-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(1): 24-27
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231301.06
Received: Dec. 18, 2022; Accepted: Dec. 30, 2022; Published: Jan. 13, 2023

The Use of Plasmapheresis for Preoperative Preparation of a Child with Diffuse Toxic Goiter
Gozibekov Jamshid Isanbayevich1, Rakhmanov Kasim Erdanovich1, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich2, Nabiyev Bobir Bakhodirovich2, Akhrorova Laylo Barno Qizi2
1Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Gozibekov Jamshid Isanbayevich, Samarkand State Medical University, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The relevance of research. In world practice, a number of scientific studies are conducted aimed at studying morpho-functional criteria for assessing the severity of the disease, including: studying the effect of colloidal goiter on morphofunctional changes in thyrocytes, the degree of which varies from minor disorders up to thyroid cancer. The aim of the study is to improve the quality of treatment of patients with toxic forms of goiter by developing a differentiated approach to choosing the volume of surgery and effective methods to reduce postoperative complications. Materials and methods of research. The study is based on the results of treatment of 112 patients with toxic forms of goiter who were admitted to the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of the Samarkand State Medical University in the period from 2012 to 2021. The results of the study. During the operation, 3 (5.8%) patients of the comparison group had intraoperative bleeding, which was stopped in all 3 cases with technical difficulties. The cause of intraoperative bleeding and the technical difficulties of stopping it are associated with the following factors: 1. all these 3 patients in the preoperative period did not regularly use iodine preparations (1% lugol solution) due to drug intolerance; 2. thyrostatics were used for a long time because of which the thyroid tissue becomes loose, easily injured with copious bleeding; 3. insufficient exposure of the surgical wound. Conclusions. Thus, the use of plasmapheresis in combination with indirect electrochemical oxygenation of plasma with sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and subsequent reinfusion of detoxified plasma in a group of patients with severe forms of thyrotoxicosis and intolerance to drugs leads to a significant decrease in hormonal background, normalization of the function of the cardiovascular system and in the early postoperative period allows cases of thyrotoxicosis to be reduced to zero.
Keywords: Toxic goiter, Thyroidectomy, Subtotal resection, Relapse
Cite this paper: Gozibekov Jamshid Isanbayevich, Rakhmanov Kasim Erdanovich, Davlatov Salim Sulaymonovich, Nabiyev Bobir Bakhodirovich, Akhrorova Laylo Barno Qizi, The Use of Plasmapheresis for Preoperative Preparation of a Child with Diffuse Toxic Goiter, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2023, pp. 24-27. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231301.06.
Article Outline
1. The Relevance of Research
- In world practice, a number of scientific studies are conducted aimed at studying morpho-functional criteria for assessing the severity of the disease, including: studying the effect of colloidal goiter on morphofunctional changes in thyrocytes, the degree of which varies from minor disorders up to thyroid cancer [3,6,10]. Of particular importance are the issues of assessing the morphofunctional state and volume of preserved thyroid tissue. Prevention of the development of recurrent toxic goiter by surgeons is considered from the perspective of a set of principles of operation of the goiter-transformed gland, the basic position of which is the choice of a method of surgical intervention with preservation of the function of the thyroid residue [2,4,5,8,11]. At the same time, some authors suggest a subfascial method of thyroid removal, confirming their opinion with a low frequency of postoperative complications, others recommend extrafascial operations as a method of preventing relapse [7,12].The analysis of the literature also indicates that at the present time, therapeutic and diagnostic tactics for toxic forms of goiter belong to one of the urgent and still unresolved problems of modern healthcare [1,9]. In this regard, there is a need to revise the criteria for the radicality of surgical intervention in toxic forms of goiter, depending on the informative value of imaging methods and morphological studies, allowing at the preoperative stage to assess the features of the node structure and identify signs of aggression of the disease, in connection with which, optimization of the diagnostic algorithm becomes especially relevant in order to choose the most radical tactics of surgical treatment in each specific case.
2. The Aim of the Study
- The aim of the study is to improve the quality of treatment of patients with toxic forms of goiter by developing a differentiated approach to choosing the volume of surgery and effective methods to reduce postoperative complications.
3. Materials and Methods of Research
- The study is based on the results of treatment of 112 patients with toxic forms of goiter who were admitted to the surgical department of the multidisciplinary clinic of the Samarkand State Medical University in the period from 2012 to 2021.Patients are conditionally divided into two groups. In 2012-2016, 52 (46.4%) patients who made up the comparison group were operated on. From 2017 to 2021, 60 (53.6%) patients who were included in the main group were under our supervision. The size of the degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland in patients with toxic forms of goiter was assessed according to the classification of O.V. Nikolaev (1955) on the basis of ultrasound and palpation of the thyroid gland. 43 (38.4%) patients were diagnosed with a toxic form of goiter of II-III degree, 69 (61.6%) of IV-V degree.According to the pathomorphological form of toxic goiter, diffuse-toxic goiter was detected in 50 (44.6%) patients, mixed toxic goiter – in 39 (34.8%), toxic adenoma – in 13 (11.6%) and in 10 (8.9%) patients, recurrent toxic goiter was noted.All patients with toxic forms of goiter were examined according to a single scheme, which included a survey and examination of the patient, blood sampling for laboratory analysis and hardware, instrumental examination.The study of the hormonal function of the thyroid gland was carried out in all 112 patients. To do this, the concentration of TSH, T3, T4, thyroid-binding globulin and the titer of antibodies to thyroglobulin were determined. An increase in TSH levels indicated in favor of hypothyroidism, and a decrease in favor of thyrotoxicosis. An increase in the concentration of T3 and T4 confirmed the presence of thyrotoxicosis. The normal value of T3 was 1.2-2.8 nmol/L; T4 - 60-160 nmol/l; TSH - 0.17-4.05 mME/l.The complexity of the preparation of patients with toxic forms of goiter is due to the fact that out of 112 patients, 24 (21.4%) revealed either inefficiency, intolerance, or complications of drug therapy that arose as a result of long-term conservative treatment. Of the 24 patients with negative results of drug therapy, 10 (41.7%) patients were from the comparison group and 14 (58.3%) patients were from the main group.The analysis of the results of drug therapy in patients with toxic forms of goiter at the prehospital stage was carried out. In 8 cases, conservative therapy had no effect, 5 patients had drug intolerance, 3 had complications (leukopenia, pathology from the gastrointestinal tract).Anamnesis collection in patients receiving conservative therapy at the prehospital stage showed that it was carried out by thyrostatics: mercazolil, tyrizol, prednisone, dexamethasone. We analyzed the frequency of complications during conservative therapy, depending on the duration of taking the drug in a dosage that allows to achieve stable remission of the disease.Basically, these complications occurred in patients with long-term conservative therapy, which they underwent, despite the lack of effect. 10 patients of the comparison group, despite the negative results of drug therapy, underwent surgical interventions. Due to ineffective preoperative preparation, in 3 (5.8% of the total number of patients in the comparison group) cases in patients with DTZ, heavy bleeding was noted intraoperatively and in 4 (7.7%) patients in the early postoperative period, a thyrotoxic crisis of moderate and severe severity was noted.These circumstances prompted us to make new decisions to improve the results of preoperative preparation of patients with toxic forms of goiter. Unlike patients in the comparison group, in the main group, patients with severe thyrotoxicosis and patients with contraindicated drug therapy were treated with plasmapheresis in combination with indirect electrochemical plasma oxygenation with sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and subsequent reinfusion of detoxified plasma.Based on the results of preoperative preparation of patients with toxic forms of goiter, we have developed a program of preoperative preparation of patients with toxic forms of goiter. The main factors that influenced the course of the operation and the results of surgical intervention were taken into account.In the preoperative period, patients were prescribed thyrostatics Mercazolil or Tyrosol 5 mg 2 tablets 3 times a day. Tachycardia was removed by ß- adrenoblockers, in particular anaprilin 40 mg 2 tablets per day. After the prescribed drug therapy, the thyroid status reached euthyroidism within a month, and within 2 months it reached hypothyroidism. These were patients with a total score of up to 9 (46 (76.7%) patients out of 60). A month after successful drug-induced euthyroidism before surgery, 1% Lugol solution was injected 10 drops after meals for 15 days. After preoperative preparation, these patients underwent surgery without PF. Patients with a score of more than 9 (14-23.3%), who had severe thyrotoxicosis and ineffectiveness of drug-induced euthyroidism for more than 3 months or intolerance to thyrostatics were prescribed ß- adrenoblockers and 1% Lugol solution for 2 weeks and before surgery 6 sessions of PF in combination with IECO plasma sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and subsequent reinfusion of detoxified plasma.The developed program of point evaluation of factors affecting the results of treatment in patients with toxic forms of goiter allowed choosing the optimal method of preoperative preparation. As a result, a reduction in the period of preparation of patients for surgery was achieved from 12 months in the comparison group to 1 month in the main group (Fig. 1).
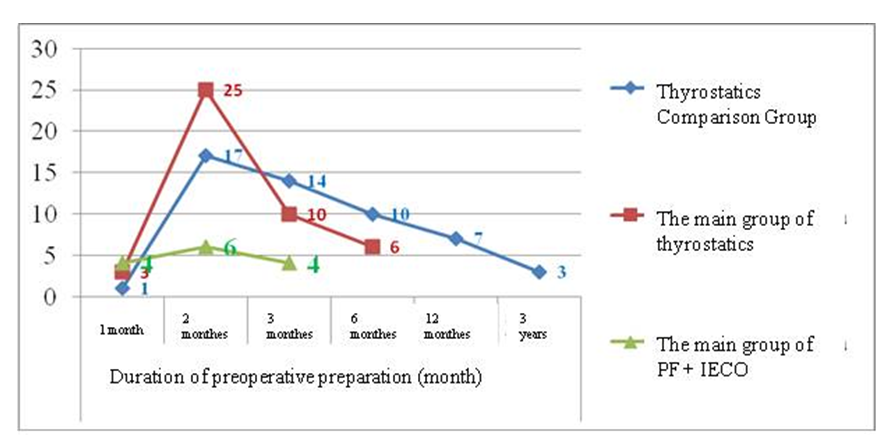 | Figure 1. Duration of preoperative preparation in the study groups (monthes) |
4. The Results of the Study
- During the operation, 3 (5.8%) patients of the comparison group had intraoperative bleeding, which was stopped in all 3 cases with technical difficulties. The cause of intraoperative bleeding and the technical difficulties of stopping it are associated with the following factors: 1. all these 3 patients in the preoperative period did not regularly use iodine preparations (1% lugol solution) due to drug intolerance; 2. thyrostatics were used for a long time because of which the thyroid tissue becomes loose, easily injured with copious bleeding; 3. insufficient exposure of the surgical wound.Thyrotoxic crisis (TTC) was observed in 4 (7.7%) patients of the comparison group, and in those out of 10 patients of the comparison group who did not use drug therapy regularly due to inefficiency, drug intolerance and complications of conservative therapy. In 14 (23.3%) patients of the main group who, for the same reasons, did not take thyrostatic drugs, and the thyrostatic status was stopped before euthyroidism using PF in combination with IECO plasma sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation of TTC in the postoperative period was not noted. We conducted a comparative analysis of the results of surgical treatment in the early postoperative period between these groups of patients. Monitoring of the possibility of developing a thyrotoxic crisis after surgery was carried out by examining blood pressure, pulse and temperature. The general condition of the vast majority of patients who underwent thyroid surgery immediately after the intervention and on the 3rd day was assessed as satisfactory and of moderate severity. Only in 4 patients of the comparison group, the condition was severe due to the development of TTC and concomitant diseases. We noted differences in the clinic of the postoperative period among patients with toxic forms of goiter, who were preparing for intervention with the use of PF in combination with IECO plasma sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and without it, that is, medicinally. After surgery, TTC appeared in 4 patients with toxic goiter prepared with medications, and in patients prepared for surgery with plasmapheresis, TTC was not noted in the postoperative period.The long-term results were analyzed in 82 (73.2%) of 112 operated patients for toxic forms of goiter. Patients were called in an active way, using letters, and archival material of the multidisciplinary clinic of SamSMU was also studied. The anamnesis of the disease was carefully studied.Of the 82 patients examined in the long term, a recurrence of thyrotoxicosis was noted in 10 (12.2%) patients, of which 9 (10.9%) patients of the comparison group and 1 (1.2%) patient from the main group.When analyzing the causes of relapse in patients of the comparison group in 7 (18.9%) cases, as already noted in chapter IV, the cause of relapse was organ-preserving surgery with proliferative changes in the tissue of the toxic thyroid gland. And in the remaining 2 (5.4%) cases, despite changes in thyroid tissue without proliferation, there was a recurrence of thyrotoxicosis, this was also facilitated by economical resection of the thyroid gland due to abundant intraoperative bleeding with inadequate preoperative preparation of patients with toxic forms of goiter.The observed 1 (2.2%) case of relapse in the main group of patients is associated with hemithyroidectomy with proliferative changes in thyroid tissue, where recurrent toxic adenoma resumed in the contralateral lobe in the long-term postoperative period.
5. Conclusions
- Thus, the use of plasmapheresis in combination with indirect electrochemical oxygenation of plasma with sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and subsequent reinfusion of detoxified plasma in a group of patients with severe forms of thyrotoxicosis and intolerance to drugs leads to a significant decrease in hormonal background, normalization of the function of the cardiovascular system and in the early postoperative period allows cases of thyrotoxicosis to be reduced to zero. In general, the use of plasmapheresis in combination with indirect electrochemical oxygenation of plasma with sodium hypochlorite with additional ozonation and subsequent reinfusion of detoxified plasma allowed to improve the quality of care by reducing the frequency of immediate postoperative complications from 15.4% to 6.7% and unsatisfactory results in the long-term postoperative period from 23.1% to 6.7%.Information about the source of support in the form of grants, equipment, and drugs. The authors did not receive financial support from manufacturers of medicines and medical equipment.Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML