-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(9): 1224-1226
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231309.10
Received: Sep. 1, 2023; Accepted: Sep. 21, 2023; Published: Sep. 22, 2023

Study of Vestibular Function in Meniere's Disease
M. T. Nasretdinova , B. SH. Baxronov , A. E. Shadiyev , N. A. Normurodov
Samarkand State Medical University, Republic of Uzbekistan, Samarkand
Correspondence to: M. T. Nasretdinova , Samarkand State Medical University, Republic of Uzbekistan, Samarkand.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The characteristics of optokinetic nystagmus (OКN) were studied in 20 healthy individuals and 30 individuals suffering from Meniere's disease in remission. The results recorded by the method of electronystagmography at frequency optokinetic stimulation 66,90 156 and field/min. found that in healthy people, the frequency of IPOs, the total amplitude and the speed of the slow phase(sp) nystagmus increases proportional to the increase in the frequency optokinetic stimulation; accordingly, consistently reduced the average amplitude window. In Meniere's disease, OКN indicators are generally characterized by lower values than normal, and an increase in the frequency of optokinetic stimulation is accompanied not only by a more pronounced decrease in the total amplitude indicators, but also by a decrease in the speed of the slow phase of OКN. After the glycerol load and with positive results of the glycerol test, the quantitative indicators of OКN increase in patients, approaching the physiological norm. It is concluded that it is appropriate to study the OКN in Meniere's disease to clarify the stage of the disease and predict the effectiveness of treatment.
Keywords: Meniere, Total amplitude, Optokinetic nystagm, Glicerol test
Cite this paper: M. T. Nasretdinova , B. SH. Baxronov , A. E. Shadiyev , N. A. Normurodov , Study of Vestibular Function in Meniere's Disease, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 9, 2023, pp. 1224-1226. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231309.10.
1. Introduction
- According to the literature, the study of optokinetic nystagmus (OКN) is widely used for the differential diagnosis of hemianopsias, oculomotor disorders, and diseases of the Central nervous system [1,2].In recent years, a number of papers have been published on the study of OКN features in disorders of both Central and peripheral parts of the vestibular analyzer [3,4]. It is experimentally proved that the peripheral labyrinth can give pathological optokinetic nystagmus. Many authors first reported the neutralization of optokinetic nystagmus by supra-threshold post-caloric or post-dictatorial nystagmus in humans and indicated that sub-threshold vestibular stimuli increase the optokinetic response. Visual assessment of OКN disorders under the influence of stimulation in all directions in limes suffering from Meniere's disease and cochlear vestibulopathy caused by vegetative vascular dystonia, cervical osteochondrosis and other causes was not revealed [3,5]. However, when analyzing electronystagmogram was certain violations of the settings window. In this regard, it is advisable to further identify violations of the peripheral parts of the vestibular analyzer, in particular, in Meniere's disease, caused by the hydrops’s of the labyrinth.The aim of the study was to determine the features of the manifestation of optokinetic nystagmus in patients with Meniere's disease.
2. Materials and Methods
- А Total number of examined people in the clinic No. 1 of the Samarkand medical Institute were 50, including 20 healthy (control group) aged 17 to 41 years, who do not suffer from vestibular dysfunction, and 30 people with Meniere's disease aged 25 to 52 years, with a prescription of the disease from 5 months to 14 years. The examination of patients was carried out in the inter-access period. Methods of work inspection, audiometric, vestibulometric study, as well as learning the OCN with the help of stat-tomographic recording. Audiometric examination was performed in a sound-attenuated chamber on an audiometer MA-30 (GDR). hearing tests included tonal threshold, supra-threshold and audiometry.During vestibulometry, statokinetic stability was determined, and spontaneous and experimental nystagmus obtained with caloric and rotational stimulation was recorded.OKN was induced by observation of the examinee for optokinetic rotation of the drum, which caused the four black vertical stripes, a Rotating cylinder was carried out at three fixed angular velocities: 99, 135, 2340 in 1 second, which provides the frequency optokinetic stimulation, respectively, 66, 90 and 156 of the bands in the I min. In assessing the entry window takes into account the frequency nystagmoid movements, the amplitude and total average speed of nystagmus slow phase (sp) and efficiency bands. In addition, the severity of optosensory and opto vegetative reactions was recorded.Based on the oral audiometry data, it was found that the examined patients had predominantly unilateral hearing loss on the side of the patient's labyrinth. The curves of the hearing thresholds were mostly horizontal, less often descending and ascending. In most cases, an interval of 10-30 dB was observed between the bone and air conduction curves. We noted low differential thresholds for the perception of sound power (0.4 0.8 dB at an over-threshold tone of 500 and 2000 Hz with an intensity of 20 dB), and a positive SISI test (80-100% of positive responses). According to vestibulometry, the predominant type of disorders was hyporeflexia, in rare cases hyperreflexia of vestibular excitability was observed.
3. Results
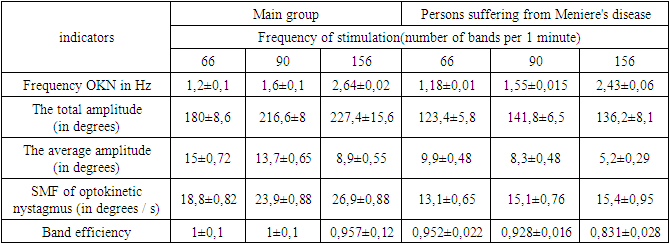
- The frequency of OKN in healthy people increased linearly as the frequency of stimulation increased (from 1.2 at the frequency of stimulation of 66 bands/min to 2.64 at the frequency of 156 bands/min). There was an increase in the total amplitude (from 180 to 227.40) and SP (from 18.8 to 26.90/c). At the same time, the average amplitude tended to decrease (from 15 to 8.90) bands (the ratio of the number of nystagmal responses to the number of bands passing in the field of view per unit of time), regardless of the frequency of stimulation, was close to one. Optosensors and opto autonomic reactions were absent (table. 1).
|
4. Discussion
- According to the results of studies after taking glycerol, patients were divided into two groups. The first group included individuals who had a decrease in tone perception thresholds by 10 to 15 dB during audiometry, and with experimental vestibular samples, the nystagmal response indicators significantly increased. The second group included patients who did not have any significant changes in auditory and vestibular functions after the glycerol test.Comparison of the results of optokinetic stimulation with the initial data showed that the subjects with a positive glycerol test showed an improvement in all the characteristics of OKN. So, for example, when stimulated 156 hollow/min, the total amplitude increased to 155.5" at the initial value of 136.2", and sp - to 17.8 /s (before taking glycerol, this value was 15.49/s), in patients with a negative glycerol test, we did not note significant changes in the considered characteristics of the OKN.Comparison of records allows us to conclude that with a positive glicerol test, there is a "revival" of the OKN in comparison with the original data.
5. Conclusions
- Based on the results of the survey, the following conclusion can be made. In healthy people, there is a linear increase in the frequency, total amplitude, and speed of the slow phase of optokinetic nystagmus and a consistent decrease in the average amplitude with an increase in the frequency of optokinetic stimulation. In individuals suffering from Meniere's disease, OKN is characterized by lower parameters, and as the frequency of stimulation increases, the total amplitude of the CMF tends to decrease. Reduced endolymphatic labyrinth as a result of the action is accompanied by an increase in the quantitative characteristics of the WINDOW.Thus, the characteristics of OKN in Meniere's disease may be important for identifying additional criteria for diagnosing diseases of the labyrinth and predicting the effectiveness of treatment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML