Akhmedov Nizom Ilkhomovich
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Akhmedov Nizom Ilkhomovich, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Today, there is no doubt that the immune system is involved in any pathological conditions in the body, whether it is an infectious process or a purulent-inflammatory process, the immune system is involved in all of them. In these pathological conditions, the quantitative and qualitative changes of specific and non-specific resistance factors of the immune system are not only diagnostic, but also prognostic.
Keywords:
Acquired heart defects, Immune status, Cellular and humoral immunity, Cytokine status
Cite this paper: Akhmedov Nizom Ilkhomovich, Description of the Immune Status of Patients with Various Enlarged Heart Defects, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 7, 2023, pp. 976-983. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231307.28.
1. Introduction
The development of clinical immunology today allows the widespread use of immunological methods in the diagnosis of various pathological conditions, it is no secret that the determination of cellular, humoral and non-specific factors of the immune system is used in the diagnosis of various nosological units. While cellular immunity can accurately provide information on the formation and development of the disease, its course and end, along with determining the quantitative indicators of immunocompetent cells, the concentration of the factors of the humoral immune system in various biological fluids of the body, and changes in the dynamics of treatment allow determining the effectiveness of the treatment. Immunological indicators are important in making the final diagnosis, as well as clinical symptoms, instrumental and laboratory tests.Identification and evaluation of cellular and humoral factors of the immune system using immunological methods used in clinical immunology is of great importance in determining the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment tactics of cardiovascular diseases, including various heart defects.Are pathological changes due to deformation of the heart walls, chambers, barriers and valves, which lead to malfunction of the heart and hemodynamics inside it. Today, heart defects are divided into congenital and life-acquired pathologies. Information on the classification, course, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of all heart defects is presented in detail in the first chapter of this thesis, so we did not find it necessary to dwell on them.Changes in the immune system in congenital and acquired heart defects in children, their specific characteristics, although there are selected materials, changes in the immune system in patients with adult heart defects, their role in the pathogenesis of the disease, quantitative changes in cellular and humoral immunity, their diagnostic and prognostic significance have not been revealed to the end. not given. For this reason, we have undertaken this scientific research work in order to clarify these issues.
2. Material and Methods
All patients diagnosed with acquired heart defects studied were 28-60 years old, with verified diagnoses of aortic heart defect (n=27), mitral heart defect (n=42), and combined and concomitant heart defects (n=51). Before giving a separate description of all of them, we found it necessary to describe the general group of patients with heart defects (n=120). A total of 15 healthy individuals without heart defects formed the control group. Following the sequence of analysis of the results, we started the interpretation with the indicators of cellular immunity.To conduct an immunological study, blood from the elbow vein was processed with heparin in the amount of 5.0 ml, taken into a centrifuge tube, 10 μl of Zadorojnyi S.I. and Dozmorova I.M. (1987) was taken to count leukocytes and lymphocytes in the Goryaev chamber using the dye. Mononuclear cells from peripheral blood were obtained by ficoll-verografin density separation at a density of 1.077 g/l according to Boum (1968). The number of cells was counted in the Goryaev chamber by the generally accepted method, under the microscope of the company "Leica" (Germany), and the concentration of lymphocytes was brought up to 2x10 6 in 1 ml, the viability of lymphocytes was determined in 0.1% trypan blue.The relative indicators of immunocompetent cells of the immune system of patients and healthy individuals were evaluated according to the expression of CD-differentiating and activating antigens. The following markers of these cells were identified: CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD16+, CD20+, CD25+, CD95+ lymphocytes. Expression of CD receptors Garib F.Yu. and all. (1995). Immunoregulatory index (IRI) - the ratio of CD4+ cells to CD8+ cells was also calculated.β cytokines in the blood serum of patients and the concentrations of IgA, IgG, IgM were carried out using IFA on the Stat Fax (Awaress Technology, USA) test system produced by "Vektor Best" (Novosibirsk, RF). Immunological studies were carried out at the Institute of Immunology and Human Genomics of the Federal Republic of Uzbekistan on the basis of a bilateral agreement.The statistical processing of the received material was carried out using the "Excel" program using traditional variational statistics methods. Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out by calculating the following parameters: average arithmetic size (M), average arithmetic error (m), the significance of differences was determined by the Fisher-Student test (P). Differences between means were considered reliable if the probability level was P<0.05. Statistical processing was carried out using a software package for medical-biological research on a personal computer based on Pentium IV processors. The principles of evidence-based medicine were used in the organization and conduct of research.
3. Results and Discussion
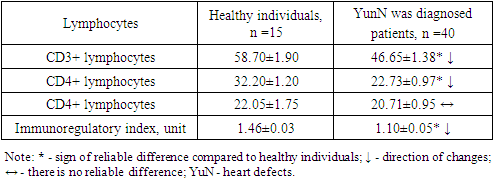
Cellular immunity consists of T- and V-lymphocytes, which are immunocompetent cells of the immune system, natural killers, activators of apoptosis and other cells, in which quantitative and relative indicators of these cells are evaluated. Their absolute indicators are calculated depending on the amount of leukocytes and lymphocytes in the blood, and in many cases, the immune system does not allow to adequately evaluate the activity of the cellular joint. As a result of various effects, changes in leukocyte concentration cause an increase in the number of these absolute indicators, which does not allow for a true assessment of the immune system. Based on this, we made an adequate assessment of the immune status by comparative interpretation and analysis of the relative amounts of immunocompetent cells.It is known that today immunocompetent cells are designated by CD markers (incl. - cluster of differentiation, cluster designation - differentiating cluster), which is the nomenclature of differentiating antigens of human leukocytes. This classification is in 1982 recommendation done is used for the identification of leukocyte surface membrane α proteins. CD - antigens as intercellular mutually in relation participating re tsep tor or in the ligand in the form of serving proteins are understood. Today's in the day a total of 350 t a CD - antigens and their tips _ known being, this the list is constantly being filled is going That's it among T- lymphocytes CD - markers there are also (CD 3+- lympho ts dogs).CD 3 + - lymphocytes (T- lymphocytes) bone _ in the grave harvest has been core from cells in timu s differen tsi rovka to be cells is immune _ system cellular immunity main cell is considered Theirs quantitative or relative in terms of decline in the body secondary immonodefe ts it developed a tree gives _ T-lymphocytes play an important role in the immune response, recognizing and eliminating foreign antigen-bearing cells. Today, many regulatory subpopulations of CD3+ cells are differentiated, the main ones being CD4+ (T-helper/inducers) and CD8+ lymphocytes (T-suppressors/cytotoxic lymphocytes). Although their tasks are different, they complement each other's activities.The results of determination of indicators of CD3+-, CD4+- and CD8+-lymphocytes in patients with various heart defects (Table 1) showed that their relative indicators were imbalanced. It was found that the CD3+-cells on the day of admission to the hospital were convincingly reduced compared to the values of healthy individuals.Table 1. Relative indicators of the immune system T-joint in patients diagnosed with various heart defects, %
 |
| |
|
As can be seen from the cited table 1, CD3+-lymphocytes averaged 58.70±1.90% in healthy individuals, and this parameter was found to be 1.26 times higher than the indicators of the studied patients - 46.65±1.38% (R<0, 05).The convincingly low level of this indicator in patients was explained by the negative effect of the pathological process on the T-joint of the immune system. Also, the differentiation of lymphopoietic stem cells into T-lymphocytes in the thymus is evidenced by this, and the formation of T-immunodeficiency in the body was considered as an aggravating factor of the pathological process in the body.Changes in T-lymphocyte regulatory subpopulations were also detected. If we take into account that CD4+-lymphocytes regulate the activities of other immunocompetent properties of the immune system, recognize antigens, control cellular immune response processes, it becomes clear how important it is to determine, and their quantitative variability has been proven to have a negative effect on the activity of the entire immune system. In our case, T-helpers/inducers (SD4+-cells) in patients was 22.73±0.97%, and this parameter was found to be 1.42 times lower than these indicators in healthy individuals (32.20±1.20%). (R<0.001). If we compare with the indicators of CD3+-lymphocytes, it can be seen that the decrease of both cells took place in different intensity, but in the same trend - their changes were proportional to each other.Such an opinion cannot be made about CD8+-lymphocytes, because even if their average amount in patients is slightly decreased compared to healthy ones (20.71±0.95% vs. 22.05±1.75% R<0.05, respectively), they it is noteworthy that it is not convincing. If we take into account that they suppress the functions of T-helpers, V-lymphocytes, control the strength and duration of the immune response, their maximum amount is observed 3-4 weeks after the introduction of a foreign antigen into the body, the decrease in their indicators is explained by the hyperactivity of the immune system.The role of immunoregulatory index (IRI) is high in evaluating the activity of the immune system T-joint. IRI is the ratio of CD4+-lymphocytes to CD8+-lymphocytes, and in healthy individuals, this unit is higher than 1.0, but its higher than 2.2 indicates a hyperactive immune system, which is also considered a pathological condition.In order to assess the state of the body's special protective immune cells, we calculated IRI in healthy individuals and adult patients with various heart defects. If in healthy individuals this indicator was on average 1.46±0.03 units, we found that it reliably decreased to an average of 1.10±0.05 units in patients (decrease by 1.33 times, R<0.001). The analysis showed that this condition was observed mainly due to CD4+-lymphocytes. Therefore, deficiency in the immune system, that is, T-joint immunodeficiency occurred due to a decrease in the relative amount of CD3+- and CD4+-cells, and activation of CD8+-cells was not observed.Taking into account the involvement of V-lymphocytes in the immune response along with the T-cell of the immune system, the relative amount of CD20+-cells - CD20+- marker-bearing V-lymphocytes was also studied in these patients with heart defects. The obtained results are presented in the form of Figure 1, in order to make their comparative analysis easier, we found it necessary to mention the relative indicators of the T-joint of the immune system.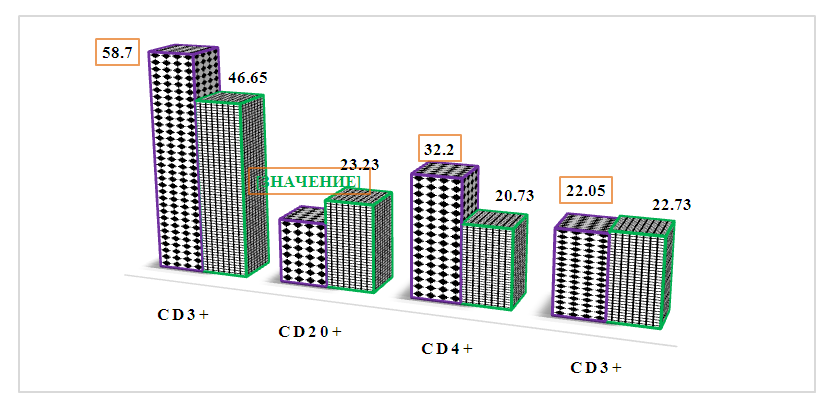 | Figure 1. Comparative analysis of T- and V-joint indicators of the immune system in patients with heart defects (green color) compared to healthy individuals (black color), % |
If we take into account the fact that V-lymphocytes differentiate into plasma cells in the immune response, synthesize immunoglobulins, provide humoral immunity of the immune system and control it, we see that their relative amount is related to the quantitative indicators of immunoglobulins in the blood serum. These immunocompetent cells of the immune system bearing the CD20+ marker have different transformation characteristics in different pathological conditions.In our case, we see that CD20+-cells in patients are convincingly increased compared to healthy individuals - 23.23±0.41% versus 16.90±0.90%, respectively (increase up to 1.37 times, R<0.001). The proliferation of these cells is associated with the stress of the immune system and T-joint deficiency in the body, because according to the "mobile principle" the immune system is characterized by a decrease in one joint and an increase in the other, which indicates that they complement each other's functions. It is known that the CD3+-lymphocyte indicators were decreased in patients, and the increase of CD20+-lymphocytes served to functionally complement this secondary immunodeficiency.CD16+-lymphocytes (natural killers, effector cells) are included in the non-specific factor of the immune system, because their quantitative indicators do not depend on the introduction of antigen into the body. Also, these immunocompetent cells are responsible for anti-tumor, anti-viral and transplant immunity. They are fundamentally different from T- and V-lymphocytes in terms of origin, function, and surface receptors.In the patients we observed, a relative increase in their relative amount in the blood was observed - 20.55±0.43% in patients, respectively, and 16.60±0.30% in healthy individuals (control group) (up to 1.24-fold increase in reliable level, R< 0.05) - Fig. 2.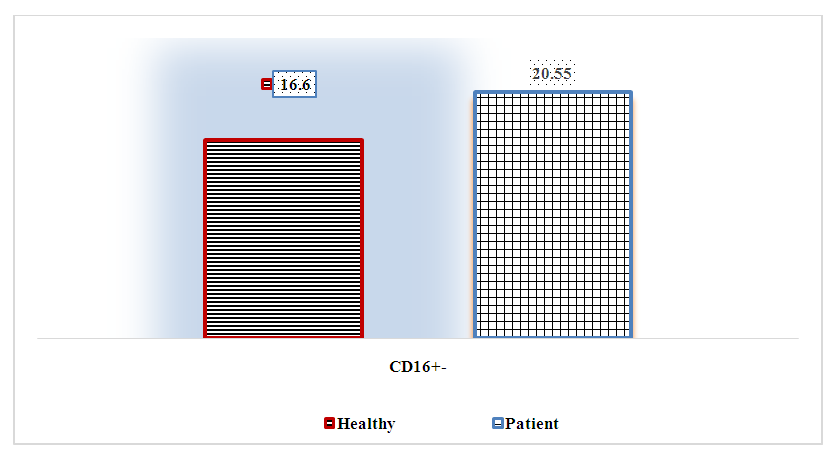 | Figure 2. Relative indicators of CD16+ lymphocytes in the blood of patients with various heart defects, % |
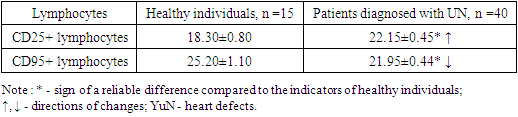
It is known that in tumor diseases, viral infections and other conditions, their concentration in the blood decreases, only in transplantation immunity, their amount increases. In our case, the structural changes in the heart were explained by the fact that the immune system perceives CD16+ cells as such and acts on the structurally changed tissue, which in turn negatively affects the course of the disease.At the next stage of the scientific work, the relative amounts of CD25+ and CD95+ lymphocytes, which are among immunocompetent cells, were determined, the results are presented in Table 2.Table 2. Results of the study of the relative indicators of CD25+ and CD95+ lymphocytes in patients with various heart defects,%
 |
| |
|
It is known that CD25+ lymphocytes are important immunocompetent cells of the immune system. They are activated T-lymphocytes that provide antibody formation and cytotoxicity. In the studies, it was found that the relative amount of these cells was slightly increased in the studied patients compared to the indicators of healthy individuals - 22.15±0.45% versus 18.30±0.80%, respectively (increase by 1.21 times, R<0.05). Compared with the relative amount of CD3+ lymphocytes, these parameters were found to be inversely proportional to each other.In the research, we found it necessary to determine CD95+-lymphocytes, because they are an indicator of apoptotic activity of lymphocytes, and it was shown that the duration of the pathological process in various pathological conditions is related to the level of apoptotic activity of lymphocytes.In patients with various heart defects, the relative amount of CD95+ cells was reliably reduced by 1.15 times compared to the parameters of healthy individuals - 25.20±1.10% against 21.95±0.44%, respectively (R<0.05). This condition was characterized by inhibition of the apoptosis process, leading to a decrease in the intensity of the immune response. In our opinion, a decrease in the relative amount of CD95+ lymphocytes can be recommended as an immunological prognostic criterion indicating a decrease in the intensity of the immune response.A comparative study of the indicators of cellular immunity of the studied immune system in the section of patients and healthy people made it possible to determine the intensity of their changes. For this purpose, we took the immunological parameters of healthy individuals as equal to 1.0, calculated the immunological parameters of patients according to it and presented them in the form of Figure 3. The obtained results showed the intensity and level of the changes of the compared indicators.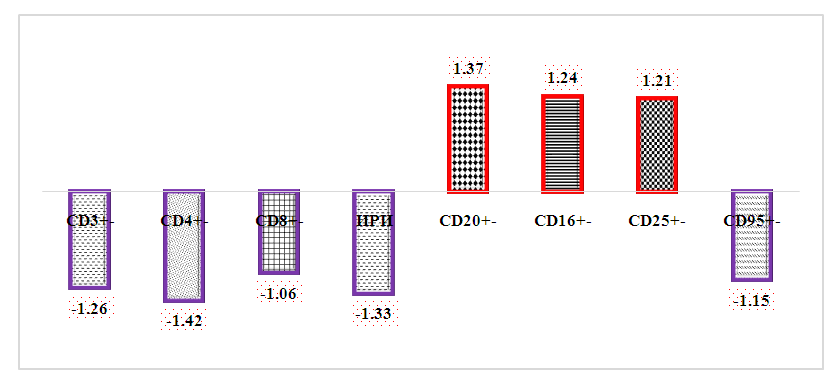 | Figure 3. In patients with various heart defects, the relative indicators of immunocompetent cells are the ratio of the corresponding differences in the parameters of healthy individuals, times |
It can be seen that the immunological parameters corresponding to cellular immunity of the immune system were manifested differently in patients. The interpretation and analysis of these immunological results led to the following peculiarities: firstly, statistically significant difference was detected in 87.5% of immunological parameters (except for CD8+-lymphocytes), where all indicators were shown to be significantly higher or lower than the parameters of healthy individuals;secondly, 5 out of 8 studied immunological indicators (CD3+-, CD4+-, CD8+-, CD95+- and IRI, 62.5%) were lower than these indicators in healthy individuals, while 3 immunological parameters (CD20+-, CD16+-, CD25+-, 37.5%) was significantly more than the data of healthy people;thirdly, if a secondary immunodeficiency was observed in the T-joint of the immune system, the indicators were high in the V-joint (R<0.05), this situation is explained by the "mobile principle", in which it is shown that the deficiency of any part of the immune system leads to an increase in the other, that is, they are one fills the function of one;fourth, the comparative determination of the relative amounts of these immunological indicators allows to estimate the strength, intensity and level of the immune response, which is a product of the body's immune system;Secondly, CD3+-, CD4+-, CD8+-, CD20+-, CD16+- and CD25+-lymphocytes were recommended as additional immunological diagnostic criteria, and IRI and CD95+-lymphocytes were recommended as immunological prognostic criteria to evaluate the activity of the immune system in elderly patients with heart failure.Quantitative changes in the specific and non-specific protective factors of the immune system were determined to be influenced by the diagnosed heart defects, and the imbalance in the amount of immunocompetent cells in the T-joint of the immune system was shown. In order to have a complete picture of the body's immune status, it was necessary to study the factors of humoral immunity and to compare and analyze the results.Based on the above, the patient's organism has humoral immunity indicators - concentrations of IgA, IgG, IgM in the blood serum and cytokines vascular endothelinal growth factor (VEGF - English) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF- β - English, transforming growth). factor- b) was studied.The main classes of immunoglobulins were selected for study because they play a key role in the immune response and are produced against exogenous agents and internal factors that enter the body. It also participates in the elimination of antigens and autoantigens from the body.The obtained results showed that (Table 3), the concentration of IgA in the blood serum of patients was 2.57±0.15 g/l, which is up to 1.71 times compared to the values of healthy individuals (1.50±0.1 g/l). showed that it was reliably overdetermined (R<0.001). If we take into account the high role of IgA in the immune response, one of the factors providing local immunity, the quantitative increase of this immunoglobulin is associated with an increase in the activity of the immune system.Table 3. Quantitative indicators of immunoglobulins in the blood serum of patients with various heart defects, g/l
 |
| |
|
A similar trend of changes was obtained for IgM, its concentration in blood serum was found to be reliably increased compared to the parameters of healthy individuals - 1.86±0.10 g/l versus 1.0±0.05 g/m, respectively (average 1, 86-fold increase r<0.001).In contrast to them, it was found that the concentration of IgG in blood serum was convincingly reduced compared to the values of healthy individuals - 6.66±0.27 g/l against 10.50±0.20 g/l, respectively (decrease up to 1.58 times, R< 0.001). If we take into account that IgG makes up 75% of all immunoglobulins, fully supports the secondary immune response, is the basis of the function of the immune system, it becomes clear why we chose this indicator.If we look at the analysis of the results obtained for all three immunoglobulins, we can see that there is an imbalance in their amount.The imbalance in the amount of immunoglobulins in the blood serum of patients was determined based on the ratio of the quantitative indicators of these immunoglobulins to the indicators of healthy individuals. According to it, IgM and IgA increased by 1.24 and 2.57 times, respectively, while IgG decreased convincingly by 1.57 times (Fig. 4). | Figure 4. Various heart defects observed patients blood in serum main immunoglobulins concentrations, g/ l |
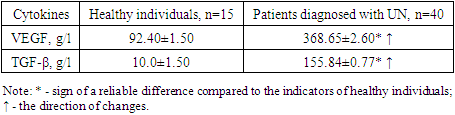
It should be noted that although the trend of IgM and IgA changes is the same, the intensity of their increase is different, the quantitative increase of IgA is related to the secretory appearance of this immunoglobulin on the surface of the mucous membranes and its function in the blood serum., was explained by the fact that it is the first synthesis, provides the primary immune response, is of little importance in the secondary immune response, and practically does not participate in the elimination of pathogens that persist for a long time.The decrease in the concentration of IgG in the blood serum compared to the indicators of healthy individuals is due to the absence of a clearly manifested inflammatory process in the body, as a result of the pathological process in the body, an irreversible process has occurred in the heart tissue.It should be noted that the changes of these immunoglobulins in the blood serum were not considered to be of great pathogenetic significance for these patients.Failure to study the amount of cytokines in the assessment of humoral immunity does not allow them to be fully described. Therefore, the aim was to determine the cytokine status of patients diagnosed with various heart defects.Today, VEGF and TGF-β cytokines, which are important in the pathogenesis of this disease, which are actively involved in the activity of the immune system performing various tasks, were identified and their quantity was compared, the obtained results are presented in the form of Table 4.Table 4. The results of the study of the amount of cytokines in blood serum in adult patients diagnosed with various heart defects, g/l
 |
| |
|
The obtained results show that both studied cytokines were statistically significantly higher (R<0.001) than healthy individuals in adult patients diagnosed with the studied pathologies.If the cytokine VEGF is produced by various cells to stimulate vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, their delivery of oxygen to tissues It is important to determine the amount of these cytokines, given that they are responsible for restoring the blood supply (in the case of insufficient blood circulation), providing collateral blood circulation. Also, VEGF induces endothelial cell mitosis and chemotaxis in endothelial cells pore formation and v azodilatation is responsible. This cytokine is important as a major angiogenic factor in heart defects.The serum concentration of this cytokine in our case was found to be 3.99 times higher in patients than in healthy individuals - 368.65±2.60 g/l versus 92.40±1.50 g/l, respectively (R<0.001). It was considered that this condition is related to the lack of blood and oxygen to the heart cells and the positive effect of this cytokine on angiogenesis, in other words, it indicates a pathological condition involving vascular endothelium.A similar trend of changes was observed in the coconcentration of TGF-β cytokine determined in the blood serum of the studied contingent, in this case the concentration of this cytokine was statistically significantly higher than the values of healthy individuals (R<0.001).The cytokine TGF-β is known to be a factor controlling many cell proliferation, cellular differentiation and other functions, and has been shown to be involved in the primary and secondary immune response. Although their participation in cardiovascular diseases has been shown, their quantitative indicators have not been practically studied and analyzed in the diagnosis of heart defects. If we also take into account that they block the activity of lymphocytes and macrophages, their effect on the activity of the immune system becomes more clear.In our case, it was found that the amount of TGF-β in the blood serum of patients increased by 15.58 times compared to the values of healthy individuals - 155.84±0.77 g/l versus 10.0±1.50 g/l, respectively (p<0.001). Although the trend of changes compared to the previous cytokine studied was the same, it appeared to be higher in intensity (Figure 5). | Figure 5. The ratio of VEGF and TGF-β cytokines in patients with heart failure to healthy individuals, times |
It can be seen from the given picture that the intensity of changes of TGF-β is higher than that of VEGF cytokine.
4. Conclusions
1. It was observed that CD3+-lymphocytes decreased by 1.26 times and CD4+-lymphocytes by 1.42 times in elderly patients diagnosed with various heart defects, but no reliable changes in CD8+-lymphocyte parameters were detected, which indicates hyperproduction of CD8+-cells against the background of secondary immunodeficiency. indicates no need. This condition was also observed when IRI was detected, it was proved that the reduction of this parameter by 1.33 times was due to CD4+-lymphocytes.2. In patients with various heart defects, the amount of CD20+ cells increased by 1.27 times compared to the parameters of healthy individuals, which in turn was explained by the increase in humoral immune activity and the observation of secondary immunodeficiency in the T-joint of the immune system. This situation corresponds to the "mobile principle", which showed that one part of the immune system decreases and the other increases.3. Patients of different ages with heart defects were characterized by a convincing increase of CD16+-lymphocytes by 1.24 times compared to healthy individuals. It was considered that the increase in their relative amount is related to structural changes in the above tissues.4. In patients with various heart defects, the amount of CD25+-lymphocytes in the peripheral blood reliably increased by 1.25 times, while the relative amount of CD95+-lymphocytes, on the contrary, decreased statistically significantly by 1.15 times. This condition indicates that as the amount of activated lymphocytes increases in this pathology, their process of preparation for apoptosis decreases. It has been shown that this condition leads to a decrease in the intensity of the immune response, which is a product of the body's immune system.5. In patients with various heart defects, IgM is 1.24 times higher, and IgA is 2.57 times higher than healthy people. it was found that the concentration of IgG was statistically significantly decreased by 1.57 times. This situation was explained by the lack of obvious inflammatory symptoms in patients, the strength and intensity of the secondary immune response.6. In patients with heart failure, the amount of VEGF was statistically significantly higher by 3.99 times compared to healthy individuals, while the difference in TGF-β concentration was 15.58 times. Although the trend of cytokine changes was the same, their intensity was dominated by TGF-β. A sharp increase in the amount of these cytokines is pathogenetically related to the observation of heart defects and is recommended as a diagnostic indicator of the severity of the disease in this pathology, as well as prognostic immunological indicators that determine the outlook for the end of this pathology.
References
| [1] | Jia Y. et al. NLRP3 inflammasome and related cytokines reflect the immune status of patients with HBV-ACLF // Molecular immunology. – 2020. – Т. 120. – С. 179-186. |
| [2] | Bruni D., Angell H. K., Galon J. The immune contexture and Immunoscore in cancer prognosis and therapeutic efficacy // Nature Reviews Cancer. – 2020. – Т. 20. – №. 11. – С. 662-680. |
| [3] | Kanmogne G. D. et al. Effects of HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy, and immune status on the speed of information processing and complex motor functions in adult Cameroonians // Scientific reports. – 2020. – Т. 10. – №. 1. – С. 14016. |
| [4] | Rienzo M. et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of sepsis: insights from preclinical and clinical development // Expert opinion on investigational drugs. – 2022. – Т. 31. – №. 9. – С. 885-894. |
| [5] | Bodinier M. et al. Identification of a sub-group of critically ill patients with high risk of intensive care unit-acquired infections and poor clinical course using a transcriptomic score // Critical Care. – 2023. – Т. 27. – №. 1. – С. 158. |
| [6] | Mallet F. et al. Herpes DNAemia and TTV viraemia in intensive care unit critically ill patients: a single-centre prospective longitudinal study // Frontiers in Immunology. – 2021. – Т. 12. – С. 698808. |
| [7] | Peng B. et al. Standardization of neutrophil CD64 and monocyte HLA-DR measurement and its application in immune monitoring in kidney transplantation // Frontiers in Immunology. – 2022. – Т. 13. – С. 1063957. |







 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


