Mukhammadjonova D. M.
Andijan State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Mukhammadjonova D. M., Andijan State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The article describes the efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation treatment of cognitive disorders in 102 children with cerebral palsy and the expression of the results in cognitive evoked potential P300 indicators.
Keywords:
Cerebral palsy, Transcranial magnetic stimulation, Cognitive disorders, Cognitive evoked potential P300
Cite this paper: Mukhammadjonova D. M., Optimizing the Rehabilitation Treatment of Cognitive Disorders in Children with Cerebral Palsy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 5, 2023, pp. 686-690. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231305.30.
1. Introduction
Worldwide, cerebral palsy (CP) is not only the most common and complex disease among all neuromotor disorders in children, but also one of the most common causes of physical disability in children in developed countries, diagnosed in one out of every 500 children [3]. To achieve the maximum values of the recovery process, it is necessary to have a clear idea about the neurophysiological and neurobiological aspects that implement these processes [7]. Central and peripheral nervous systems have significant compensatory capabilities [5,6,8]. Neuroplasticity is the basis for the implementation of restorative and compensatory processes that develop in response to an impact [1].The use of TMS in children with cerebral palsy has made it possible to diagnose many foci of pathology in the central nervous system: the cerebral cortex, corticospinal pathways, as well as the motor control system [9]. Pathology of cortical neurons is often combined with dysfunction of inhibitory-type GABA-dependent neurons in the central nervous system, with an emphasis on motor-type cortical adaptation-dependent ipselateral responses [2,8].
2. The Purpose of the Study
To evaluate the effectiveness of rehabilitation treatment with memantine drug and transcranial magnetic stimulation of motor function in children with cerebral palsy.
3. Research Material and Methods
The mean age of the patients was 9.3 ± 3.3 years (95% CI: 8.6–9.9). All studied subjects were diagnosed with CCP (coding G80 according to KXT-10). All patients were then divided into 5 groups based on ICD Among those studied, spastic and quadriplegic (G80.0) TsF was found in 20.6% of cases, which was 21 people, diplegia (G80.1) - in 24 people (23.5%), while at the same time spastic type TsF and hemialegia (G80.2) occurred in 32.4% of cases and accounted for 33 children, dyskinetic TsF (G80.3) - 13 children (12.7%) and ataxic cerebral palsy (G80.4) - 11 children (10, 8%) occurred in patients. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy in children with cerebral palsy, we analyzed all our patients based on the clinical data of complaints, questionnaires and scales, and the results of clinical-instrumental examination.In order to evaluate the therapeutic effectiveness of transcranial magnetic stimulation in children with cerebral palsy, we used two courses of transcranial magnetic stimulation for 3-4 months after treatment in the hospital, as well as drug therapy: memantine in drops according to the following scheme: 1 - a group of 28 patients was selected who received 5 drops in the morning in the 2nd week, 5 drops in the morning and lunch in the 2nd week, 10 drops in the morning and 5 drops in the lunch in the 3rd week, 10 drops in the morning and lunch in the 4th week for 3-4 months.Neuro-MS/D apparatus equipped with a "butterfly" type inductor and with an inductance of 1.6 Tl was used for TMS treatment. Before undergoing TMS, all patients were screened for contraindications, and the safety of the procedure was assessed.The use of TMS was carried out according to the following schemes: to reduce spasticity - high-frequency stimulation, 10 Hz, 100 % Motor threshold (MT), 15 minutes, spastic, contralateral to the arm and leg (or to both sides in diplegia and quadriplegia) - 10 sessions, and in order to improve cognitive disorders - F3 was stimulated (left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, DLPFC) '5 Hz (120 % MT) - 10 minutes - in total 10 sessions.There were no differences between the groups in terms of duration and time of treatment in the methods of inpatient treatment of children with cerebral palsy. The only difference was that in the control group, TMS treatment was additionally performed.
4. Research Results and Discussion
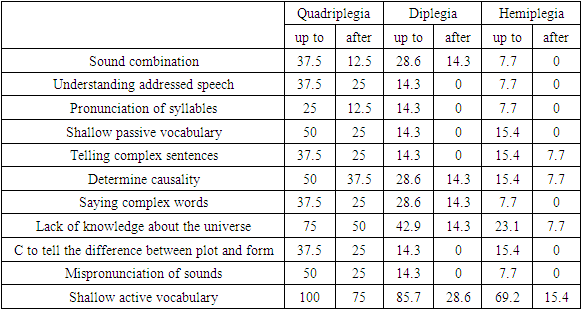
The data show that children with quadriplegia after the treatment course have better pronunciation of sounds and sound combinations, as well as intellectual abilities in the form of an expansion of basic knowledge about the surrounding world, enrichment of active and passive vocabulary.The analysis of the dynamics of psycho-speech development in children with diplegia revealed excellent results of this therapy with the recovery of almost 70% of the lost functions, which was much higher than in the group with traditional methods of treatment.Table 1. 1st advance Psycho-speech in children with cerebral palsy functions and dynamics
 |
| |
|
As can be seen from the table, children who have problems with understanding the addressed speech, as well as with impaired pronunciation of sounds, syllables and complex sentences, and with problems with vocabulary, did not complain about these problems.The study of the dynamics of psycho-speech development in children with hemiparesis has its own characteristics, because previously this contingent of patients had mild psycho-speech disorders, and their motor skills were sufficiently developed, in particular, in the undamaged limb. Improvement of psycho-speech development in this group of children occurred in 10 out of 13 patients, which was more effective than patients treated with conventional methods, who also showed a significant increase in motor abilities and a decrease in spasticity, as well as an increase in the child's psycho-speech development.In conclusion, the combined rehabilitation therapy of individuals with limited cognitive processes using new methods, including TMS, not only gives positive dynamics in motor abilities, but also increases the psycho-speech potential of the child. The development of motor activity served to stimulate the functions of the cortex, which served to increase vocabulary and develop basic knowledge about the universe. The obtained data do not contradict the results of Simonova's research, which increased the motivation to communicate by more than two times and the mental status by 1.5 times.In order to study the dynamics of cognitive improvements in more detail, the Luria test, Wechsler test and Raven test were conducted according to the obtained results, and the primary and secondary indicators of the test performance in both groups were compared. Memory size A. R. Psychological testing using Luria's 10-word recall method showed that nearly all children had memory impairment, with a mean Luria test score of 6.4 ± 1.1 (95% CI: 6.1–6.6). The final test showed a statistically significant increase in the Luria short-term memory capacity values in this group and was 7.4 ± 0.9 points (95% CI: 6.9–7.6) (r < 0.001), which was also higher than in conventionally treated children. At the end of the memory study, it was found that the formation of this function of cognitive type has a convincing result. The final values can be justified by the fact that the formation of memory takes place in attempts to memorize new action processes. Memory training can be done in the process of mastering the actions being performed, during the control and correction of the actions.Before conducting these trainings, two groups of individuals with cerebral palsy were subjected to a comprehensive Wechsler's examination of the values of the formation of cognitive functions. In the image, the average value of the general level of intelligence in quadriplegic patients is 74.9 points; in patients with diplegia - 78.3; and in the hemiplegic group it was 87.1 points.Research aimed at studying the initial level of basic cognitive functions made it possible to study not only the general values of the development of the intellectual type, but also the formation of the processes of thinking, attention, perception, as well as visual-motor coordination and the expression of the status of quick type memory. The effectiveness of the implementation of certain test tasks depends more on the current knowledge of the subject, as well as the level of socialization of his judgments. The lowest values were found on the Deciphering subtest, which depends on the child's attention status, as well as perception, visual-motor coordination, and motor skills. In 50% of cases, there was a deficiency of the skills required to perform this subtest.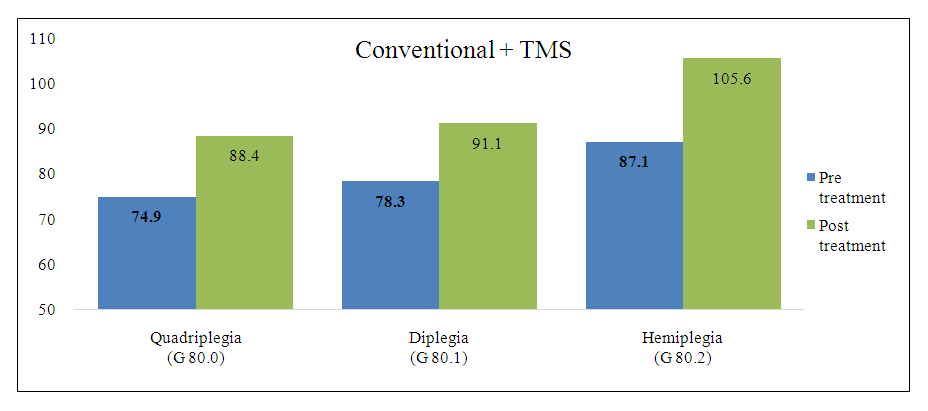 | Figure 1. Dynamics of cognitive evoked potentials P300 |
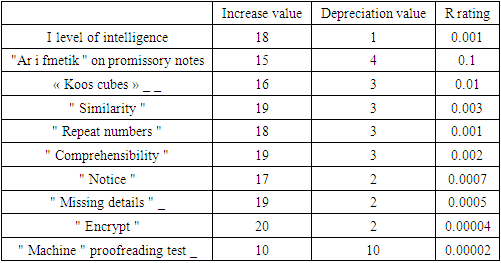
A repeated test showed that the Wechsler mean values of the general level of intelligence in children treated with TMS were statistically significantly higher than in children who underwent a traditional restorative treatment course (p < 0.05). As we can see, the average score increased by 14 points in quadriplegic patients, 13 points in diplegic patients, and 18 points in children with hemiparesis.In addition, it should be noted that in this group, the cognitive functions, which were isolated separately, had a bright positive dynamic, because these elements were responsible for the total value of intelligence.Statistically significant changes for the better were observed for all Wechsler test scales except for the Arithmetic scale. It should be noted that the most significant changes were observed in the intelligence level and the Koos cube scale, while the most insignificant changes were observed in the Encryption scale. At the end of the research of the test results according to these methods, the calculation of points for the mistakes made was carried out.In conclusion, the presented tables show the positive development in the formation of independent attention, perception, as well as sensitive and dynamic coordination of hands. Changes of statistical significance indicate an increase in effectiveness in the formation of functions such as perception, attention, memory, thinking and imagination during the recovery course.Table 2. Analysis of shifts in the values of test indicators for different cognitive functions in the experimental group
 |
| |
|
The Encrypting Scale, which includes courses that increase attention, perception, and visual-motor coordination, is the most complex test. Therefore, it can be concluded that analytical aspects, as well as opportunities for logical thinking, the volume and long-term memory, and the formation of attention, were developed during the recovery courses. A study of the development of intellectual abilities of children with spastic cerebral palsy using the Raven test revealed positive dynamics in the cognitive field. It should be noted that the most striking changes in the intellectual sphere were observed in persons with low intelligence, while psychological status did not change significantly in persons with an acceptable level of intelligence.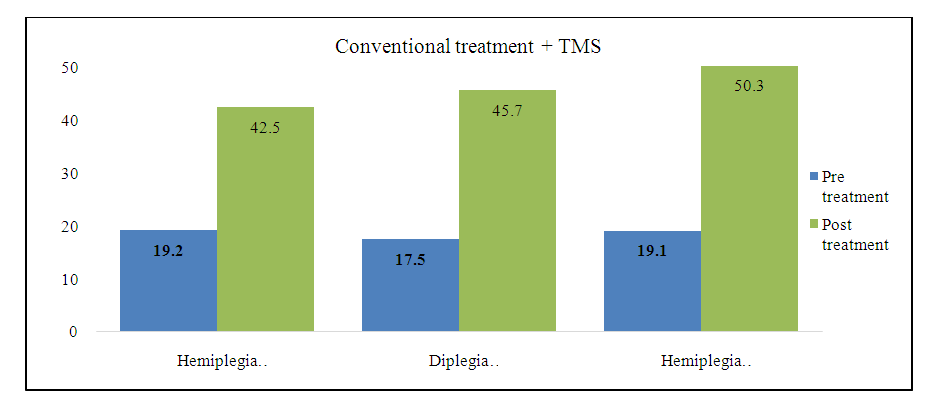 | Figure 2. CCP different to the forms played in patients intellect research reach results (Raven test data by) |
Curation was the most effective in increasing intellectual values in hemiplegic individuals and was 19.1 and 50.3 percent, it should be noted that these values in diplegic individuals were slightly lower, with an average increase of 28 points, and the least changes were found in quadriplegic individuals, in which the increase was It was up to 23 points.Clinical-type studies have also gained grounding in the study of CEP values (P300).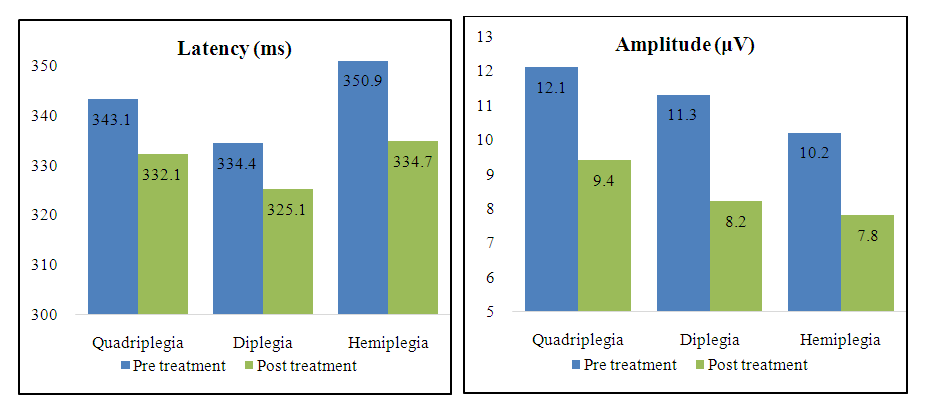 | Figure 3. Cognitive called potentials dynamics |
In the background of the ongoing treatment, it was carried out according to the data of CEP (P300). the study of neurophysiological values ended with some changes. These changes were in the shortening of the latent interval and the reduction of R ratios. The results of the study confirm the reduction of exchange processes in the brain cells of children with cerebral palsy, and the clinic of this condition is expressed both in the process of passing a neuropsychological test and in terms of P300 peak values.The results of the work carried out indicate an increase in metabolic processes in the brain of the studied individuals, this improvement was recorded by the clinical neuropsychological test and the results of CEP P300.
5. Conclusions
optimization of therapy with memantine drug and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) sessions most effectively improved intellectual productivity in hemiplegic patients (19.1% and 50.3%, respectively), slightly less in children with spastic diplegia and quadriplegia, where the increase was on average 28 points, and the smallest increase in intellectual productivity was observed in quadriplegia, where the increase was 23 points.
References
| [1] | Adeeva T.N. Dynamics of the self-concept and the internal picture of the defect in children with sensory impairments // Scientific notes. Electronic scientific journal of Kursk State University. - 2019. - № 3 (51). - Pp. 231-237. |
| [2] | Artemenkova L.F. Rehabilitation measures in the system of work with young children diagnosed with cerebral palsy // The world of science, culture, education. 2016. No. 3(58). pp. 76-78. |
| [3] | Berezhanskaya S.B., Vostrikh N.N. et al. Non-drug correction of neurodynamic and regulatory disorders in children with the consequences of hypoxic-ischemic lesions of the central nervous system // Medical Bulletin of the South of Russia. - 2020. - Vol. 11. No. 1. - pp. 27-33. |
| [4] | Borisenko A.M. Influence of transcranial magnetic stimulation on bioelectrogenesis of the cerebral cortex in children with cerebral palsy in the early residual period // Bulletin of Physiotherapy and Balneology. - 2018. - Vol. 24. No. 3. - pp. 81-85. |
| [5] | Budarnaya E.A., Smolyakova V.I. On the issue of diagnosis and correction of communicative activity of young children with cerebral palsy // Student. - 2019. - № 19-2 (63). - Pp. 51-53. |
| [6] | Hassan M.V., Sedinina A.S. Cerebral palsy: diagnosis, prevention, treatment: Fundamental scientific and practical research: current trends and innovations. collection of scientific papers based on the materials of the XXVI International Scientific and Practical Conference. - Anapa, 2022. - pp. 23-27. |
| [7] | Grishchenko M.V. Features of diagnostics of the development of higher mental functions in children with cerebral palsy: Innovative rehabilitation technologies in the system of psychological and medical pedagogical support for children with special educational needs. Collection of scientific papers. - Moscow, 2021. - pp. 17-24. |
| [8] | Ermolenko, N. A. Clinical and psychological analysis of the development of motor, perceptual, intellectual and speech functions in children with cerebral palsy / N. A. Ermolenko, I. A. Skvortsov, A. F. Neretina // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S. S. Korsakov. - 2000. - No. 3. - pp. 19-23. |
| [9] | Kudrina K.S. Features of the development of the cognitive sphere of a child with cerebral palsy of preschool age: Humanities. Student Scientific Forum. collection of articles based on the materials of the XXIII International Scientific and Practical Conference. -2019. - pp. 26-30. |
| [10] | Kolker, I.A. Auditory evoked potentials in neurology / I.A. Kolker // International Neurological Journal. - 2006. - Net6. – Access mode: http://www.mif-ua.com/archive/article/2343. |
| [11] | Majidova Ya.N., Saidhodzhaeva S.N. Cognitive evoked potentials 300 in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. All-Russian conference with international participation "Oxidative stress in psychiatry and neurology" St. Petersburg, 2016 102-103bet. |
| [12] | Nemkova S. A., Maslova O. I., Karkashadze G. A., Kurbatov Yu. N., Podkorytova I.V. The use of a polypeptide stimulator in the complex treatment of cognitive disorders in children with diseases of the central nervous system // Pediatric Pharmacology, 2012. No.5. |
| [13] | Ryzhov B.N., Mikhailova O.V. Systemic features of mental performance of people with cerebral palsy // Systems psychology and sociology. - 2014. - № 4 (12). - Pp. 13-20. |
| [14] | Samsonenko E.A. Cognitive development in adolescents with cerebral palsy // Synergy of Sciences. - 2020. - No. 44. - pp. 233-236. |
| [15] | Studenikin V. M., Pak L. A., Shelkovsky V. I. et al. The use of cortexin in pediatric neurology: experience and prospects // Pharmateca. 2008; 14: 23-29. |
| [16] | Semenova, K. A. Restorative treatment of children with perinatal damage to the nervous system and cerebral palsy /K. A. Semenova. - M.: Law and Order, 2007. - 616 p. |
| [17] | Troska Z.A., Shershneva O.A. Improvement of professional rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy // Scientific notes of the Russian State Social University. 2015. No. 14(3/130). pp. 156-167. |
| [18] | Shagrov L.L., Morozova L.V. Assessment of visual perception in children with cerebral palsy: SCIENCE AND INNOVATION - MODERN CONCEPTS. collection of scientific articles based on the results of the International Scientific Forum. - Moscow, 2021. - pp. 205-209. |
| [19] | Stavsky M., Mor O., Mastrolia S.A., etc. Cerebral palsy – trends in epidemiology and recent developments in the field of prenatal mechanisms of the disease, treatment and prevention. Anterior pediatrician. 2017; 5: 21. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2017.00021. |
| [20] | Wolfenden S., Galea S., Smithers-Sheedy H. and others. The influence of social disadvantage on the severity of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Pediatric Neurology. 2018; 17. DOI: 0.1111/dmcn.14026. |





 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML
