-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(8): 1061-1064
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231308.06
Received: Jul. 9, 2023; Accepted: Aug. 2, 2023; Published: Aug. 12, 2023

Reomannisol: Effect on Endogenous Intoxication, Lipid Peroxidation Activity and Activity of Antioxidant System Enzymes in Clinical Practice
Larisa Shevchenko, Timur Alimov, Khamid Karimov
Department of Molecular Medicine and Cellular Technologies, Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Hematology MoH RUz, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Timur Alimov, Department of Molecular Medicine and Cellular Technologies, Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Hematology MoH RUz, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

To study the effect of the drug for intravenous infusions Reomannisol on the degree of endogenous intoxication, the activity of lipoperoxidation and the activity of antioxidant system enzymes in clinical practice. The efficacy of the drug Reomannisol was determined in 60 patients in critical states: with hemorrhagic, traumatic and septic shocks. The study results showed that the use of Reomannisol in patients in critical states can reduce the values of endogenous intoxication, which confirms its detoxification efficacy. Reomannisol more markedly suppresses intensification of LPO in the blood of patients in critical states and increases the activity of AOS enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPO), glutathione reductase (GR), compared with the drug Rheosorbilact.
Keywords: Drug for intravenous infusions, Patients, Critical states, Endogenous intoxication, Lipoperoxidation (LPO), Antioxidant system (AOS)
Cite this paper: Larisa Shevchenko, Timur Alimov, Khamid Karimov, Reomannisol: Effect on Endogenous Intoxication, Lipid Peroxidation Activity and Activity of Antioxidant System Enzymes in Clinical Practice, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 8, 2023, pp. 1061-1064. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231308.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- For many years, the worldwide interest in free-radical oxidation processes in critical states has not diminished. Thanks to the development in this field of biochemistry and molecular biology, it became possible to decipher the subtle mechanisms of pathological processes in critical states, and prospects for studying the effect on these processes with the help of new antioxidant agents have opened up. These agents are capable of inhibiting the intensity of lipid peroxidation processes, increasing the activity of antioxidant protection and reducing the indices of endogenous intoxication [6]. Their introduction into medical practice is of great importance for clinical medicine. Our laboratory has developed and introduced into medical practice a new blood substitute «Rheomannisol», which has antioxidant and disintoxication effects, containing two bioenergetic antioxidants in its composition (patent ) [3].
2. Main Body
2.1. The Purpose of Our Research
- The aim of the work is to study the effect of the drug "Reomannisol" on endogenous intoxication, lipid peroxidation activity and the activity of antioxidant system enzymes in clinical practice.
2.2. Material and Methods of Study
- In 60 patients with reliably detected hemorrhagic, traumatic and septic shock who were treated at the clinic of the Republican Specialized Scientific-Practical Medical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics (RSNPMT&O), the main subgroup of patients receiving the complex treatment "Reomannisol", numbering 30 patients, were aged 18 and more: men (n=21) and women (n=9). The average age in this group was 44.9±2.3 years. The mean age of the men was 51.8±4.5 and that of the women was 41.9±2.5.The comparison subgroup consisted of 30 patients with the same diagnoses and corresponding age (19 men, 11 women), whose mean age was 45.63±3.03 years. At the same time, the mean age of men was 41.4±3.3 and women 53.0±5.4 years.In the blood of patients we measured the content of indicators of endogenous intoxication, the activity of lipoperoxidation processes and the state of the antioxidant system.In blood the following endogenous intoxication indices were determined: erythrocyte sorption capacity in a modified technique of Kopytova (2006), the level of medium molecules, oligopeptides; according to appropriate formulas there were calculated toxemia indices, intoxication index and distribution coefficient СМpl./СМер [2,5]. The results of the analyses were measured on a spectrophotometer UNICO2800 (USA).Intensity of lipid peroxidation (LPO) in blood serum was determined by the level of malonic dialdehyde (MDA) [7]. Activity of antioxidant system enzymes (AOS) was determined: catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) [8], glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione peroxidase (GP) [2]. All measurements were performed on a UNICO2800 spectrophotometer (United Products and Instruments, Inc., USA).The level of MDA was determined according to the method of L.I. Andreeva et al. The products were calculated using the molar extinction coefficient and expressed in nmol/mg. Diene conjugates and diene ketones were determined according to the method of Titeeva G.R. and Korovina N.N. (1996) [9]. SOD activity was determined according to the method of V.G. Mkhitryan et al [1]. Activity was calculated by the percentage of inhibition (T%) of tetrazolium blue reduction in alkaline medium. The activity of the enzyme was expressed in units/min x mg of protein. The activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPO) was determined by the accumulation of oxidized glutathione (GSSG) as a result of lipoperoxide decomposition. The activity of the enzyme was expressed in units/min x mg Hb per min. Activity of erythrocyte glutathione reductase was determined in reaction medium of phosphate buffer at wavelength 340 nm and by the decrease of NADPH*H and expressed in µM NADPH2/min x g Hb (Vlasova S.N. et al., 1990) [10]. Activity of catalase was determined according to the method of M.A. Korolyuk et al. (1998), the principle of which is based on the ability of H2O2 to form a stable colored complex with molybdenum salts. Measurements were performed at a wavelength of 410 nm [4].Statistical processing of the obtained data was performed using "Excel" and "Biostat 4.03" programs. The criterion for statistical significance was p<0.05.
2.3. Results of the Study
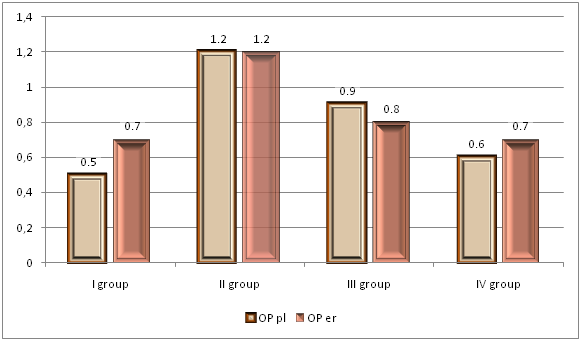
- The results of clinical studies have shown that among the patients of the RSSPMСT&O MoH RUz clinic in the treatment of critical conditions such as hemorrhagic, traumatic and septic shock, the use of the new drug for infusion therapy "Reomannisol" proved to be very successful.According to the results of the study of endogenous intoxication indicators presented in Figure 1 we can see that after reomannisol therapy the content of SMpl in blood plasma was lower by 1, 7 times (p<0.05), OPpl - 2.0 times (p<0.05), ITpl - 3.1 times (p<0.05), and in blood erythrocytes SMer was lower 1.8 times (p<0.05), OPer 1.7 times, ITer - 3.1 times (p<0.05). Intoxication index (II) after infusion of Reomannisol decreased by 3.1 times (p<0.05) (Figure 1). As seen in Figure 1, SCE decreased by 1.9 times (p<0.05), approaching the norm, indicating a good desintoxication effect of "Reomannisol" therapy. At the same time, after "Rheosorbilact" therapy the SMpl decreased by 1.2 times (p<0. 005), OPpl - 1,3 times (p<0,05), IT pl - 1,7 times (p<0,05), SM er - 1,3 times (p<0,05), OP er - 1,5 times (p<0,05), IT er - 2,0 times (p<0,05), AI - 1,8 times (p<0,05). Sorption capacity of erythrocytes (SCE) decreased 1.4-fold (Fig. 1).
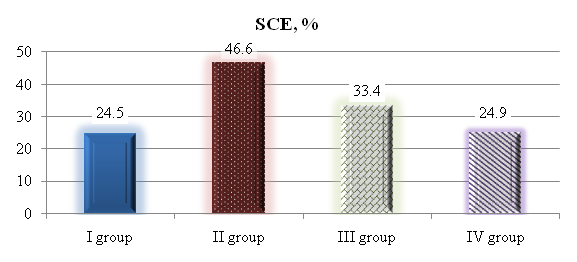 | Figure 1. Sorption capacity of erythrocytes in the study groups before and after administration of blood substitutes |
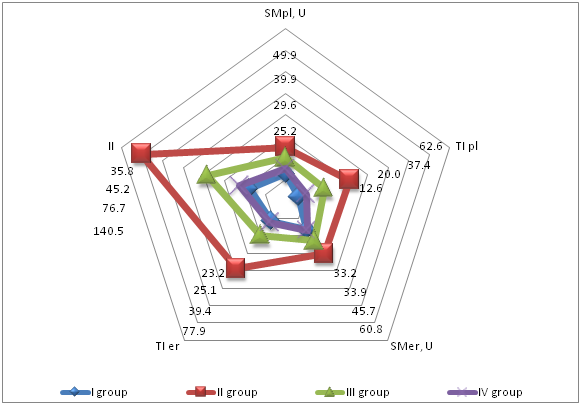 | Figure 2. State of endogenous intoxication in patients before and after the use of blood substitutes |
 | Figure 3. State of endogenous intoxication in patients before and after the use of blood substitutes |
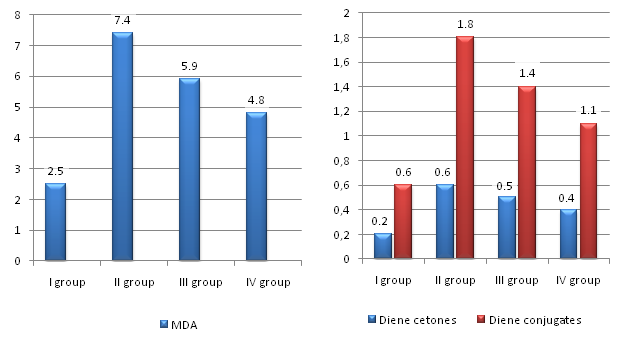
 | Figure 4. Lipoperoxidation indices in patients before and after infusion of the studied drugs |
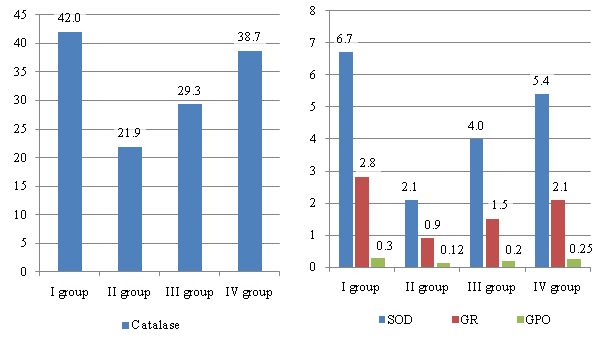
 | Figure 5. Antioxydant system indices in patients before and after infusion of the studied drugs |
3. Conclusions
- The use of the drug "Reomannisol" in patients in critical states allows to reduce the values of endogenous intoxication, which confirms its detoxification efficacy.The drug for infusion "Reomannisol" more markedly suppresses the intensification of lipoperoxidation processes in the blood of patients in critical states and increases the activity of antioxidant system enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase, compared with the drug "Rheosorbilact".
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML