-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(9): 1300-1301
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231309.26
Received: Sep. 11, 2023; Accepted: Sep. 21, 2023; Published: Sep. 23, 2023

Estimation of Quality of Life in Patients with Psoriasis
Ermatov Nizom1, Tashkenbaeva Umida2, Khajiev Dilshod3
1Head of the Hygiene of Children, Teenagers and Nutrition Department, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Head of the Department of Dermatovenerology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
3Researcher of the Hygiene of Children, Teenagers and Nutrition Department, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Ermatov Nizom, Head of the Hygiene of Children, Teenagers and Nutrition Department, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The article presents the results of the analysis of indicators of the quality of life of patients with psoriasis in the main group and in the control group of healthy people. In two groups, the profile of the quality of life was studied, revealing the main directions of their life problems: physical and mental health, social functioning, and more. The quantitative characteristics of the physical, emotional and social components of the quality of life of the respondents are shown. It was emphasized that it is necessary to develop a set of preventive and rehabilitation measures to improve the quality of life of patients.
Keywords: Patients with psoriasis, Quality of life, SF-36 questionnaire, Psycho-emotional state
Cite this paper: Ermatov Nizom, Tashkenbaeva Umida, Khajiev Dilshod, Estimation of Quality of Life in Patients with Psoriasis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 9, 2023, pp. 1300-1301. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231309.26.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Psoriasis is a genetic, autoimmune inflammatory disease of the skin and joints, in which inflammation within the lesion causes basal keratinocyte stem cells to hyperproliferate [1,3].Analysis of the quality of life of patients with psoriasis depending on gender showed the presence of significant differences between the quality of life of men and women. Moderate statistically significant correlations were found between gender and general indicators of quality of life, so women suffering from psoriasis rated their quality of life lower than men [2].Studying the quality of life in various diseases is an urgent problem in the treatment of patients. The study of quality of life is closely related to human health and is based on a person’s subjective feelings [6].Patients with psoriasis express concern about the presence of rashes on the skin of the trunk, limbs, and scalp; they are nervous, anxious, experience difficulties in social contacts, and serious restrictions in life: at work, when communicating with other people, on vacation [11-17].The SF-36 (Medical Outcomes Study Short-Form 36) questionnaire is a standardized questionnaire widely used in the study in the population. It helps most patients assess various components of their life during the course of the disease, and the quality of life of patients has been assessed using this questionnaire in various studies [4,5].
2. Purpose of the Research
- The purpose of the study is to study and analyze the quality of life of patients with psoriasis using the SF-36 questionnaire.
3. Materials and Methods
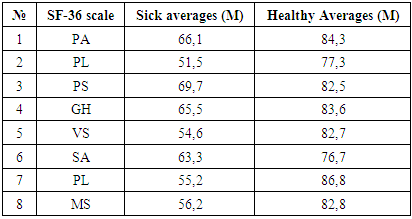
- The SF-36 Quality of Life Questionnaire was performed and compared between psoriasis patients (80) and healthy controls (80). For the quality of life study, each question on the SF-36 questionnaire was scored and calculated on each scale. Questions were asked on 8 scales. Includes physical activity - (PA), Based on the role of physical activity in a person's life - (PL), Pain scale - (PS), General health - (GH), Vitality scale - (VS), Scale calculated and analyzed scales reflecting social activity - (SA), mental state - (MS).
4. Results and Discussion
- Data were collected based on quality of life indicators of sick people and healthy people in each group. When studying the age indicators of patients, 10% of them were patients under 18 years old, 30.6% were patients from 20 to 39 years old, 59.4% were patients over 40 years old. In the second group, 38.6% were patients from 20 to 39 years old, 61.5% were over 40 years old.During the examination, the questionnaire showed that the physical and mental state of the patients at the time of the examination was significantly lower (Table 1).
|
 | Figure 1. Comparisons of the general physical and mental components among sick and healthy people |
5. Conclusions
- All average indicators on 8 scales of the SF-36 questionnaire of physical and psychological components of health among sick people are much lower than people in the healthy group. This affects their physical condition, activity, social component of life, general physical condition, low psychological state, high likelihood of stress and depression. Especially damage to exposed skin areas affects the emotional state and psychological status of patients with psoriasis, influencing the choice of clothing, daily and professional activities.Therefore, the help of psychotherapy and drug therapy of patients is recommended. The psychotherapy is prescribed in combination with medication, patients' anxiety levels quickly decrease, vitality increases, and the patient's emotional state improves. This improves the effectiveness of patient care.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML