Kenjaeva Nargiza Kuvatovna1, Rizaev Jasur Alimjanovich2, Magzumova Shaxnoza Shaxzadeyevna3, Umirov Safar Ergashevich4
1Department of Psychiatry, Medical Psychology and Narcology of the Samarkand State Medical University, Director of the Samarkand Branch of the Republican Drug Center, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
2Rector of Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
3Professor of the Department of Psychiatry and Narcology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
4HIV/AIDS Problem Course Instructor of Tashkent Insitute of Improvement of Doctors, Tashkent Insitute of Improvement of Doctors, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
A clear downward trend is observed in the multi-year dynamics of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome in Samarkand region during 2010-2022. Most patients use heroin (45.9%) and cannabis (26.3%). The incidence is high in Urgut district, Samarkand city and neighboring districts bordering the neighboring country, these areas belong to the dangerous area and the residents of these areas belong to the risk group. Currently, the majority of people who are addicted to drugs are male and over 40 years old. These aspects must be taken into account when planning and implementing measures to prevent drug addiction syndrome and providing medical and social services to patients.
Keywords:
Drug addiction, Prevalence, Regional distribution, Risk factor
Cite this paper: Kenjaeva Nargiza Kuvatovna, Rizaev Jasur Alimjanovich, Magzumova Shaxnoza Shaxzadeyevna, Umirov Safar Ergashevich, Some Factors of Determining the Incidence of Drug Addiction Syndrome and Its Formation, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 7, 2023, pp. 984-989. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231307.29.
1. Introduction
Illicit trafficking and consumption of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances and precursors belong to the group of problems characterized by negative medical, economic, legal and moral consequences of international social importance [3,5]. The use of narcotic drugs or psychotropic substances is one of the dangerous factors that determine the physical, mental and spiritual decline of the population, as well as the criminogenic situation, having a negative impact on the peace, socio-economic and cultural basis of the society, the health of the next generation, the ability to leave offspring and education. Today, not only the number of drug addicts is increasing in the world, but also the activation and internationalization of the drug business and the attempt to involve young people in the process are becoming increasingly stronger [1,2,7]. As a result, in most regions of the world, along with the growth of addiction to drugs in recent years, there is also a clear increase in the proportion of young people and women among drug addicts [4,6].Drug dependence syndrome is a global problem, but it also has specific characteristics in different regions. These specific aspects are determined by many factors, such as the geographical location of the region, the current situation in neighboring countries/territories, the intensity and manifestations of mutual relations with these regions, the socio-economic situation, the demographic structure of the population [1,4-6]. 52.3% of the population of Uzbekistan are citizens under the age of 30. It is natural for the country to attract the attention of international drug business representatives both as an attractive market and as a route to larger markets due to its geographic location [3,5]. Due to the fact that drug addiction and its negative consequences are of particular importance in the current globalization conditions, it is necessary to assess the level of drug addiction of different classes of the population, especially people of different ages and genders, to clarify the mechanisms of drug addiction, to increase the effectiveness of strategic programs to combat drug addiction in society, and to use existing opportunities wisely and purposefully. is specified [2,6].In order to effectively protect against diseases, first of all, it is necessary to determine the causes of their occurrence, and then to influence the risk factors underlying these causes. The incidence of drug addiction syndrome is largely socially determined. However, most risk factors may not be independent determinants in a separate case, therefore, it is appropriate to consider and analyze various socio-demographic factors in a common way - as a whole complex [2,6].Some researchers have studied the role of social, psychological and biological factors in the formation and development of drug addiction syndrome [3,5,7]. At the same time, the prevalence of drug addiction syndrome in Uzbekistan, regional features of its dynamics, risk factors unique to certain regions have not been sufficiently evaluated. However, a comprehensive assessment of risk factors and their related cause-and-effect relationships allows for the development of a set of rational preventive measures aimed at reducing the negative effects of these factors, both for individuals in the high-risk group and for the entire population. Ignoring these aspects are the main obstacles that negatively affect the success of the anti-drug program.Thus, in medical practice, it is very important to comprehensively evaluate both universal risk factors on the scale of the relevant population for the formation of drug addiction syndrome, as well as factors specific to the area where patients live, because the results of this analysis provide an opportunity for the development and application of more effective and economically beneficial approaches to the problem. Therefore, the study of the regional features of the formation and course of drug addiction syndrome is of great scientific and practical importance.The purpose of this study is to comprehensively assess the prevalence of drug addiction syndrome and demographic risk factors contributing to the formation of drug addiction syndrome in Samarkand region.
2. Research Material and Methods
Relevant medical documents reflecting the dynamics of new cases of drug addiction in Samarkand region during 2010-2022 (information about newly registered patients in Samarkand region regional branch of the Republic of Specialized Narcology Scientific and Applied Medical Center during 2010-2022, 066-1-h/sh, 025-h/sh, 030-2-h/sh) and annual reports were analyzed.Indicators reflecting the manifestation (dynamics and intensity) of drug addiction syndrome were evaluated in the context of demographic, regional risk factors, and the causal relationship between them was evaluated from the point of view of statistical significance. Demographic risk factors statistically significantly associated with the development of drug addiction include parameters such as age, gender, and place of residence.In order to assess the extent to which the urban environment and the specific lifestyle of the urban population and the location in the border area with the neighboring country influence the formation of drug addiction syndrome as a risk factor, 2010-2022. The dynamics of drug addiction was analyzed according to the territorial groups of Samarkand region, i.e. "Samarkand city", "City districts", "Urgut district" and "Rural districts". In this case, only Samarkand and Okdarya districts directly adjacent to the city of Samarkand are included in the "City districts" group. The "Rural Districts" group includes all administrative regions of the region, except "Samarkand City", "City Districts", "Urgut District".Social-hygienic, statistical methods were used during the research. The obtained results were statistically processed using generally recognized statistical methods (M.I. Petrukhina, N.V. Starostina, 2003). Digital material was analyzed using Epi-Info software, version 3.3.4. M, m, t were calculated and r was found using Student's table. A value of r<0.05 was considered as a reliable difference.
3. Research Results and Their Discussion
Initially, the composition of the category of drugs consumed by 2211 primary patients diagnosed with drug addiction in Samarkand region during 2010-2022 and their dynamic changes were analyzed (Table 1).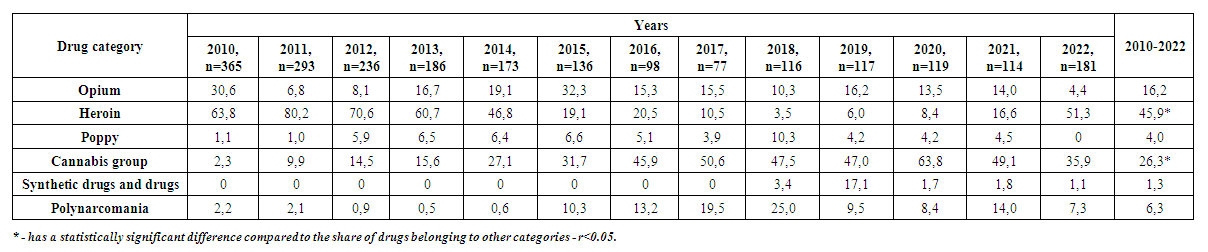 | Table 1. Category and dynamics of drugs consumed by primary patients with drug addiction syndrome, Samarkand region, 2010-2022, (N=2211), % |
According to the results of the analysis, the average total composition of the category of consumed drugs includes the following substances from the opium group: raw opium-16.2%, heroin 45.9%, poppy 4.0%, cannabis group 26.3%, synthetic narcotics and drugs 1.3%, as well as the consumption of drugs belonging to several categories was 6.3%. The consumption of heroin (45.9%) and cannabis (26.3%) drugs belonging to the opium group has a leading position, and the share of these drugs is significantly higher than the share of drugs belonging to other categories (р<0.05). At the same time, the share of narcotic drugs consumed has changed dynamically over the 13 years under analysis. In particular, the share of opioids was 30.6% in 2010, but by 2022 (4.4%) it has decreased by 7 times. The contribution of the heroin drug was 63.8% in the first year of the analysis - 2010, and has been decreasing almost continuously for a number of years, and in 2018 it was the minimum figure, i.e. 3.4% (18.8 times decrease). However, the share of heroin drug consumption has started to grow again since 2019 and will reach 51.3% by 2022, which is 15.1 times higher than in 2018 and 3.1 times higher than in 2021. In our opinion, the recent increase in the share of heroin consumption should be considered as an unpleasant prognostic sign. Poppy addicts were not observed in 2022, and in other years the consumption of this drug fluctuated from 1.1% (2010) to 10.3% (2018). In 2010, 2.3% of drug addicts used cannabis, and in 2022 (35.9%), it increased 15.6 times and took the second place among drugs according to its share. The consumption of synthetic drugs and medicines in the region has been recorded since 2018 (3.4%). In 2019, the contribution of these tools was 17.1%, and in 2022, it was 1.1%. During the studied years, the contribution of polynarcotics fluctuated from 0.5% (2013) to 25.0% (2018), and in 2022 it was 7.2%.At the next stage of the study, the change in the rate of formation of drug addiction syndrome (dynamics of the disease) was evaluated. The results of the analysis of the long-term dynamics of the primary incidence of drug addiction in the Samarkand region show that the average rate of incidence in the period 2010-2022 fluctuated from 2.1 (2017) to 11.5 (2010) per 100,000 inhabitants (Table 2).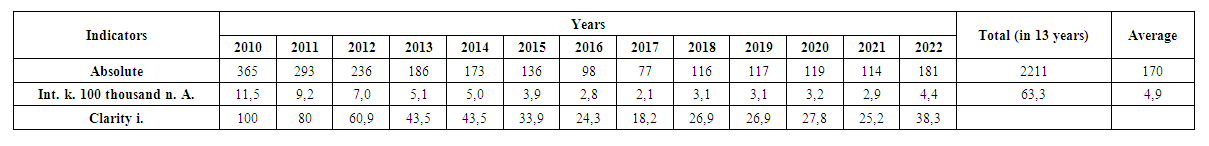 | Table 2. Dynamics of primary disease with drug addiction syndrome, Samarkand region, 2010-2022 |
In 2022, the incidence rate of drug addiction syndrome in the region decreased by almost 2.3 times compared to 2010, i.e. by 61.7%, the average annual rate of decrease is 4.7%. The incidence rate was 18.2 in 2017 and 38.3 in 2022 compared to 2010 (100.0). The median of the intensive index is 3.9 (2.8-9.2). The average intensive indicator is 4.9. It was observed that the indicators during 2010-2014 were 1.02-2.3 times higher than the average rate of incidence ("high" period of morbidity), on the contrary, they were 1.1-2.3 times lower in 2015-2022 ("low" period of morbidity). Therefore, in the next stages of the research, it is appropriate to analyze these periods separately and by mutual comparison.The incidence decreased by 56.5% by 2014 compared to 2010. The average annual rate of decline is 11.3%. Compared to the average indicator in the "high" period (2010-2014) (7.56 per 100,000 population), the average incidence rate (3.18) in the "low" period (2015-2022) decreased by 57.9% (Table 3).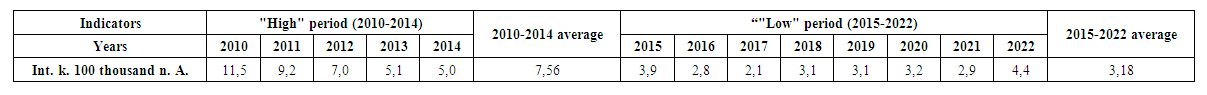 | Table 3. Periods in the dynamics of primary disease with drug addiction syndrome, Samarkand region, 2010-2022 |
At the same time, it should be noted that even after 2015, the downward trend of incidence continued for several years, but in the last year of the analysis - in 2022 (4.4), a 1.5-fold increase was observed compared to 2021 (2.9). The incidence rate of drug dependence syndrome in 2022 increased by 12.8% compared to the rate in 2015 (3.9), with an average annual growth rate of 1.6%. So, acknowledging the decreasing trend of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome in Samarkand region in the long-term dynamics, it is also worth noting the fragility (relative) of this situation. This situation shows that, first of all, it is necessary to analyze the underlying conditions, risk factors, and evaluate the cause-effect relationship between the incidence rate and risk factors, and according to the results, to correct the entire set of measures aimed at the problem.Based on this point of view, newly registered patients were analyzed according to demographic risk factors - age, gender and place of residence - which have the possibility of statistically significant association with the development of drug addiction syndrome.The analysis of the dynamics of the distribution of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome by age groups in Samarkand region shows that during the researched period, a new incidence of the disease among the 0-17 age group was recorded only in 2010 (0.5%) and averaged 0.1%. reached (Table 4).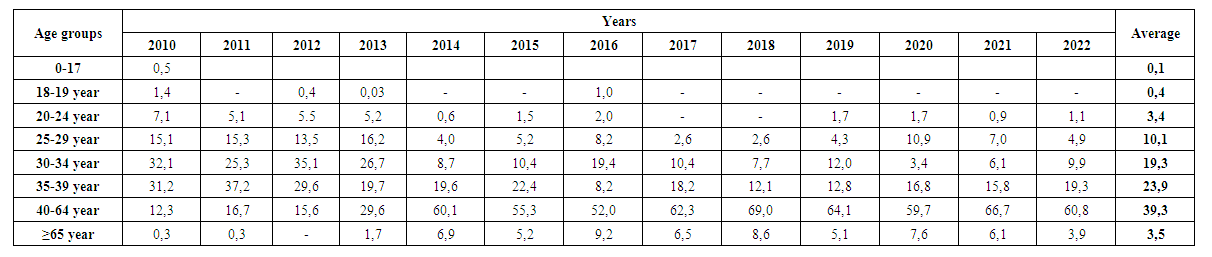 | Table 4. Dynamic distribution of drug addiction by population age groups, Samarkand region, 2010-2022, % |
The share of the 18-19 age group was 1.4% in 2010, but it has sharply decreased in the following years. In general, the contribution of people in the 0-17 age group is 0.1%, among them since 2011, and among those in the 18-19 age group (0.4% on average) since 2017, no new cases of drug addiction have been recorded. During the years 2010-2013, the majority of cases were determined by the 20-39 age group - the most active segment of the population, and since 2014, the share of these groups has been decreasing. In particular, the share of people in the 20-24 age group (3.4% on average) in 2022 (1.1%) decreased by 6.5 times compared to 2010 (7.1%). In the same period, the share of the 25-29 age group (10.1% on average) was 3.1 times, the 30-34 age group (19.3% on average) was 3.2 times, the 35-39 age group (23.9% on average) contribution decreased by 1.6 times. On the contrary, the share of those in the age group 40-64 (average 39.3%) in 2022 (60.8%), 4.9 times compared to 2010 (12.3%), those in the age group ≥65 years (average 3.5%) and its share (3.9% and 0.3%, respectively) increased 13.0 times. Since 2014, people in the age group of 40-64 have had a priority position (52.0-69.0%) in the age group of patients (р<0.05).The analysis of the gender composition of new cases of drug addiction syndrome shows that among the sick patients in the years 2010-2022, male persons have priority, and the absolute number has been recorded in the range from 74 (2017) to 357 (2010) patients (Table 5). The average number of cases among men over 13 years is 161. The share of men among the newly identified general patients in dynamics ranges from 73.4% (2014) to 99.4% (2022), with an average of 94.7%.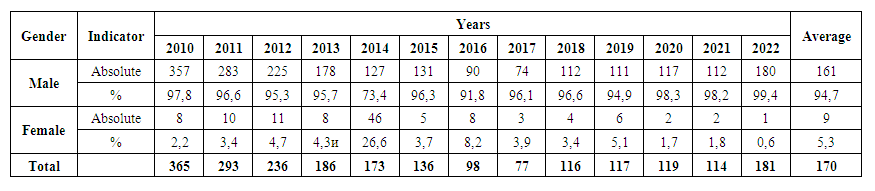 | Table 5. Dynamics of distribution of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome by sex, Samarkand region, 2010-2021 |
Among newly identified patients, the absolute number of women ranges from 1 (2022) to 46 (2014), and their average morbidity is 9. The average incidence rate of women is 17.9 times lower than that of men (r<0.05). The share of women among the newly identified total patients fluctuates dynamically from 0.6% (2022) to 26.6% (2014) and averages 5.3%. Relatively low share of women in the sexual composition of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome can be evaluated as a positive product of oriental values specific to the population of the region and its lifestyle.In order to assess the extent to which the city conditions and the specific lifestyle of the city dwellers, as well as the location in the border area with a neighboring country, affect drug addiction as a risk factor, the incidence rates for the years 2010-2022 in "Samarkand city", "City districts", "Urgut district" and "Rural districts" were divided into groups and analyzed (Table 6). | Table 6. The dynamics of incidence of drug addiction syndrome by territorial groups of Samarkand region, 2010-2022, per 100,000 inhabitants |
The results of the analysis show that the average incidence rate of drug addiction syndrome in the population of Samarkand during 2010-2022 was 10.6 per 100,000 inhabitants, which is 2.2 times higher than the average incidence rate in the region (4.9). (r<0.05). In Urgut district (11.8), which is a border region with the neighboring country, the rate is 2.4 times higher than the regional average (р<0.05). On the contrary, in comparison with the average indicator of the region, "Urban districts" (4.5) had 1.1 times, and "Rural districts" (1.9) 2.6 times lower average incidence rate (r<0.05).The analysis of the dynamics of morbidity by separate regional groups shows that, compared to 2010, the incidence of drug addiction syndrome in 2022 will increase 5.2 times in the city of Samarkand (32.9 and 6.3, respectively), in "City districts" (9.1 and 9.1, respectively 2.3) decreased by 3.9 times, in Urgut district (34.5 and 15.5 respectively) by 2.2 times and in "Rural districts" (2.8 and 2.1 respectively) by 1.3 times.In the long-term dynamics of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome by regional groups, in general, in most regional groups, a similar trend to the regional trend is observed, but in "Rural districts" this situation is not observed. That is, in this territorial group - "Rural districts", there is no difference between "high" and "low" periods of morbidity, as observed at the regional level. The reason why relatively low indicators of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome in the "rural districts" remain stable in the long-term dynamics is explained by the fact that the main factors determining the formation of drug addiction syndrome in these regions remained almost unchanged during the period under study (13 years).In all territorial groups except "City districts", as observed by the region, the increase in incidence in 2022 compared to 2021, in particular in the city of Samarkand by 1.4 times (annual growth rate of 37.4%), in Urgut district by 3 times (annual growth rate of 203, 9%) and 1.2 times (annual growth rate of 23.5%) was recorded in "Rural districts". On the contrary, in "City Districts" in 2022, compared to 2021, the incidence decreased by 1.9 times, and the annual rate of decrease is 48.9%. It can be seen that the increase in morbidity in the region in 2022 was mainly determined by the increase in morbidity in Urgut district.The analysis of the dynamics of morbidity by regional groups shows that the risk of developing drug addiction syndrome is higher for residents of Urgut district, a bordering region with neighboring countries, than for residents of other regional groups, including the city of Samarkand. In general, the data obtained as a result of the analysis indicate that districts bordering neighboring countries, large cities, suburban districts are "dangerous areas" for the formation of drug addiction syndrome, and according to the level of morbidity, the residents of these areas belong to the "risk group". The risk of developing drug addiction syndrome is especially high in regions bordering neighboring countries.
4. Conclusions
In the long-term dynamics of the incidence of drug addiction syndrome in Samarkand region, there is a clear downward trend and a difference between the "high incidence period" (2010-2014) and the "low incidence period" (2015-2022), and the incidence rate in 2022 is higher than in 2010. decreased almost 2.3 times, the average annual rate of decrease is 4.7%. It was found that most patients used heroin (45.9%) and cannabis (26.3%). In the age structure of patients, during 2010-2013, the contribution of persons in the age groups of 20-39 was the priority, and since 2014, the contribution of these groups has been decreasing. On the contrary, since 2014, people in the age group of 40-64 have a priority position in the age group of patients. In 2022, the share of people in the age group 40-64 increased by 4.9 times compared to 2010, and the share of people in the age group ≥65 years increased by 13.0 times. Among patients with a newly diagnosed drug addiction syndrome, the average share of men is 94.7%, and the average share of women is 5.3%. The average incidence rate of women is 17.9 times lower than the incidence rate of men. There is a sharp difference in the incidence rate in regional groups, that is, the average incidence rate is 11.8 per 100,000 inhabitants in Urgut district and 10.6 in Samarkand city, while in "Rural districts" it is 1.9.Thus, this study shows that the prevalence of drug addiction syndrome in Samarkand region is decreasing. In comparison to rural districts, the incidence is higher in Urgut district, Samarkand city and districts adjacent to the city bordering the neighboring country. At present, the majority of people with drug addiction syndrome are male and over 40 years old. These aspects must be taken into account when planning and implementing measures aimed at preventing drug addiction syndrome and providing medical and social services to patients.
References
| [1] | Report of the International Narcotics Control Board 2020. Recommendations to governments, the United Nations and other relevant international and national organizations // J. NARCOLOGY. - M.: 2021, No. 11.- Pp 3-11. |
| [2] | Kenjaeva N.Q., Rizaev J.A., Magzumova Sh.Sh., Baymirov S.L. Some factors determining the regional distribution of drug addiction // Fundamental and Clinical Medicine BULLETIN.-#4, 2022.-p.125-130. |
| [3] | Kenjaeva N. K., Rizaev J. A., Umirov S. E. Description of the dynamics of sex and age composition of drug addicts // J. Journal of Biomedicine and Practice. Volume 7, No. 5 (2022), 178-185. |
| [4] | Kenjaeva N.K., Umirov S.E., Yusupov Sh.R. Disease status of drug addicts with some sexually transmitted infections // J. Infection, immunity and pharmacology, No. 5, 2022, p. 131-140. |
| [5] | Sirliev B. N. Causes of drug addiction and psychological aspects of its prevention // National and foreign experience of combating crimes involving illegal dealing with narcotic drugs or psychotropic substances: current situation and prospects for improving legislation. Resp. scientific-practical conference materials. T.: 2017. - 79-86 p. |
| [6] | Strategy UNP OON na 2021-2025. // J. NARCOLOGY.- M.: 2021, #12.- Str. 3-25. |
| [7] | Umirzakov Z.B., Kenjaeva N. Q., Umirov S.E., Some aspects of HIV infection // Scientific and practical journal of the sanitary-epidemiological peace and public health service of the Republic of Uzbekistan. -№4, 2022. -p. 107-111. |
| [8] | Report of the International Narcotics Control Committee, 2021. INTERNET resource. |
| [9] | Kenjaeva N. K., Umirov S.E., Yuldashev K.Kh. Some aspects of the socio-demographic description of drug addicts //. |
| [10] | National manual for the organization of drug support. Mirazimov D.B., Tursunkhodzhaeva L.A., Baymirova L.T., Tursunkhodzhaev M.Kh. under the editorship of Professor A.V. Alimov, Tashkent-2016. |




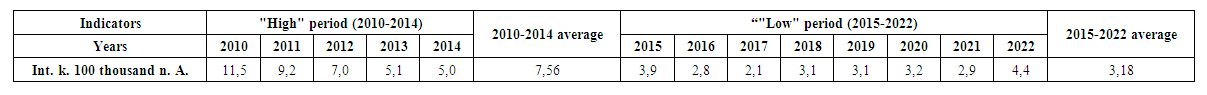



 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML