-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(3): 308-310
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231303.24
Received: Feb. 21, 2023; Accepted: Mar. 13, 2023; Published: Mar. 16, 2023

Bone Osteosynthesis of the Acromial End of the Clavicle
Shukurov Esandavlat1, Jabborov Anvar2
1Doctor of Medical Sciences, Senior Researcher, State Institution "RSNPMCTO", Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Traumatologist of the Polyclinic, State Institution "RSNPMTSTO", Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

We have developed two devices for the treatment of fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle. (FAP: 20180119. From 10.08.18; FAP: 20220214. from 09.06.22). A biomechanical experimental study was carried out with the developed devices in the “device-bone” system and an experimental study was conducted to study the acute toxicity and irritant effect of the developed device. The results obtained allowed the use of the device in patients with fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle. The developed device was used in 10 patients with a positive result of treatment.
Keywords: Fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle, Experimental study, Surgical treatment
Cite this paper: Shukurov Esandavlat, Jabborov Anvar, Bone Osteosynthesis of the Acromial End of the Clavicle, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 3, 2023, pp. 308-310. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231303.24.
1. Introduction
- Problems and "capriciousness" of the treatment of fractures of the clavicle create the complexity of its anatomical "S"-shaped form and the mobile biomechanical "image" of functioning in the clavicular-acromial and clavicular-sternal joints. [3,5,7]. The problem of treating lateral fractures of the clavicle alone and in combination with dislocation of the acromial end of the clavicle, accompanied by rupture of the acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments, is still relevant. [1,2,4,6,8].The aim of the study was to improve the results of treatment of patients with fractures and fracture-dislocations of the acromial end of the clavicle by developing and implementing a developed more advanced osteosynthesis, which, along with a strong fixation of bone fragments, will fully restore the function of the damaged limb.
2. Materials and Methods
- During the reporting period (2018-22) in the Department of Adult Traumatology, 216 patients with fractures and fracture-dislocations of the acromial end of the clavicle were operated on. In 44+13 patients with fracture-dislocations of the acromial end of the clavicle, lavsanoplasty and pin fixation were performed, 89+ patients underwent intramedullary osteosynthesis with pins and 83+69 patients with osteosynthesis with AO plate (LCP). In 15 patients, an angle-stable hook-shaped plate was used for lateral clavicle fractures and damage to the acromioclavicular joint. In the postoperative period, the patient was prescribed drugs to support consolidation: alendronic acid, colecalciferol (vit. D3), calcium carbonate. Conducted anticoagulant therapy. 8 weeks after the operation, a control radiography was performed and, due to the absence of secondary mixing of fragments and the initial signs of fracture consolidation, dosed loading on the limb was allowed. The rehabilitation period proceeded without complications. Satisfactory anatomical and functional results, restoration of limb function were obtained.The age of the patients ranged from 18 to 60 years. There were 156 men and 60 women. All patients underwent the main diagnostic measures: complete blood count; general urine analysis; radiography of the clavicle in a direct (anteroposterior) projection; determination of the clotting time of the duration of bleeding; biochemical analysis of blood. Determination of blood group and Rh factor.According to the indications of the consultation, in the presence of a concomitant disease, a neurologist, neurosurgeon, surgeon, vascular surgeon. Conducted clinical, X-ray, Doppler examinations.Surgical methods are also not without drawbacks, because physical activity after osteosynthesis until the fracture heals, inadequately selected metal fixators or their early removal lead to unsatisfactory outcomes.When using only spokes or smooth pins, their migration is revealed.The insufficient effectiveness of existing methods of treatment forces us to look for new ways to solve this problem. A device for the treatment of fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle has been developed. (FAP: 20180119. From 10.08.18).The device for the treatment of dislocations and fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle is made in the form of a plate 1, with holes 2, moreover: one end of the plate is rounded, and the opposite end is made with three teeth 3,4,5 with pointed ends, two of which are made symmetrically perpendicular axis of the plate, and the third is made in the longitudinal direction.Experimental studies of the device of the laboratory "Experimental studies of the strength of structures and seismic resistance of structures" of the Institute of Mechanics and Seismic Resistance of Structures of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan were carried out. (Hoz. Contract. No. 06.. 2019).Experimental studies of the device were carried out in the laboratory "Experimental studies of structural strength and seismic resistance of structures" of the Institute of Mechanics and Seismic Resistance of Structures of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan. The maximum numerical values of the load are determined at which the system operates in an elastic mode, which is P = 16.0 kgf. The investigated device-fixator in the "device-bone" system has sufficient strength and stability when fixing the fracture site.The data obtained in the course of the pilot study reliably indicate the feasibility of using the new clinic device in clinical practice in patients with clavicle fractures. An experimental study was conducted to study the acute toxicity and irritant effect of the developed device in the laboratory of the Scientific Center for Standardization of Medicines.Research protocol. (from 27.05.20 to 19.06.20 contract No.). The acute toxicity of the extract from the test sample was determined according to GOST R ISO 10993.11-2011 on 6 white mice weighing 19-21 g, mixed sex, quarantined. The studied extract from the medical product did not irritate the intact skin of rabbits and did not irritate the conjunctiva of the eyes of rabbits.After a pre-clinical study of the developed device, it was used in 16 patients with damage to the acromial end of the clavicle.In the course of work, the first device revealed some shortcomings:- the shape of the developed device does not correspond to the shape of the acromial end of the clavicle.Because of this, it creates inconvenience in the location of the plate in the shape of the clavicle. The size of the conical spines located on the inner surface of the plate, due to the large size, made it difficult to insert the spines on the cortical clavicle.In the course of work, we developed the second version of the device, which improved the design of the plate, adapted it to the shape of the acromial end of the clavicle, created ease of use and increased fixation stability. (FAP: 20220214. 09.06.22).DEVICE FOR OSTEOSYNTHESIS OF FRACTURESACROMIAL END OF CLAVEFigure 1 shows a device for osteosynthesis of fractures of the acromial end of the clavicle, where: 1 - plate, 2 - groove of the combined hole for blocking the plate with locking screws, 3 - groove of the combined hole for compressing fragments with cortical screws, 4 - hole for fixing fragments in the distal part of the clavicle with a cortical screw, 5 - notches, 6 - fixing knot in the form of a fork, consisting of two teeth, 7 - spikes, 8 - cortical screws, 9 - blocking screws (general view, axonometric projection);
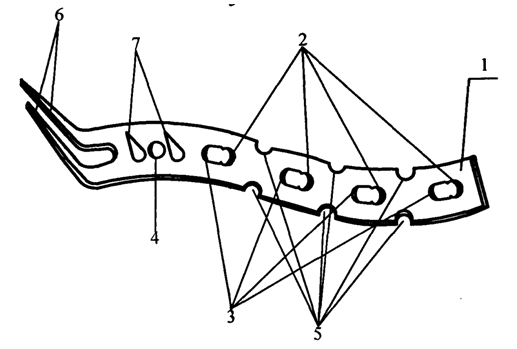 | Figure 1 |
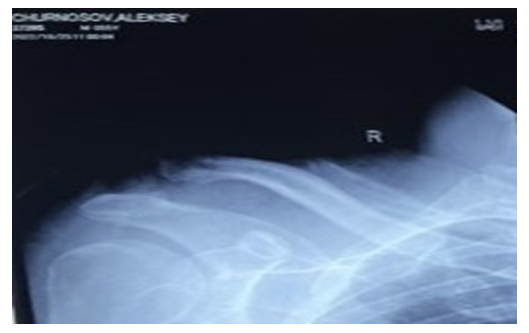 | Figure 2. Radiographs of the clavicle in direct projection before treatment |
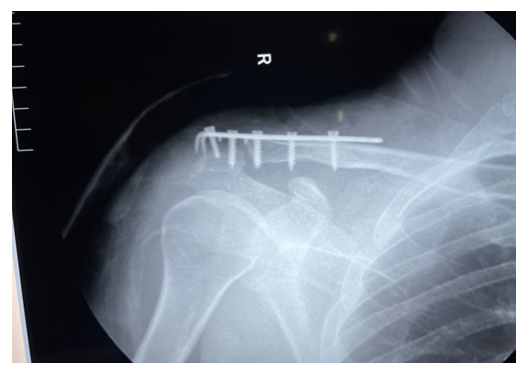 | Figure 3. Radiography after treatment |
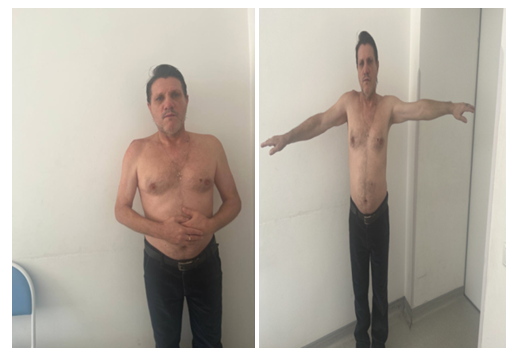 | Figure 4. Photo of the patient. In the process of treatment |
3. Conclusions
- The developed method with a new bone device makes it possible to avoid postoperative use of prolonged external immobilization, promotes early activation and reduces the recovery time of the functions of the operated limb, shortens the operation time, and begins early functional treatment in the postoperative period. The device is light, simple, stable and easy to use. All this leads to a reduction in the terms of treatment and prevention of disability.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML