-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(6): 814-820
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231306.09
Received: May 20, 2023; Accepted: Jun. 15, 2023; Published: Jun. 21, 2023

The Importance of Digital Technologies in the Teaching of Fundamental Sciences in Medical Universities
Bazarbayev M. I., Raximov B. T., Sobirjonov A. Z., Sayfullayeva D. I., Jurayeva Z. R., Ixrorova S. I.
Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Due to the most rapid technological development, globalization and integration processes, huge changes and problems in the world education system are becoming real problems of rapid technological changes in the whole world. In this article, I will analyze the systems of ARM (Information Resource Center) in the foreign state education system and make recommendations for improving electronic library systems. The relevance of information and resource centers in the development of our country, the policy of digitalization of the medical field, the creation of amenities for the population, the development of medicine using the world's advanced technologies, and the training of competitive personnel have a special place.
Keywords: Information-resource center, System IRC, DSpace, Open access, Repository, Research capital, Archiving, Digital technology
Cite this paper: Bazarbayev M. I., Raximov B. T., Sobirjonov A. Z., Sayfullayeva D. I., Jurayeva Z. R., Ixrorova S. I., The Importance of Digital Technologies in the Teaching of Fundamental Sciences in Medical Universities, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 6, 2023, pp. 814-820. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231306.09.
1. Introduction
- Under the conditions of globalization, fundamental changes are being made in the world higher education system. Modern information technology is a tool that determines the strategy and tactics of the development of large libraries. The introduction of computer technology, telecommunications and electronic resources has led to a radical change in all aspects of the provision of resources and information about them, from the reader and librarian to the forms and quality of service.All the laws and normative-regulatory documents related to the field of education envisage the development of the higher and secondary special education system in our republic in accordance with world standards, bringing the quality of education to the level of international standards.The aim of this work is to study the directions of development, legal bases, management structure and characteristics and standards of the information-resource center system in a higher education institution, to develop appropriate conclusions and proposals based on them.The object of the work is the information resource centers in the higher education system, and the subject is the study of the features of the DSPACE software in the information resource centers of the higher education system.Globalization of the educational space, ensuring the mobility of personnel, development of international standards for the quality of education, the 21st century puts new tasks before the educational system.
2. Materials and Methods
- Today, several licensed information resources are used in the local network of the National Library in Uzbekistan. They are: Scopus, Web of science, EBSCO Academic, EBSCO Audio, eLibrary, JSTOR, Library Press Display, ProQuest and so on. Open information resources are free links over the public Internet that allow users to read, download, copy, distribute and print, search and cite, index, transmit, or use information for other purposes. Today, 33 open information resources are used in the library. Users have the opportunity to use these open information resources not only from the National Library, but also from any address via the Internet.
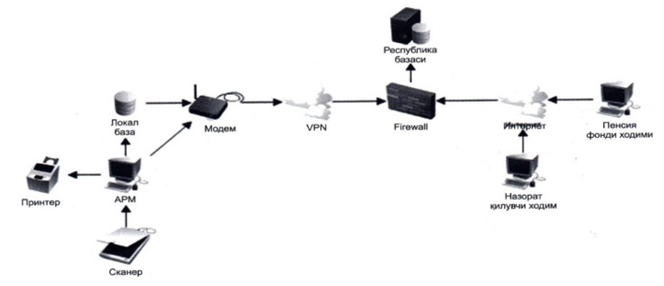 It opens up new opportunities for users to support the implementation of scientific research and educational processes. They have a convenient interface and an excellent search system, which allows access for several users at the same time without being limited by IR address.Also, users can use foreign scientific and educational online information resources not only from the computers of the library's reading rooms, but also through its website www.natlib.uz.
It opens up new opportunities for users to support the implementation of scientific research and educational processes. They have a convenient interface and an excellent search system, which allows access for several users at the same time without being limited by IR address.Also, users can use foreign scientific and educational online information resources not only from the computers of the library's reading rooms, but also through its website www.natlib.uz.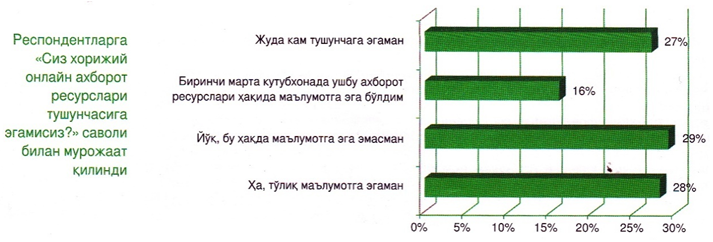 Also, it is possible to find and use resources related to the activities of information-library employees from these scientific and educational online databases. They are: Cambridge JOURNALS, East View, EBSCOHOST, Emerald, JSTOR, Library and Archives Canada, ProQuest Royal Society Publishing, Springer Link, ProQuest information companies are among them.Today, sociological research shows the following indicators regarding the use of foreign scientific and educational online information resources along with printed resources by the users of the National Library and the level of need for these resources.
Also, it is possible to find and use resources related to the activities of information-library employees from these scientific and educational online databases. They are: Cambridge JOURNALS, East View, EBSCOHOST, Emerald, JSTOR, Library and Archives Canada, ProQuest Royal Society Publishing, Springer Link, ProQuest information companies are among them.Today, sociological research shows the following indicators regarding the use of foreign scientific and educational online information resources along with printed resources by the users of the National Library and the level of need for these resources.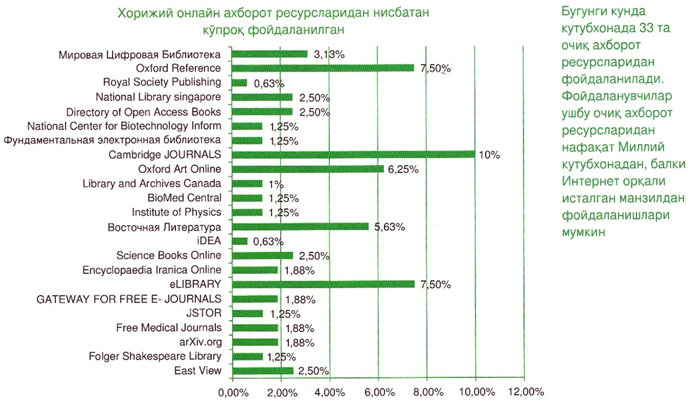 Respondents use the resources of the leading international information production companies: Oxford Art Online, Oxford Reference, Cambridge JOURNALS, eLIBRARY, Vostochnaya Literatura, ProQuest in the folder called "Zarubezhnye elektronnye resursy" ("Foreign electronic resources"), which is located on the computers of the reading rooms, compared to other information resources. showed.We have studied the indicator of users' use of foreign online information resources. The results of the study showed that 7% of students did not know how to use this site at all, and 21% of respondents said that they did not know because they had not used these resources before.The remaining 71 percent of users said that they are familiar with these sites and work on them. When the advantages of these sites were studied, 44% of users found these sites to be preferred, 30% of users asked to increase the network of these sites, and the remaining 26% of users did not find these networks to be preferred.
Respondents use the resources of the leading international information production companies: Oxford Art Online, Oxford Reference, Cambridge JOURNALS, eLIBRARY, Vostochnaya Literatura, ProQuest in the folder called "Zarubezhnye elektronnye resursy" ("Foreign electronic resources"), which is located on the computers of the reading rooms, compared to other information resources. showed.We have studied the indicator of users' use of foreign online information resources. The results of the study showed that 7% of students did not know how to use this site at all, and 21% of respondents said that they did not know because they had not used these resources before.The remaining 71 percent of users said that they are familiar with these sites and work on them. When the advantages of these sites were studied, 44% of users found these sites to be preferred, 30% of users asked to increase the network of these sites, and the remaining 26% of users did not find these networks to be preferred.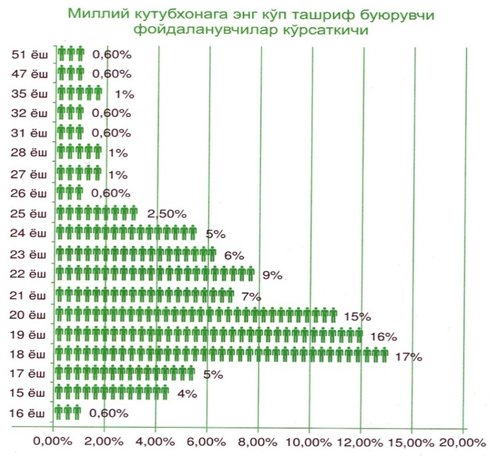 These indicators indicate that many citizens of our country connect to the database of leading foreign companies and use them to improve the efficiency of their profession. It is necessary to collect, store, and allow others to use or restrict the use of all this information. Open Access to Research means the realization of the rights of the author of the innovation to any person at any place and time of his choice through scientific communication. There are a number of software programs available to do this, which will perform the above processes.
These indicators indicate that many citizens of our country connect to the database of leading foreign companies and use them to improve the efficiency of their profession. It is necessary to collect, store, and allow others to use or restrict the use of all this information. Open Access to Research means the realization of the rights of the author of the innovation to any person at any place and time of his choice through scientific communication. There are a number of software programs available to do this, which will perform the above processes. World information resources are scientific and educational electronic resources of the world's leading companies and publishers, which make a great contribution to the development of science, education, culture and business. Licensed information resources - they are information resources based on license agreements, which users can use only for scientific and educational purposes in the local network of the institution. Commercial use of the information in them is prohibited. Users also assume full responsibility for compliance with license requirements.The DSpace electronic library platform was created together with the Hewlett-Packard company and the Federation of Universities created to implement the project. The federation includes Cambridge University, Columbia, Cornell, Massachusetts Institute of Technology - MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Library, Ohio State, University of Rochester, University of Toronto and Washington State University. On November 4, 2002, this system was launched as a working service of the library of the institute. This program was formed as a result of scientific research in the field of electronic library. There is another program similar to DSpace, which focuses on supporting scientific articles - Eprints - which originated from the "Scholarly Communication" movement. optimized for placement. But in addition to the above functions, the DSpace platform allows long-term storage of digital data in academic research.Let's get acquainted with the functionality of the DSpace platform: • A clear data model is assigned to the general organization of data;• The system stores and indexes metadata in various formats;• The system stores information about system users;• Allows users to be authorized to use the system according to the levels of authorization (in order to ensure security);• The so-called absorption process, that is, the possibility of receiving information entering the system from the outside;• In some cases, the data to be archived or the metadata associated with the data must be verified or filled in by a user who can perform this process. Such a sequence of actions is called a work-flow (work-flow);Тизим архивидаги маълумотлар келтирилган аниқ элементнинг баёни йўналишлари (ссылки) асосида рухсат берилади. Шунинг учун архив маълумотини бу баёнини библиографик йўналиш (ссылка) кўринишида ифодалаш мумкин;• End users must be able to view and search the repository system. In this regard, the system should provide search and viewing functions (navigation);• Collection of metadata - creates the possibility of generalized search of data in the system using the OAI-PMH protocol;• In the system (repository), the end users have the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the latest information in the system, that is, to create an opportunity for the user or administrator to know that there will be any change in the system even without entering the system. For this, the system has the function of automatically sending a message to the system administrator or the end user to his e-mail;• Creation of the possibility of processing data in the format created in the system, that is, data typing from simple text documents and data in digital video format;• Allowing all the above functionality through the web interface;• We can see the organization of data on the DSpace platform in the following block diagram:
World information resources are scientific and educational electronic resources of the world's leading companies and publishers, which make a great contribution to the development of science, education, culture and business. Licensed information resources - they are information resources based on license agreements, which users can use only for scientific and educational purposes in the local network of the institution. Commercial use of the information in them is prohibited. Users also assume full responsibility for compliance with license requirements.The DSpace electronic library platform was created together with the Hewlett-Packard company and the Federation of Universities created to implement the project. The federation includes Cambridge University, Columbia, Cornell, Massachusetts Institute of Technology - MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Library, Ohio State, University of Rochester, University of Toronto and Washington State University. On November 4, 2002, this system was launched as a working service of the library of the institute. This program was formed as a result of scientific research in the field of electronic library. There is another program similar to DSpace, which focuses on supporting scientific articles - Eprints - which originated from the "Scholarly Communication" movement. optimized for placement. But in addition to the above functions, the DSpace platform allows long-term storage of digital data in academic research.Let's get acquainted with the functionality of the DSpace platform: • A clear data model is assigned to the general organization of data;• The system stores and indexes metadata in various formats;• The system stores information about system users;• Allows users to be authorized to use the system according to the levels of authorization (in order to ensure security);• The so-called absorption process, that is, the possibility of receiving information entering the system from the outside;• In some cases, the data to be archived or the metadata associated with the data must be verified or filled in by a user who can perform this process. Such a sequence of actions is called a work-flow (work-flow);Тизим архивидаги маълумотлар келтирилган аниқ элементнинг баёни йўналишлари (ссылки) асосида рухсат берилади. Шунинг учун архив маълумотини бу баёнини библиографик йўналиш (ссылка) кўринишида ифодалаш мумкин;• End users must be able to view and search the repository system. In this regard, the system should provide search and viewing functions (navigation);• Collection of metadata - creates the possibility of generalized search of data in the system using the OAI-PMH protocol;• In the system (repository), the end users have the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the latest information in the system, that is, to create an opportunity for the user or administrator to know that there will be any change in the system even without entering the system. For this, the system has the function of automatically sending a message to the system administrator or the end user to his e-mail;• Creation of the possibility of processing data in the format created in the system, that is, data typing from simple text documents and data in digital video format;• Allowing all the above functionality through the web interface;• We can see the organization of data on the DSpace platform in the following block diagram: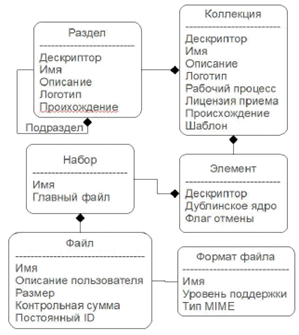 This hierarchy is necessary to organize the search system in the system (repository). The advantage of the DSpace platform is that due to a carefully designed hierarchy, there is physical proximity to the data located in a single collection, at the source. As a result, the time spent on the search for the user's information is reduced.There are 4 types of repositories.
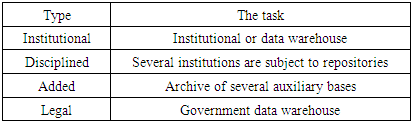
This hierarchy is necessary to organize the search system in the system (repository). The advantage of the DSpace platform is that due to a carefully designed hierarchy, there is physical proximity to the data located in a single collection, at the source. As a result, the time spent on the search for the user's information is reduced.There are 4 types of repositories.
|
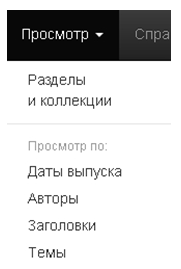 If you are registered with the Repository, you will use the following services:• Subscription to collections and receiving information about the added resource via e-mail; • Go to "My archive" ("Moy arxiv resursov") page. This page will display all user-written documents, which are the information posted by the user himself;• The user can edit his data.Posting a new resource is a function of the DSpace platform, and users with special rights have the right to post information to the repository. The process of document posting is filling the document with metadata and uploading its digital image.My resources archive - is a personal page that the user himself has the right to work with. This section contains a list of documents in the deployment process or a list of documents that the user needs to edit.Edit profile – edit information about the user.An obstacle to the creation of repositories in an educational institution is the existing libraries in an educational institution. (funding, limitations of Internet technologies and insufficient level of knowledge of the English language of specialists in posting information).
If you are registered with the Repository, you will use the following services:• Subscription to collections and receiving information about the added resource via e-mail; • Go to "My archive" ("Moy arxiv resursov") page. This page will display all user-written documents, which are the information posted by the user himself;• The user can edit his data.Posting a new resource is a function of the DSpace platform, and users with special rights have the right to post information to the repository. The process of document posting is filling the document with metadata and uploading its digital image.My resources archive - is a personal page that the user himself has the right to work with. This section contains a list of documents in the deployment process or a list of documents that the user needs to edit.Edit profile – edit information about the user.An obstacle to the creation of repositories in an educational institution is the existing libraries in an educational institution. (funding, limitations of Internet technologies and insufficient level of knowledge of the English language of specialists in posting information).3. Conclusions
- All educational institutions and scientific research institutions in the world can download Dspace software free of charge from the Internet and can adapt their policy according to the institution's educational orientation, because it is an open source program. According to the OpenDOAR catalog data are divided into several types of institutional repositories1. Software types of archives2. Platforms of repositoriesIn the Tashkent Medical Academy (TTA), scientific articles, literature in all areas available in the ARM, dissertations and abstracts are placed on the Dspace repository platform, which is adapted to the policy of the institution. Not only TTA, but also scientific products created in its branches are placed on the platform. To date, the number of products placed in all directions is about 6,000 and it is possible to use them after passing authorization. This, in turn, is the conditions created for employees, masters and students engaged in scientific work at the institution.
 Summarizing the above information, with the introduction of modern information communication technologies, network technology, the mechanism of rapid data exchange and the placement of information on electronic platforms, the traditional information exchange has changed.
Summarizing the above information, with the introduction of modern information communication technologies, network technology, the mechanism of rapid data exchange and the placement of information on electronic platforms, the traditional information exchange has changed. First, new technologies have accelerated traditional methods of scholarly communication. The massive exchange of verbal information and large experimental data has accelerated significantly. For some scientists in the fields of physics and mathematics, it has become a common form of communication to introduce archival data to others interested in the field before publication.Secondly, the number of important scientific researches is increasing, because their work processes and results are not required to be published. For example, white papers and technical reports are funded by various financial foundations, computer science research organizations, and quantum or biotechnology analysts. Third, with the increase in the availability of primary search results on the web, the dependence on the traditional publication of information will decrease.
First, new technologies have accelerated traditional methods of scholarly communication. The massive exchange of verbal information and large experimental data has accelerated significantly. For some scientists in the fields of physics and mathematics, it has become a common form of communication to introduce archival data to others interested in the field before publication.Secondly, the number of important scientific researches is increasing, because their work processes and results are not required to be published. For example, white papers and technical reports are funded by various financial foundations, computer science research organizations, and quantum or biotechnology analysts. Third, with the increase in the availability of primary search results on the web, the dependence on the traditional publication of information will decrease. This, in turn, creates an opportunity for a group of scientists working with primary data to check the results of work, rewrite the results, analyze the results and provide visualization of the results. The printed data, in turn, serve as the final result of the search.Why did you choose Dspace software?1. Free;2. Open source software;3. Cross-platform i.e. universality (Windows, Linux);4. Uncomplicated requirements for the operating system;5. Programming language and ability to work with other software: JDK (Java Development Kit), Tomcat, Apache Maven, Apache Ant, etc.;6. Metadata and other types of data storage system, i.e. database management system (MBBT): PostreSQL, Oracle, etc.;7. Ability to place information in any format (text, table, graphic, audio, video); Мета маълумотлар формати- Dublin Core;8. Availability of JINR Document Server service;9. Availability of a multi-criteria search system - module WebAlert;10. Availability of WebSubmit and ElmSubmit service;11. The main feature of the institutional repository: providing free access to the results of scientific research, gathering all information in one place, hosting other types of electronic information, as well as unpublished information (known as seraya literatura) such as dissertations and technical reports;12. Availability of quotation; 13. Using the Dspace repository gives high results in WEBOMETRICS analytics (THE World University Rankings);14. It also gives high results in Google Analytics.
This, in turn, creates an opportunity for a group of scientists working with primary data to check the results of work, rewrite the results, analyze the results and provide visualization of the results. The printed data, in turn, serve as the final result of the search.Why did you choose Dspace software?1. Free;2. Open source software;3. Cross-platform i.e. universality (Windows, Linux);4. Uncomplicated requirements for the operating system;5. Programming language and ability to work with other software: JDK (Java Development Kit), Tomcat, Apache Maven, Apache Ant, etc.;6. Metadata and other types of data storage system, i.e. database management system (MBBT): PostreSQL, Oracle, etc.;7. Ability to place information in any format (text, table, graphic, audio, video); Мета маълумотлар формати- Dublin Core;8. Availability of JINR Document Server service;9. Availability of a multi-criteria search system - module WebAlert;10. Availability of WebSubmit and ElmSubmit service;11. The main feature of the institutional repository: providing free access to the results of scientific research, gathering all information in one place, hosting other types of electronic information, as well as unpublished information (known as seraya literatura) such as dissertations and technical reports;12. Availability of quotation; 13. Using the Dspace repository gives high results in WEBOMETRICS analytics (THE World University Rankings);14. It also gives high results in Google Analytics. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML