-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(4): 507-510
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231304.33
Received: Apr. 10, 2023; Accepted: Apr. 22, 2023; Published: Apr. 26, 2023

Some Characteristics of Children's Illnesses under One Year and Ways to Reduce Them
Mamatkulov B. M., Rakhmatullayeva M. K.
Tashkent Medical Academy, School of Public Health, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Mamatkulov B. M., Tashkent Medical Academy, School of Public Health, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Diseases of children under one year of age are one of the main indicators of public health. It is a unique barometer-indicator that shows the socio-economic development of the country, the sanitary-demographic situation of the population, the quality of medical services, the efficiency of sanitary-epidemiology, prevention and treatment. Analyzing the diseases of children under one year of age, their causes and dynamics, equips health institutions with the necessary information to improve children's health.
Keywords: One-year-old children, Diseases, Structure, Level, Causes of diseases, Ways to reduce diseases
Cite this paper: Mamatkulov B. M., Rakhmatullayeva M. K., Some Characteristics of Children's Illnesses under One Year and Ways to Reduce Them, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 4, 2023, pp. 507-510. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231304.33.
1. Introduction
- Bringing up a healthy, all-around mature, well-rounded generation is one of the priority tasks of our country, not only medical and social, but also raised to the level of state policy. That is why it is one of the pressing issues of the present day to study the health of children, especially children under one year of age, the factors related to the external environment affecting them, the living conditions and lifestyle of the population, and the development of systematic science-based measures to improve the health of infants by determining the interrelationships between them. is [3,6,7,8]. The level of diseases and its reliability depends not only on the proximity and popularity of medical care to the population, but also on the timely appeal of the population to medical institutions with various diseases, full-blooded recording of the diseases detected there. This depends, firstly, on the responsibility of medical workers for their duties, knowledge and skill level, and secondly, on the medical culture of parents, their participation in the economy and production, their responsible approach to children's health, and their employment [1,2,4,5,9,10].
2. Aim
- Diseases of children under one year of age and ways to reduce them.
3. Materials and Methods
- In order to study the diseases of children under one year of age, we studied the health of 1240 babies born in 2020-2021 in Tashkent using a short-term cohort method. We analyzed diseases according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision), diseases were studied according to children's gender and certain age groups.
4. Results and Discussion
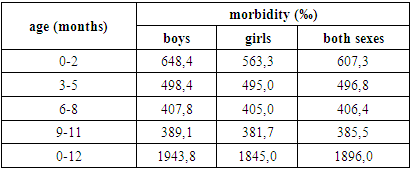
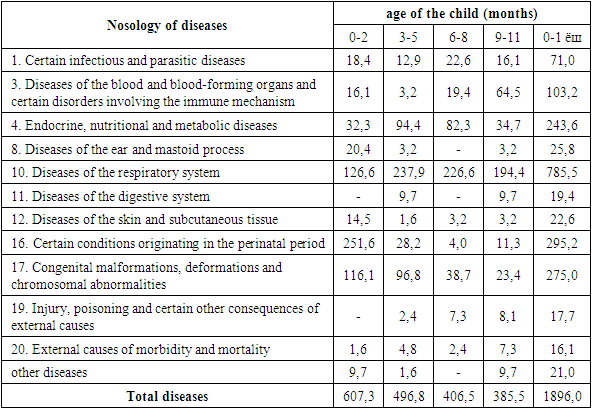
- According to the results of our research, the incidence rate of children under one year of age in Tashkent was 1896.0 cases per 1000 children, and the incidence rate of boys (1943.7‰) was slightly higher than that of girls (1845.0‰). But the reliability of this difference was not confirmed statistically (P>0.05). In studies devoted to the study of children's diseases, it was noted that the incidence of boys under one year of age is slightly higher than that of girls.Among the diseases of one-year-old children (in the period of 0-12 months), respiratory tract diseases take the first place in 785.5‰ (41.4%), some cases occurring in the perinatal period - 295.2‰ (15.6%), third place is congenital disorders - 275‰ (14.5%), the fourth place is endocrine system, nutrition and metabolic diseases - 243.5‰ (12.8%), and the fifth place is diseases of blood and blood-forming organs and some disorders involving the immune mechanism - It was 103.2‰ (5.4%). The mentioned 5 classes of diseases accounted for 89.8% of one-year-old children's diseases.The growing age of children is characterized by their anatomical, physiological and mental development and their resistance to external environmental influences. In our opinion, the above factors have a positive effect on the health of children, leading to the improvement of their health and the reduction of diseases.The results of our observations showed that with increasing age of children, their morbidity rates decrease in boys and girls (table 1).
|
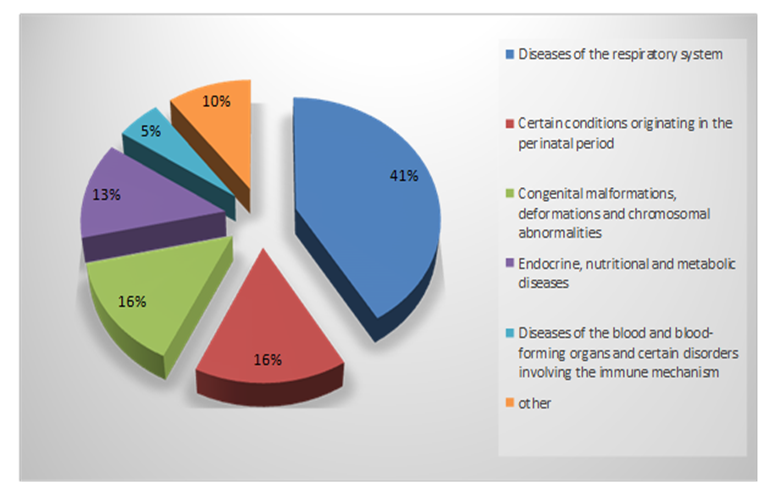 | Figure 1. The incidence structure of children under 1 year (%) |
|
5. Conclusions
- 1. In the city of Tashkent, the overall level of children's disease was 1896.0 cases per 1000 children of this age group in the first year of life. As the age of the child increased, the incidence rates decreased. Although it is noted that the incidence rate of first-year-old boys is slightly higher than that of girls, this difference is not statistically significant (r>0.05).2. The incidence rate and structure of children under one year of age include diseases of the respiratory system (41.4%), special conditions occurring during the perinatal period (15.6%), diseases related to the endocrine system, metabolic disorders (12.9%), congenital anomalies (14.5%), diseases of blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving immune mechanisms (5.4%) took the leading places. These diseases accounted for 89.7% of all diseases in the first year of children.3. In children under one year of age, it was found that the highest morbidity rate corresponds to the first three months of their life (607.3‰), and the lowest to the period of 9-11 months (385.5‰). In 32.0% of cases, the first illness or disease was recorded in the first month of the child's life, while 72.5% of the diseases recorded in the first three months of the child's life were recorded in the period of 0-1 months. So it was found that the period of 0-2 months of the child is of great importance in the health and upbringing of children.4. The leading positions in the level and structure of children's diseases in the period of 0-2 months were given by special situations that occurred during the perinatal period (41.4%). The morbidity of babies with certain conditions that occurred in the perinatal period was 251.6 cases per 1000 children in this age group. Among the diseases of this class, perinatal injuries of the nervous system (PPNS), asphyxia and injuries of respiratory disorders during childbirth, congenital jaundice took the lead.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML