Gulandom Zikriyayevna Shodikulova, Dilshod Karimovich Samatov
Department of Internal Diseases No. 3., Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The aim of the study was to investigate the aspects of pharmacological correction of upper gastrointestinal pathology in patients with connective tissue dysplasia. In the course of the research it has been revealed that the drug magnerot, especially in combination with tivortin, improves parameters of local haemodynamics of the GIT organs and connective tissue that pathogenetically justifies its prescription as an adequate preventive and prophylactic therapy in patients.
Keywords:
Upper gastrointestinal pathology, Connective tissue dysplasia, Pharmacological correction, Flow-dependent vasodilation
Cite this paper: Gulandom Zikriyayevna Shodikulova, Dilshod Karimovich Samatov, Aspects of Pharmacological Correction of Upper Gastrointestinal Pathology in Patients with Connective Tissue Dysplasia, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 5, 2023, pp. 668-671. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231305.26.
1. Introduction
The assessment of the need for therapeutic measures is largely determined by the clinical form of CTD. The problem of treating different clinical forms of CTD is extremely complex and requires consideration of the clinical manifestations of this pathology (vegetative dysfunction). Thus, a comprehensive therapeutic approach using non-medicinal and medicinal therapies is required in generalised forms of CTD with involvement of different organs and systems. According to the literature, comprehensive therapy and prevention in CTD includes:1. Non-medicinal therapy (appropriate regimen, exercise therapy, physiotherapy and psychotherapy).2. Nutritional therapy (a nutritious diet enriched with combinations of amino acids, lipids and other nutritional supplements).3. Medicinal therapy (correction of metabolic disorders to stimulate collagen formation, stabilise glycosaminoglycan metabolism, improve the bioenergetic state of the body, etc.).4. Surgical correction of malformations of the internal organs (GIT).Nonmedicamental methods include psychological support, individualisation of the daily regimen, physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, and diet. Diet therapy should take into account the patient's increased need for proteins, essential amino acids and micronutrients. Only early diagnosis and timely comprehensive treatment of CTD could lead to positive results. The pathogenetic drug therapy is of a substitute nature. It is carried out in several directions. First of all, it is stimulation of collagen formation, pharmacological correction of glycosoaminoglycan synthesis disorders, reduction of degradation of these compounds. Stabilisation of mineral metabolism, maintenance of adequate levels of free amino acids in blood serum, and improvement of bioenergetic state of the organism must not be forgotten. Drugs, that enable stimulation of collagen formation, include ascorbic acid, chondroitin sulphate, glucosamine sulphate and their analogues, vitamin D, carnitine chloride, etc. They must be combined with B vitamins and microelements (copper, zinc, magnesium, manganese, etc.) because mentioned substances are cofactors of enzymes involved in biochemical reactions of intra- and extracellular formation of collagen molecule and other structural elements of connective tissue. As noted earlier, patients with CTD have autonomic dysfunction. Therefore, its correction is an important aspect of the drug therapy for this pathology.The aim of the study was to examine aspects of pharmacological correction of upper gastrointestinal pathology in patients with connective tissue dysplasia.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
The study covered 144 patients with upper GI tract diseases aged 20-55 years, mean age – 32.5±13.8 years. Patients were divided into 2 groups: in the first group - 45 (31.25%) patients with upper GI tract diseases without signs of СTD, in the second group - 99 (68.75%) patients with signs of СTD, and also 20 patients which were in the control group, participated in the study. In patients with СTD with the presence of GIT diseases a significant decrease of serum magnesium level and endothelium dysfunction were observed, whose degree of manifestation depended on the severity and form of pathology. Therefore, depending on the method of treatment the patients we divided the main group into 2 subgroups: subgroup "A" consisted of 35 patients, particularly 15 with GERD, gastritis, gastroduodenitis and 20 with duodenal ulcer, treated with the standard therapy of the main disease plus "Magnerot" by "Wörwag Pharma" at a daily dose of 3.0 (2 tablets 3 times a day) for 10 days and further 1 tablet 3 times a day for 6 months;- subgroup "B", which consisted of 41 patients (20 and 21, respectively) with gastrointestinal diseases were treated for 6 months with the preventive and therapeutic agent "Magnerot" + L-arginine Tivortin (company ЮРiЯ-ФАРМ, Ukraine) in addition to the standard therapy in a daily dose of 4.2 g in 100 ml of physiological solution for 7-10 days with a daily intravenous drip, followed by a dose of Tivortin syrup - 1 table spoon 3 times a day for 2 months.;Group I patients received only standard therapy for the primary disease.Examinations were carried out on admission and 6 months after the start of treatment. The effectiveness was assessed on the basis of clinical, laboratory and instrumental investigations. Controls for all compared groups were data from 20 conditionally healthy subjects, who gave informational consent for the study.Statistical analysis of the results was performed using a standard Microsoft Office 2010 software package for personal computers. Standard processing of variation series included calculation of arithmetic mean values (M), standard deviations (m). Variation series were compared using two-sample Student's test (t). The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was calculated to determine the relation between the studied indicators.
3. Research Results
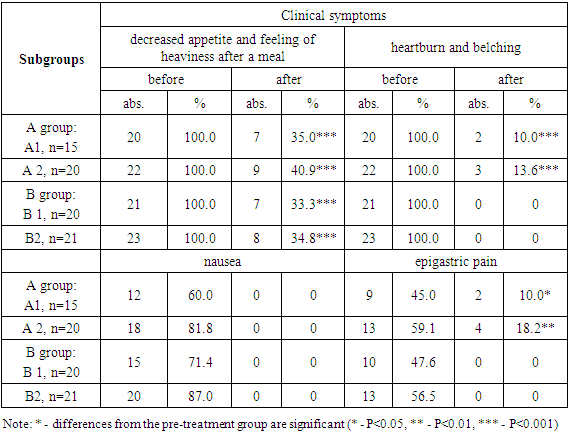
Studies demonstrated a high efficacy of the proposed treatments (Table 1). Thus, at use of Magnerot (group A) frequency of patients' complaints of decreased appetite and feeling of heaviness after a meal has statistically significantly decreased in 2,86 (P<0,001) and 2,44 (P<0,001) times, complaints of heartburn and belching - in 10 (P<0,001) and 7,35 (P<0,001) times, respectively to subgroups A1 and A2.Table 1. Dynamics of regression of clinical manifestations of СTD in patients with upper gastrointestinal pathology during treatment, %
 |
| |
|
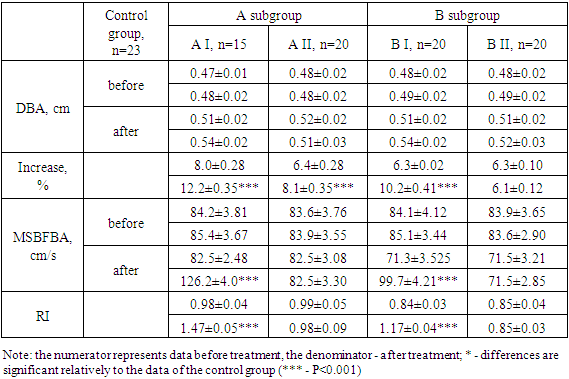
Despite the fact that, 35 and 40.9% of patients complained of decreased appetite and feeling of heaviness after a meal, these symptoms after treatment passed to a milder degree in most of the cases. After treatment, severe and moderate heartburn and belching persisted or manifested in a mild form in 10 and 13.6% of patients in the A1 and A2 subgroups, consequently. Nausea was noted in 2/3 to 4/5 patients, depending on the subgroup. The frequency of epigastric pain in patients decreased by 4.5 (P<0.001) and 3.25 (P<0.001) times, respectively, in subgroups. As it can be seen from the above data, the prescription of Magnerot had a favorable effect, contributing to a significant reduction of clinical manifestations of the diseases, contributing to the complete elimination of nausea in these patients.The supplementation of Tivortin to magnesium according to the above-mentioned scheme (group B) contributed to an even greater increase in the efficacy of treatment. For example, the frequency of appetite and heaviness decreased by 3 (P<0.001) and 2.87 (P<0.001) comparatively to the pre-treatment values of subgroups B1 and B2, respectively. It is also should be noted that this combination of treatment was 5.1 and 17.5% (P<0.05) more effective than the one of subgroups, treated with Magnerot alone, respectively. In this group after long-term treatment patients did not complain of heartburn and belching, while in subgroups of group A they persisted in 10 and 15.6% of patients. Complaints of nausea and epigastric pain (whereas in the group of patients receiving magnerot only they persisted in 10 and 18.2% of those treated) were completely eliminated inpatients of subgroups B1 and B2 after treatment with Magnerot and Tivortin. The data obtained indicate a high efficacy of the combined use of magnerot and Tivortin for the treatment of CTD. In our opinion, it is due to significant improvement of collagen and elastin synthesis in fibroblasts under the influence of magnesium ions. We suppose that more expressed positive effect of combination of Magnerotin and Tivortin on regress of clinical symptoms is connected with antihypoxant, membrane stabilizing, cytoprotective, antioxidant action of Tivortin. Evident clinical efficacy of the proposed therapy in CTD patients with gastrointestinal diseases was noted after 6 months of treatment. The phenomenon of flow-dependent vasodilation is associated with changes in vascular tone as a response to changes in regional blood flow. Previously it was thought to be a merely myogenic vascular response to changes in blood flow in the microcirculation, however it is now generally accepted that 'flow-dependent' vasodilation is closely related to the modulating properties of the vascular endothelium. Thus, the study of this aspect of our problem may be useful for a better understanding of it.Analysis of flow-dependent vasodilation in the compared groups during the 6-month prophylactic treatment showed that Magnerot therapy had no measurable effect on brachial artery diameters before and after the test in patients. Only a tendency for an increase in brachial artery diameter after the test was detected. In this regard, the increase of diameter after test in subgroup A1 increased statistically significantly 1.53 (P<0.01) times in comparison with pre-treatment values and approached the values of practically healthy individuals (Table 2). However, despite the fact that the maximum speed of blood flow-values of brachial artery (MSBFBA) before treatment had only a tendency to increase, after the test this index statistically significantly increased 1.53 (P<0.01) times relative to the initial values, which resulted in a 1.5 (P<0.01) times increase of the resistance index relative to the values before treatment.Table 2. Flow-dependent vasodilation in the compared groups before (numerator) and after (denominator) 6 months of prophylactic treatment, M±m
 |
| |
|
At the same time, patients with AII who received Magnerot treatment for 6 months, the values of DBA before the and after the test did not change significantly, and the values of increase went up statistically significantly by 1.27 (P<0.05) times. Simultaneously, the MSBFBA values before and after the test, as well as the resistance index did not change relatively to the initial values. All studied parameters of patients of this subgroup were statistically significantly different from the values of practically healthy individuals.In group B patients treated with Magnerot+Tivortin, a positive trend was noted in B1 subgroup patients. DBA values before and after the test tended to increase, with a statistically significant increase of 1.62(P<0.001) times comparatively to the pre-treatment values. However, it was still significantly below the normative values. The MSBFBA index before treatment had only a tendency to increase, while its values after the test significantly increased by 1.4 (P<0.05) times, resulting in a 1.39 (P<0.05) times increase in the resistance index compared to the pre-treatment values. All the studied indexes differed statistically significantly from the values of practically healthy persons.In B2 subgroup patients receiving Magnerot+Tivortin, the values of flow-dependent dilatation did not significantly differ from the initial parameters and reliably differed from those of practically healthy individuals. As evident from the above data, the application of Magnerot and in combination with Tivortin had a positive effect on the parameters of the vascular wall.Our observations demonstrated that Magnerot in combination with Tivortin has a more pronounced pharmacological effect with long-term use. This is probably due to the potentiation of Magnerot action under the influence of Tivortin. Special attention should be paid to fact that Tivortin itself corrects the observed endothelial dysfunction. It is widely used not only in cardiology, but also in neurology for correction of chronic brain ischaemia. It has a vasorelaxant effect, reduces the vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin and, as a consequence, increases the reserve capacity of arteries, contributing to an increase in the velocity of blood flow through them and providing tissues with oxygen. The combination of these properties, apparently, leads not only to improvement of local hemodynamics, but also to reduction clinical manifestations of the disease in the examined patients.Thus, the results of studies evidenced that drug Magnerot, especially in combination with Tivortin, improves the indices of local haemodynamics of the GIT organs and connective tissue, which pathogenetically justifies its prescription as an adequate preventive therapy and prophylactic measure for patients.
References
| [1] | Батаев Х.М. Гастроэзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь у лиц подросткового возраста с проявлением дисплазии соединительной ткани: иммунологические аспекты. / Батаев Х.М., Шихнабиева М.Д. // Вестник Дагестанской государственной медицинской академии. - 2016. №1 (18). - С. 17 - 20. |
| [2] | Земцовский Э.В. Малые аномалии сердца и диспластические фенотипы / Э.В. Земцовский, Э.Г. Малев // СПб.: Изд-во «ИВЭСЭП», 2011. - С.160. |
| [3] | Кононов А.В. Морфогенез атрофии слизистой оболочки желудка как основа фенотипа хронического гастрита / А. В. Кононов, С. И. Мозговой, М. В. Маркелова, А. Г. Шиманская // Арх. пат. - 2011. - Вып. 3. - С. 26-31. |
| [4] | Национальные рекомендации по диагностике, лечению и реабилитации пациентов с дисплазиями соединительной ткани. Под ред. А.И. Матынова, Г.И. Нечаевой. М.: ООО «Бионика Медиа», 2016. С. 12. |
| [5] | Саблина О.Ф. Особенности клинических и структурных проявлений атрофического процесса в слизистой оболочке желудка при дисплазии соединительной ткани / Л.А. Наумова, О.Ф. Саблина, Е.Е. Чичагова // Вестник Новгородского Государственного Университета имени Ярослава Мудрого. Серия «Медицинские науки». – 2011. – № 66. – С. 83–87. |
| [6] | Чернуха С.Н. Особенности лечения атрофических гастритов у пациентов с недифференцированной дисплазией соединительной ткани / С. Н. Чернуха. - Текст: непосредственный // Молодой ученый. - 2014. - № 10 (69). - С. 94-97. |
| [7] | Шихнабиева М.Д., Батаев Х.М., 2014. Дисплазия соединительной ткани и ее роль в развитии патологии органов пищеварения. // Врач. - 2014. - №2. - С. 7 - 9. |
| [8] | Шодикулова Г.З., Бабамурадова З.Б Клинико-диагностическое значение некоторых аутоантител к коллагенам при недифференцированной дисплазии соединительной ткани // IV съезд евразийской ассоциации терапевтов совместно с республиканской научно-практической конференцией терапевтов Узбекистана. - Ташкент, 2018. - С.31. |
| [9] | Шодикулова Г.З. Клинико – лабораторные показатели и их взаимосвязь с уровнем магния при НДСТ. «Достижения науки и образования» Россия, 2019 №10 (51), стр. 41-45. |
| [10] | Goldenring J. R. Oxyntic atrophy, metaplasia, and gastric cancer /J. R. Goldenring, K. T. Nam // Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. - 2010. - Vol. 96. - P. 117-131. |
| [11] | Salis G., 2011. Systematic review: Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Latin America. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam V.41 (1). P. 60-69. |
| [12] | Shodikulova G.Z., Mirzaev O.V., Babamuradova Z.B. Prevalence of clinical options of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia in uzbek population // LXIV international correspondence scientific and practical conference “EUROPEAN RESEARCH: innovation in science, education and technology” / - London, United Kingdom, 2020. - Р. 90-92. |
| [13] | Gulandom Shodikulova, Dilshod Samatov, Zarangis TairovaPeculiarities of the clinical course and diagnosis of the pathology of the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients with connective tissue displasion // Журнал биомедицины и практики. -2021. -№1. стр. 160-166. |
| [14] | A Berdeaux,C Drieu La Rochelle, M Gosgnach, E Roupie, V Richard, J F Giudicelli. Flow-dependent vasodilation. Pharmacology and physiopathology // Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1991 Sep; 84 Spec No 3:67-72. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML
