-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(5): 756-758
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231305.44
Received: May 16, 2023; Accepted: May 28, 2023; Published: May 31, 2023

Development of a Prognostic Map of Development in Patients with Urological Diseases
Shadmanov Mirzamakhmud Alisherovich
Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Shadmanov Mirzamakhmud Alisherovich, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In medical practice, an electronic program has been developed by specialists, which has the ability to apply a predictive map of targeted assessment of urinary tract diseases on phones and computers, and it is possible to analyze the results obtained and prevent urological pathologies, self-control of patients, monitoring the condition of patients. At the same time, the threshold value of the final prognostic coefficient and risk groups of the origin of the pathological condition were determined.
Keywords: Urological diseases, Prognostic map, Risk factors, Credit-module system, Educational process
Cite this paper: Shadmanov Mirzamakhmud Alisherovich, Development of a Prognostic Map of Development in Patients with Urological Diseases, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 5, 2023, pp. 756-758. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231305.44.
1. Introduction
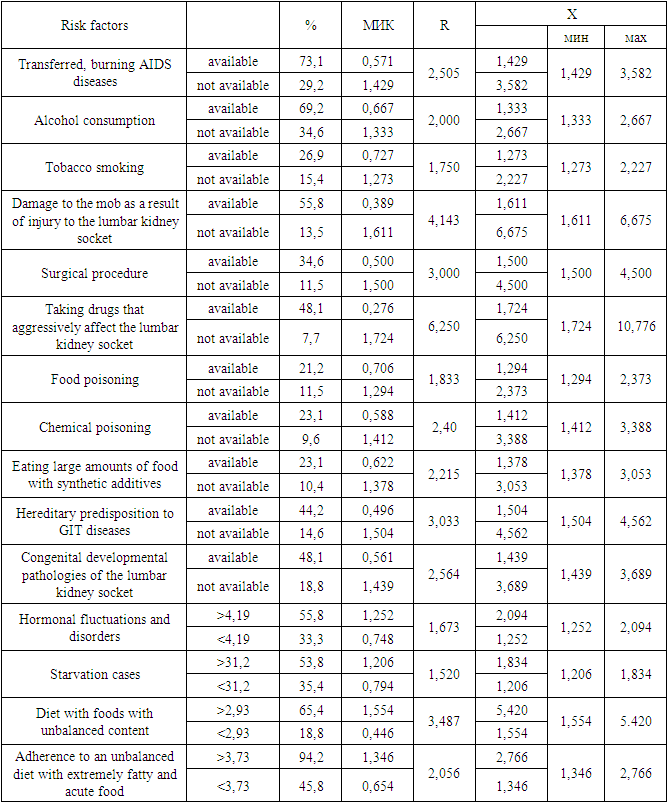
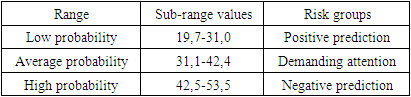
- Currently, computational methods have been developed for the diagnosis and prognosis of a number of somatic diseases. But the method of predicting risk factors in urinary tract disorders has not been implemented [1,3].It should be noted rightfully that in the Prevention of urinary tract diseases, the separation of risk factors for the development of external and internal secretory insufficiency by comparing different prognostic criteria in patients with urinary tract diseases was considered a very important approach [2].For the purpose of compiling a forecasting table, comparable indicators were obtained for situations that are relatively important and make it possible to give predictions depending on the gradient of common risk factors. The degree of significance of the factors and their gradation were determined by applying relative risk indicators (R). This indicator in turn is expressed in each individual factor bias relative to the minimum (d) in terms of the degree of indicator intensity (s) of the maximum relationship (r=c/d). If the factor does not have a sphere of influence, then this factor is calculated as equal to one. To what extent the R indicator is higher, the degree of significance of the risk factor in the origin of this pathological condition is thus higher [4,6]. The main essence of this method is that instead of the usual intensive indicators, a normalized intensive indicator (MIK) is used, and the calculation is possible using the following formula: N=R/M, in which: N is a normalized intensive indicator, R is an intensive indicator, M is a "normalizing indicator".During the study, an average frequency of urinary tract diseases with external and internal secretory insufficiency is accepted according to all examination data (100 patients involved in scientific inspection) as a normalizing magnitude on this condition. For example, in patients with urinary tract diseases, the frequency of development of the state of renal failure (R) is 46.7, while the normative indicator with external secretory insufficiency is 54.5. This indicator was 51.0 among all those examined. This magnitude was taken as a “regulatory” indicator (m). In the case of other risk factors related to urinary tract disorders, the NII was also calculated in this way. The resulting mic is the initial standard, with which it is possible to carry out an integrated assessment of the risk of developing kidney failure in patients with urinary tract diseases, as well as a set of factors [5].
2. Material and Methods
- It is known that each factor has a different impact force on the development of kidney failure in patients with urinary tract diseases. Taking into account this principle, we took into account the relative risk indicators on each factor. Knowing the relative risk indicator of disease development (R) as well as the normalized intensive indicator (n), it is possible to determine the impact strength of each individually obtained risk factor, i.e. the prognostic coefficient (X), in relation to the development of a state of external kidney failure in SP. This magnitude is determined as follows: X=R•N, in which X is an integrated indicator of risk from the strength of influence of a particular factor (prognostic coefficient); N is a NII for the development of kidney failure in patients with urinary tract diseases; R is an indicator of relative risk.
3. Results
- Considering the data in our sample, that is, the relative risk factor (R) is 1.17, NII1 – 0.916, NII2 – 1.069, then the integrated indicator of the impact force of each individual factor, that is, the prognostic coefficient, is expressed as follows: if a patient with urinary tract diseases - 1.17•0.916=1.072; if with external secretory insufficiency 1,17•1,069=1,25.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- It can be said that the credit-module system, increasing the effectiveness of the educational process, directing students to independent research, contributes to ensuring the appropriate training of specialists in medical higher education institutions.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML