-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(4): 467-470
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231304.23
Received: Apr. 2, 2023; Accepted: Apr. 20, 2023; Published: Apr. 22, 2023

Analysis of the Course of Childbirth/Delivery and the Postpartum Period in Pregnant Women with Mitral Stenosis
Asatova M. M., Abdukarimova N. T., Dauletova M. J.
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

We conducted a retrospective analysis of the outcomes of childbirth/delivery in pregnant women with mitral stenosis. The article describes the course of pregnancy and childbirth/delivery in pregnant women with mitral stenosis using the method of retrospective analysis.
Keywords: Mitral stenosis, Pregnancy, Childbirth, Delivery
Cite this paper: Asatova M. M., Abdukarimova N. T., Dauletova M. J., Analysis of the Course of Childbirth/Delivery and the Postpartum Period in Pregnant Women with Mitral Stenosis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 4, 2023, pp. 467-470. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231304.23.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Pregnancy and childbirth/delivery with heart defects put the mother and fetus at exceptional risk. Of the total number of pregnant women suffering from heart defects, 90% of them have acquired rheumatic defects, and 88% of them have mitral stenosis [1,2]. It is known that overload and hypertrophy of the myocardium is observed with heart defects of various etiologies, accompanied by a decrease in myocardial contractility and a decrease in stroke volume [5]. In conditions of reduced systolic volume, the maintenance of the most important indicator of hemodynamics of cardiac output at an adequate level is possible due to an increase in heart rate and an increase in circulating blood volume [2,4]. Mitral stenosis is the most severe form of heart defects in pregnant women [3,6]. Mitral stenosis, "pure" or predominant when combined with mitral valve insufficiency, is the most common form of rheumatic disease, which is found in 75-90% of pregnant women suffering from acquired heart defects [3,4]. Unfortunately, the current tactics of pregnancy management, the proposed methods of childbirth/delivery, relief of delivery pain over the past 20 years have not allowed to significantly reduce the frequency of complications, maternal perinatal mortality [2]. It is known that defects and the related functional state of the heart affect the course of pregnancy in different ways and provide different degrees of risk to the mother and fetus.In this regard, the retrospective analysis of the childbirth / delivery histories of pregnant women with mitral stenosis was conducted.The purpose of the study. To study the frequency and course of pregnancy in women with mitral stenosis.
2. Research Material and Methods
- At the first stage of the studies, the retrospective analysis of the course and outcome of pregnancy, the condition of the fetus and newborns was carried out in 176 pregnant women with mitral stenosis in City perinatal center No. 1 for the period from 2018 to 2021. The average age of women was 26.1±0.4 years.
3. Results and Discussion
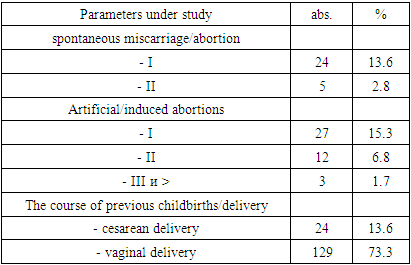
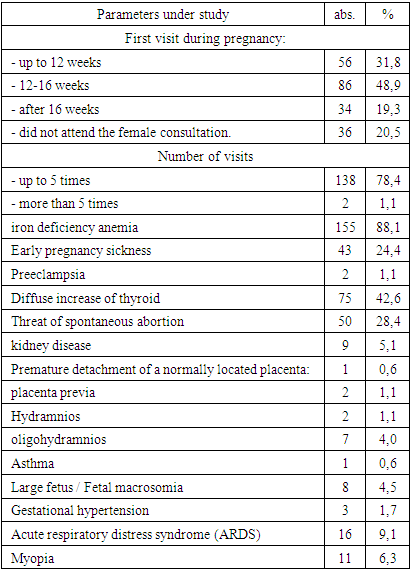
- As follows from the data in Figures 1 and Table 1, among the patients, multigravida and multiparous women predominated. Thus, the proportion of primigravida was 31.8% and primiparous 36.9%. The high indicators of II and III pregnancies in women with mitral stenosis (25.0% and 18.2%, respectively) draws attention. In women with mitral stenosis, the high percentage of multiparous women was noted, the proportion of IV births was 11.4%. The results of the analysis indicate an unfavorable outcome of previous pregnancies.
|
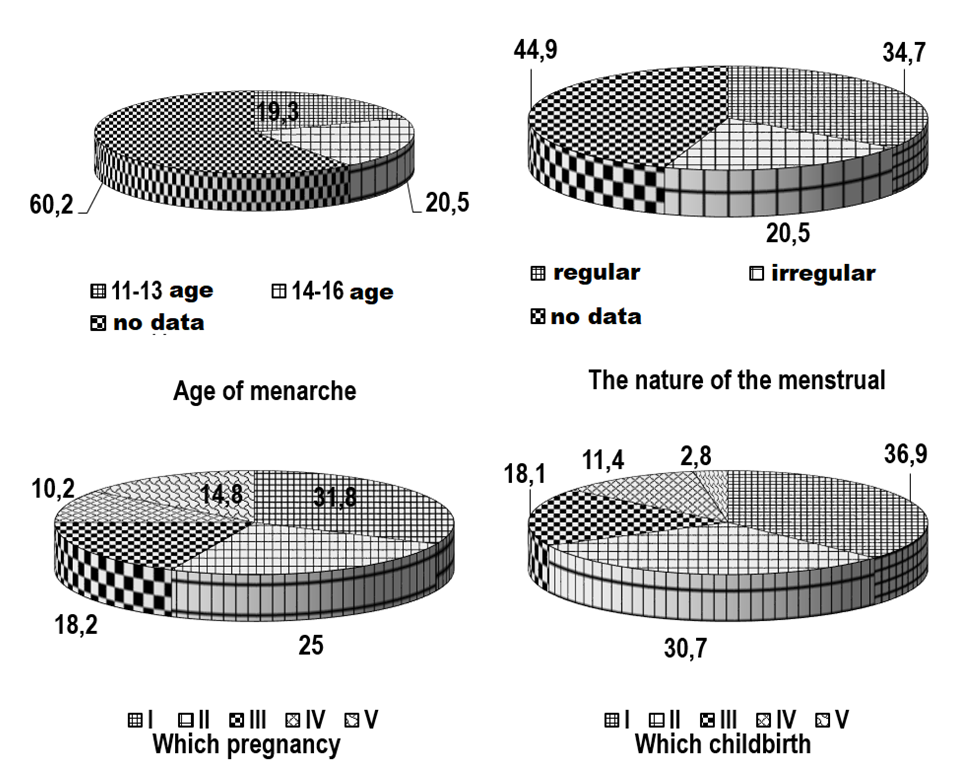 | Figure 1. The results of the analysis of obstetric and gynecological history in pregnant women with mitral stenosis |
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
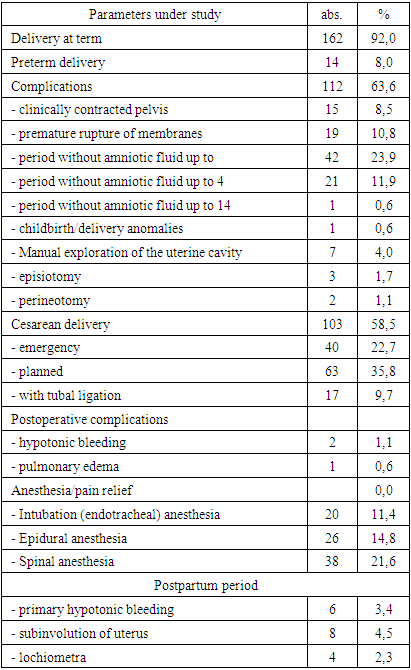
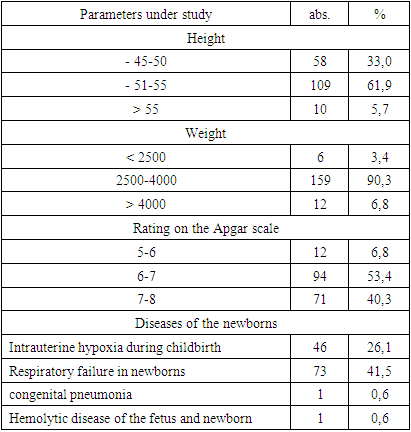
- Thus, the results of the retrospective analysis of the course of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period in 176 women with cardiovascular diseases indicate that the formulation of the diagnosis, the determination of the degree of blood circulatory insufficiency do not meet modern requirements and the classification adopted in the world and in our country. This circumstance creates problems in the diagnosis and choice of tactics.The results of the analysis showed complicated course of both pregnancy and the postpartum period, the high percentage of operative delivery. A generalized analysis of the course of pregnancy and childbirth in women with mitral stenosis was uninformative, since the tactics of managing pregnancy, childbirth, and the outcomes of childbirth largely depend on the type of heart defects and the severity of heart failure. Of particular interest is a differentiated approach to assessing the course and outcomes of pregnancy and childbirth, depending on the type of acquired defect, the state of myocardial contractility. The results of the retrospective analysis showed the absence of a unified tactics and strategy for managing pregnancy and childbirth in pregnant women with mitral stenosis. As for obstetric tactics, preference was given to operative delivery. High rates of caesarean section did not correlate with the condition of newborns in this cohort and led to high rates of perinatal morbidity and mortality. The current situation requires a revision of many regulations in the tactics of managing pregnancy and childbirth, leading to the issues of reclassification of cardiovascular diseases, pregravid preparation and the principles of managing childbirth and the postpartum period in accordance with international standards.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML