), then IgE was significantly reduced in all study groups (control and main groups). The increase in IgA was 1.48-1.66 times, IgM by 2.48-2.81 times, the decrease in IgE by 1.81-2.38 times in relation to healthy people (P <0.001), there were significant differences in IgG content there was no (P >0.05). It is noteworthy that no significant differences were found between the indicators of the control (sewing and weaving shops) and the main (processing, scattering, carding, spinning shops) groups. Considering that all parameters IgA (reference values 1.69-3.85 g/l), IgM (0.89-4.08 g/l), IgG (8.85-13.34 g/l) and IgE (0-100 IU/ml) were at or at the upper limit of normal values, it becomes clear that the workers’ parameters were at the level of normal values. The presence of an increased background of IgA and IgM indicates the presence of a weak antigenic stimulus, and a decrease in IgE indicates the absence of an allergic background. This fact may be a harbinger of a pre-pathological state of the body of workers in this production.In addition, nonspecific body defense factors were determined in the blood serum of the examined workers - complement component C3 (C3C) and lactoferrin (LF). The research results are given in table. 8.Table 8. Comparative indicators of complement component C3 and lactoferrinau among spinning workers
 |
| |
|
The results obtained show that among spinning production workers, C3C and LF changed in different directions, if C3C parameters were significantly reduced in relation to the data of healthy individuals by 1.86-2.56 times in the control groups (P <0.001) and 1.75-2.25 times in the main groups (P <0.001) of the study. But it must be emphasized that all parameters of the examined were within normal values or constituted the lower limit of reference values (0.76-1.8 g/l) - P >0.05. The content of lactoferrin was increased in all study groups compared to the data healthy people (P <0.01), but, as in the case of C3C, the data were within the reference values (190-500 ng/ml).Thus, the study of the content of nonspecific protection factors C3C and LF in spinning production workers showed that their quantitative content changed in different directions in relation to healthy individuals, C3C in all groups was significantly reduced (P <0.001), and LF was significantly increased compared with data from healthy controls (P <0.001). Nonspecific resistance factors of the body were not involved in the prepathological state of the body. They are not specific and not sensitive to the influence of production factors, and also do not have diagnostic and prognostic value in determining pre-pathological and pathological conditions of the body of spinning workers.Studies were carried out to determine the cellular resistance factors of the body of spinning workers, depending on their work experience. All respondents (n = 137) were distributed according to work experience as follows: work experience up to 5 years (n = 18); up to 6-10 years (n =47); 11-15 years (n =37); 16-20 years old (n =34); 21 years or more (n =11). The results obtained are shown in table. 9.Table 9. Comparative parameters of cellular resistance factors in workers depending on work experience
 |
| |
|
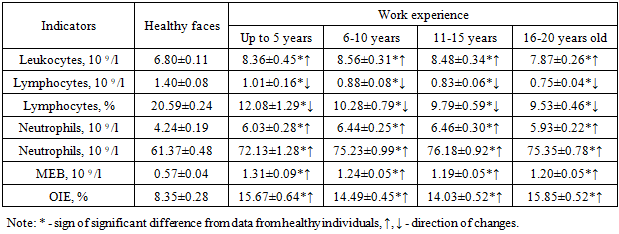
The results obtained show that in all periods of work experience, cellular resistance factors were significantly increased in relation to the data of healthy individuals (P <0.05). This applied to all periods of work. It is interesting to note that all parameters of the total number of leukocytes were close to each other, regardless of length of work and did not differ significantly between groups (P < 0.05). We observed almost the same trend of changes in the relative and absolute indicators of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils and basophils (P <0.05).The same studies were carried out on the main classes of immunoglobulins and nonspecific protective factors. The results of comparative studies are given in table. 10.Table 10. Results of the study of humoral and nonspecific protective factors in workers depending on work experience
 |
| |
|
From the given table. Figure 10 shows that all parameters of IgA and IgM were significantly increased in relation to the data of healthy individuals (P <0.05).In addition, all IgE parameters were significantly reduced in relation to the parameters of healthy controls (P < 0.05). Such reduced indicators were noted in workers compared to healthy indicators (P <0.05).It is interesting to note that all IgG parameters in the subjects did not differ statistically significantly from the parameters of healthy individuals, which indicates the absence of an antigenic stimulus during the research.I would like to emphasize the fact that all the studied indicators did not differ significantly from each other, regardless of the work experience of the workers, that is, the work experience did not affect the content of humoral and nonspecific factors in the workers’ body.Thus, the study of the parameters of cellular, humoral and nonspecific factors of the body’s resistance, depending on the work experience of spinning workers, showed that all parameters, regardless of work experience, were significantly different from those of healthy individuals, the changes were multidirectional depending on the indicator. No significant differences were found between the groups of subjects divided by work experience (0-5 years, 6-10 years, 11-15 years, 16-20 years) (P >0.05), which indicates that there is no influence of work experience on cellular indicators, humoral and nonspecific factors of body resistance in spinning production workers.
4. Conclusions
1. It has been established that an increase in leukocytes indicates the formation of inflammation in the body of workers, and a decrease in the total number of lymphocytes indicates a decrease in the activity of the immune system, which leads to secondary immunodeficiency. An increase in the relative and absolute number of neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils is a compensatory reaction of the body to a decrease in lymphocytes. Analysis of the cellular composition of specific and nonspecific factors shows that a prepathological condition develops in the body, which does not manifest itself clinically, but is noted at the cellular level. The prognosis of the prepathological state of the body is unfavorable, since if the causes of the formation of the prepathological state are not eliminated, the process turns into a pathological process.2. It was revealed that all the studied parameters were significantly different from those of healthy individuals. The smallest differences concerned the total number of leukocytes, the relative and absolute number of neutrophils, and the greatest differences concerned the relative number of lymphocytes and the absolute number of monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. When assessing the state of the body's resistance factors, the most informative is the relative number of cells, which directly depends on the total number of leukocytes, which changes under the influence of any external and internal factors.3. When studying the cellular factors of body resistance in spinning production workers, in comparison with standard indicators, the following features were identified:firstly, all the studied parameters (total number of leukocytes, relative and absolute numbers of lymphocytes, neutrophils (granulocytes), monocytes, eosinophils, basophils (macro- and microphages)) were significantly different from the data of healthy individuals in spinning workers (P <0. 05- P <0.001);secondly, all workers showed a significant decrease in the main cells of the immune system - lymphocytes and a significant increase in the main cells of nonspecific protective factors - neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils and the total number of leukocytes (P <0.05- P <0.001);thirdly, all parameters had the same trend of changes with different intensity of differences among themselves;fourthly, the relative and absolute cell content of body resistance factors were cellular precursors of the prepathological state of the body of spinning workers;fifthly, a decrease in the content of lymphocytes led to an increase in the level of neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, since according to the “principle”, a decrease in one indicator of the immune system leads to an increase in another parameter of this system, that is, the cells complement each other’s function;sixth, the blood content of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils in spinning workers are recommended as diagnostic criteria for determining the prepathological state of the workers’ body and prognostic criteria for predicting the transition of the prepathological state to a pathological state;seventh, the studied parameters of cellular resistance factors of the body (total number of leukocytes, relative and absolute parameters of lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils) are recommended to be determined during periodic medical examinations of spinning production workers as an addition to other clinical and laboratory indicators.4. Study of the main immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, IgG, IgE) in the blood serum of spinning workers; indicators of imbalance between the parameters of these immunoglobulins. If IgA and IgM were significantly increased in relation to healthy individuals, then IgE was significantly reduced in all study groups. The increase in IgA was 1.48-1.66 times, IgM by 2.48-2.81 times, and the decrease in IgE by 1.81-2.38 times compared to healthy people.5. No significant differences were found between the immunoglobulin parameters of the control (sewing and weaving workshops) and the main (processing workshop, scattering, carding, spinning workshops) groups. If we consider that all parameters IgA, IgM, IgG and IgE were at the level or at the upper limit of normal values, then it becomes clear that the parameters of the workers were at the level of normal values.6. The study of the content of nonspecific protection factors C3C and LF in spinning production workers showed that their quantitative content changed in different directions in relation to the data of healthy individuals, C3C in all groups was significantly reduced, and LF was significantly increased compared to the data of healthy individuals. But given the fact that all parameters of the control and main groups were within the reference values, we believe that nonspecific factors of the body’s resistance were not involved in the pre-pathological conditions of the body. They are not specific and not sensitive to the influence of production factors, and also do not have diagnostic and prognostic value in determining pre-pathological and pathological conditions of the body of spinning workers.7. The study of the parameters of cellular, humoral and nonspecific factors of the body’s resistance, depending on the work experience of spinning workers, showed that all parameters, regardless of work experience, were significantly different from those of healthy individuals, the changes were multidirectional depending on the indicator. No significant differences were found between the groups of subjects divided by work experience (0-5 years, 6-10 years, 11-15 years, 16-20 years), which indicates the absence of influence of work experience on the indicators of cellular, humoral and nonspecific factors of body resistance among spinning workers.
References
| [1] | Andrienko L.A., Peskov S.A., Smirnova E.L. State of cellular and humoral immunity under industrial dust exposure // Journal of Siberian Medical Sciences. – 2014. – No. 1. – P. 1-7. |
| [2] | Ilyinykh M.V., Serebryakov P.V., Antoshina L.I. Reactivity of peripheral blood neutrophils under exposure to industrial aerosols // Hygiene and Sanitation. – 2016. – No. 95(11). – pp. 1052-1055. |
| [3] | Iskandarova G.T., Mamatkulov Zh.G. Complex of production factors of textile production and damage to professional health O'zbekiston Respublikasi Sanitariya-epidemiologikosoyishtalikvajamoatsalomatligixizmatijurnali – 2022. – No. 3. – P. 67-70. |
| [4] | Iskandarov A.B., Characteristics of thermoregulation indicators among workers of knitting production // Medical news - 2019 - No. 8 - P. 79-80. |
| [5] | Zakharenkov V.V., Kazitskaya A.S., Mikhailova N.N., Romanenko D.V., Zhdanova N.N., Zhukova A.G. Influence of harmful production factors on the immune status of the body // Occupational and Industrial Medicine ecology. – 2017. – No. 12. – pp. 19-23. |
| [6] | Kryuchkova E.N., Saarkoppel L.M., Yatsyna I.V. Features of the immune response during chronic exposure to industrial aerosols // Hygiene and Sanitation. – 2016. – No. 95(11). – pp. 1058-1061. |
| [7] | Kurchevenko S.I., Boklazhenko E.V., Bodienkova G.M. Comparative analysis of the immune response in workers exposed to various production factors. – 2018. – No. 97(10). – pp. 905-909. |
| [8] | Mikhailova N.N., Kazitskaya A.S., Gorokhova L.G., Fomenko D.V., Kizichenko N.V. Experimental studies of the immune status of the body in the dynamics of the development of occupational diseases // Occupational Medicine and Industrial Ecology. – 2015. – No. 9. – P. 98. |
| [9] | Slavinskaya N.V., Iskandarov A.B. Results and prospects of research in the field of hygiene and occupational safety of women in Uzbekistan // Journal of Theoretical and Clinical Medicine - 2014 - No. 1 - 56-59 pp. |
| [10] | Chin-Ching Wu, Yi-Chun Chen Assessment of Industrial Antimony Exposure and Immunologic Function for Workers in Taiwan // Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. – 2017. – No. 14. – P. 1-9. |
| [11] | Hiremath RB, Kattumuri R., Kumar B., Hiremath GR Health and safety aspects of textile workers from Solapur (India) textile industries // Indian Journal of Community Health. – 2016. – Vol.26, Number 4 – P.363-369. |
| [12] | Y. Sri Harika, Sadaf Sultana, QurratulAyenAdeeba, B. Raja Narender Prospective study on the effect of immunological consequences and the modulation of the respiratory system by occupational diseases // World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. – 2019. –Vol.8(5). – P. 1504-1512. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML








