-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2023; 13(1): 10-12
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20231301.03
Received: Dec. 8, 2022; Accepted: Dec. 28, 2022; Published: Jan. 13, 2023

Optimization of Therapy of Rheumatoid and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis with Genetically Engineered Biological Drugs
Babamuradova Zarrina Bakhtiyarovna, Iskandarova Farida Ismoilovna
Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Babamuradova Zarrina Bakhtiyarovna, Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The article discusses the effect of the basic anti-rheumatic drug (BARD) – metatrexate both in monotherapy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), and in combination with the genetically engineered biological drug (GEBD) -infliximab, their effect on the general clinical conditions of patients, on the levels of acute phase indicators (ESR, CRP), as well as levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1B, IL-6, TNF-a). The aim of our study is to study the effect of infliximab and methotrexate on clinical, immunological and cytokine parameters in patients with RA and JIA. According to the results of our study of the efficacy and tolerability of infliximab in combination with methotrexate, it was shown that this combination of drugs significantly expanded the possibilities of treating patients with severe RA and JIA.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Interleukins, Methotrexate, Infliximab
Cite this paper: Babamuradova Zarrina Bakhtiyarovna, Iskandarova Farida Ismoilovna, Optimization of Therapy of Rheumatoid and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis with Genetically Engineered Biological Drugs, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 13 No. 1, 2023, pp. 10-12. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20231301.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- RA is a chronic progressive autoimmune disease characterized by the involvement of peripheral joints in the pathological process, with the development of erosive and destructive changes in them. The prevalence of RA in the population ranges from 5 to 1% of cases, and in the structure of rheumatic diseases it occurs in 10% of patients [1].JIA is a chronic inflammatory joint disease that began in children under the age of 16, is one of the most severe and socially significant forms of chronic pathology in children. The high frequency of occurrence, in comparison with other rheumatic diseases of childhood, the tendency to early disability and the possibility of systemic manifestations involving internal organs in the pathological process, dictate the need for a more thorough and comprehensive examination and selection of adequate therapy [2].In recent years, GEBD has been used in the treatment of RA and JIA. The introduction of these drugs into clinical practice has made it possible to formulate the standards of pharmacotherapy of RA and JIA in a new way.
2. The Purpose of the Study
- To study the effect of GEBD infliximab and BARD methotrexate on clinical, immunological and cytokine parameters in patients with rheumatoid and juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
3. Materials and Methods
- The study included 96 patients, 50 of them RA patients (32% men and 68% women). The average age of RA patients was 54.3±2.2. The total number of children with JIA included in the study was 46 who were treated in the period from 2021-2022. The age of the sick children ranged from 7 to 17 years. The criteria for excluding patients in the study were: severe concomitant diseases in the stage of exacerbation or decompensation, the presence of concomitant cardiovascular pathology; the presence of chronic renal, hepatic insufficiency, pregnancy [3].All patients underwent standard clinical and laboratory tests: the level of acute phase indicators (ESR, CRP), standard radiography of the hands and distal parts of the feet was performed.The degree of RA activity was assessed by the DAS28 index (disease activity score). The studies were conducted on the basis of the Rheumatology Department of the Samarkand City Medical Association and in the Department of Cardiorheumatology of the Samarkand Regional Multidisciplinary Hospital. Immunological studies (TNF-a, IL-IB, IL-6) were conducted in the private clinic “MEDSI" before the start of treatment and 6 months after the start of treatment. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistica 6.1 software package for Windows. The arithmetic mean (M) and the error of the mean (m) were determined for each attribute in the compared groups. The hypothesis of equality of general averages in the compared groups was tested using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney U–test for two independent samples.
4. The Results of the Study
- As a result of the examination, joint pains were the main complaints in 75.0% of RA patients. Arthritis of small joints of the hands was observed with the greatest frequency (in 75.0% of patients). In almost half of the patients, the early manifestation of the disease was the involvement of the metatarsophalangeal joints in the process (45%). Knee joints (65.3%), ankle joints (56.1% of cases), shoulder joints (42.4%) and elbow joints (27.4%) are affected. The defeat of the hip joints and the joints of the tarsus was not characteristic. Extra-articular manifestations of RA occurred in 45.5% of patients. The presence of rheumatoid nodes was detected in 6.81% of patients, polyneuropathy - in 2.27% of patients, anemia - in 20.5% of patients, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head - in 3.4% of patients, Raynaud's syndrome — in 3.4% of patients.JIA was more common in girls (56.8%) than in boys (43.1%). Articular syndrome at the time of examination was represented by polyarthritis in 21.5% of children, oligoarthritis in 78.4% of children, with a predominant lesion of the knee, ankle and interphalangeal joints of the hands and feet.The increase in laboratory indicators of inflammatory activity of the disease was equally characteristic in RA and JIA. An increase in ESR was observed in 68.18% of patients. An increase in the level of CRP was observed with almost the same frequency - in (65.3%) patients.To prescribe appropriate therapy, the patients were divided into 2 groups: group 1, patients receiving basic methotrexate therapy, group 2, patients receiving infliximab therapy in combination with methotrexate. Methotrexate was prescribed 15mg per week orally. Infliximab was administered intravenously at the rate of 3 mg per kg of body weight of the patient. The second infusion was carried out 2 weeks after the first, the third - 4 weeks after the second, each subsequent infusion was carried out 8 weeks after the previous one [4].The changes in the interleukin content: IL-1B, IL-6, TNF-a in blood serum for RA and JIA patients were evaluated.The dynamics of changes in serum interleukins in patients with RA and JIA against the background of basic therapy and therapy with GIBP - infliximab is shown in Figures 1-2.
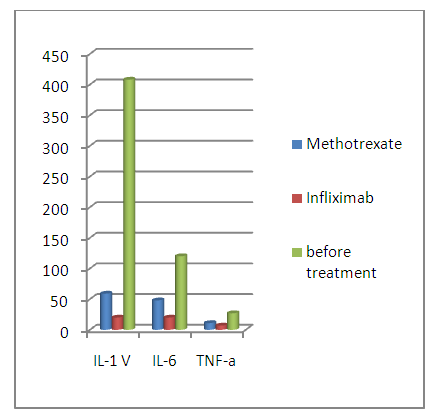 | Figure 1. The level of interleukins in the blood, depending on the basic therapy in JIA |
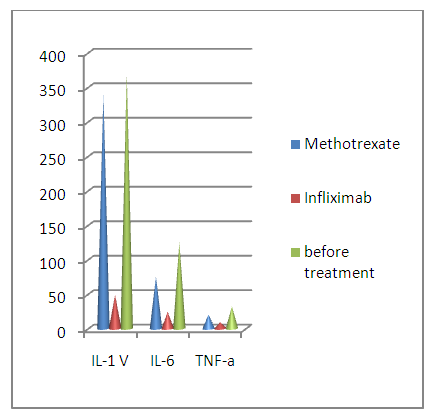 | Figure 2. The level of interleukins in the blood depending on the basic therapy in RA |
5. Conclusions
- The results of our study of the efficacy and tolerability of infliximab showed that this drug significantly expanded the possibilities of treating patients with severe RA and JIA. This was manifested in the rapid and pronounced positive dynamics of indicators reflecting the activity of the inflammatory process (the number of inflamed and painful joints, ESR, CRP, etc.) in most patients. A distinct improvement was often recorded after the first infusion. This result deserves a very high assessment, since previously these patients were treated for a long time and very actively without a significant positive effect.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML