Iroda Abroldzhanovna Akramova
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Epidemiology, Microbiology, Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Iroda Abroldzhanovna Akramova, Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Epidemiology, Microbiology, Infectious and Parasitic Diseases, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The production of IL - 6 is induced in response to exposure to microbial toxins and certain cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-17), after which it enters the bloodstream, where it can be quantified. In COVID-19, high levels of IL-6, IL-17 during antimicrobial therapy, especially in the absence of a trend towards their decrease, are an important prognostic factor, especially in patients with severe chronic diseases.
Keywords:
COVID-19, Interleukin-6, Interleukin-17
Cite this paper: Iroda Abroldzhanovna Akramova, The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Immunopathogenesis of COVID 19, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 12, 2022, pp. 1239-1243. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221212.14.
1. Introduction
The pandemic of a new coronavirus infection in 2019 COVID-19 drew the closest attention to the problems of human immunopathology, to the development of hyperimmune pathology, called the “cytokine storm” syndrome, which are among the most severe complications of coronavirus infection [1,5,6,12]. In the spectrum of cytokines involved in it, great importance is attached to interleukin-6. Interleukin-6 is a pleiotropic cytokine with a molecular weight of 21–28 kDa with a wide range of biological activity, produced by both lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells. It regulates the immune response, acute phase response, inflammation, oncogenesis, and hematopoiesis. Coronavirus has been found to be able to lead to an excessive unregulated immune response in the host organism, which is one of the main factors in the severity of the course of the disease and mortality in patients with COVID-19. In a study by Wu et al. patients in the assessment of risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death had a significant increase in the level of interleukin-6 [2,4,13,19]. In this connection, one of the objectives of our study was to study the relationship of IL-6 with other autoimmunization triggers in COVID-19.Purpose of the study: to study the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in immunopathogenesis in patients with COVID 19.
2. Materials and Methods
For immunological studies, 53 patients with moderate, severe and extremely severe course of the disease were selected, who were hospitalized in the Zangiata Specialized Multidisciplinary Infectious Diseases Hospital of Block B. Analyzing the anamnestic data, we found that, on average, patients were admitted to the hospital on the 4-5th day of the disease. Immunological tests were carried out in dynamics on the day of hospitalization, on the 7th day and before discharge on the 27th-28th day of hospitalization.Determination of the concentration of cytokines interleukin-6 and interleukin-17 (IL-6 and IL-17) was carried out using a set of reagents from Vector-Best (Novosibirsk). The determination method was based on a solid-phase "sandwich" - a variant of enzyme immunoassay.
3. Results and Discussion
Analysis of the results of the study of complaints of patients with coronovirus infection showed that the symptoms of intoxication (fever, diarrhea, nausea, headache) and signs characteristic of this disease, such as loss of smell and taste, prevailed in the group with a moderate course. Symptoms of respiratory failure were more in the group with severe course - 96.6%. (Fig. 1.)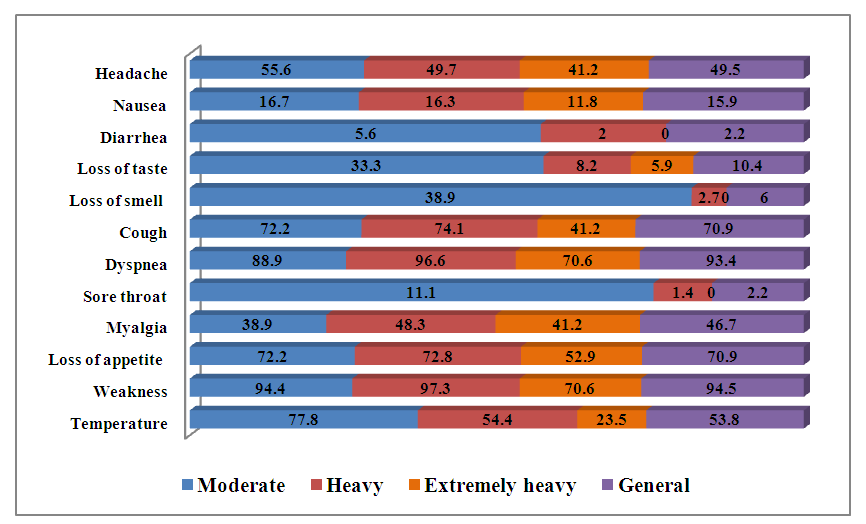 | Figure 1. Complaints of examined patients |
Among the complications in the group of patients with extremely severe coronovirus infection, the percentage of coronary heart disease (70.6%), double-strand interstitial pneumonia (76.5%) and respiratory failure of the 3rd degree (82.4%) was higher than in the group with severe and moderate degree. (Fig. 2.)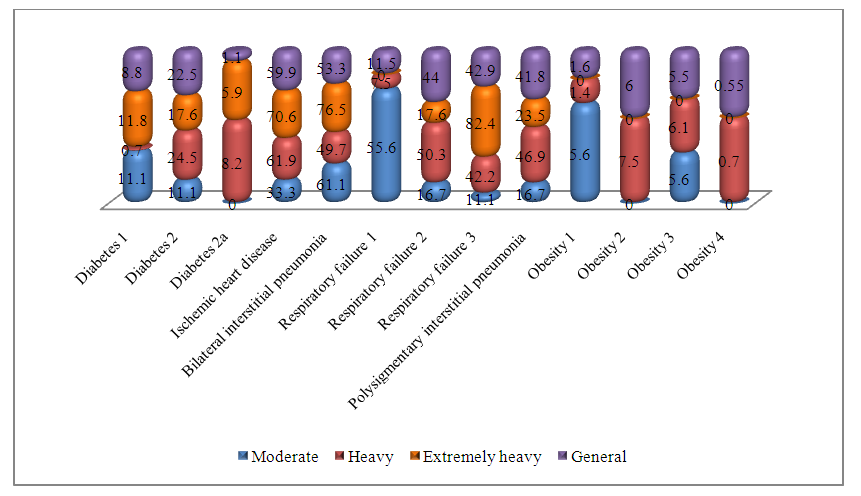 | Figure 2. Complications of the underlying disease of the examined patients |
When analyzing the results obtained for the study of the level of IL 6, in the dynamics of treatment, we received the following data:The concentration of the level of IL 6 at the time of admission was36.5 ± 4.1 pg / ml, in the middle of treatment there was a tendency to increase its level, and by the end of therapy its decline was observedin1.92 times. (Fig. 3.)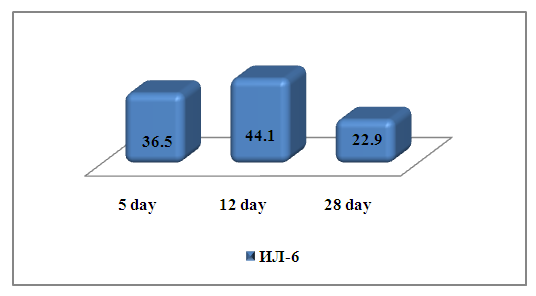 | Figure 3. The level of total IL-6 in the examined patients |
According to the severity of the disease COVID 19, IL-6 levels differed from the general indicators.With a moderate degree, the synthesis of the level of IL 6 was initially lower than in the group with a severe degree -10.8±4.1 pg/ml at the beginning of therapy. In the middle of treatment, there was a tendency to increase its level, and after therapy, the level of IL-6 significantly decreased by 4.1 times (3.01±1.4 pg/ml). (Fig. 4.)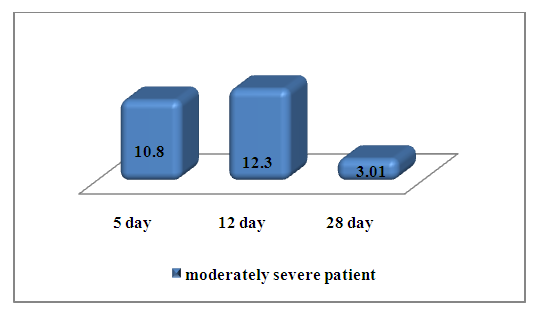 | Figure 4. The level of IL-6 in the examined patients in the group of moderate severity |
With a more severe course, the concentration of IL-6 on the day of admission was 39.9±5.2 pg/ml, on the 7th day there was a slight decrease in its level to 38.5±5.8 pg/ml; 1.67 times and amounted to 23.1±6.0 pg/ml. (Fig. 5.)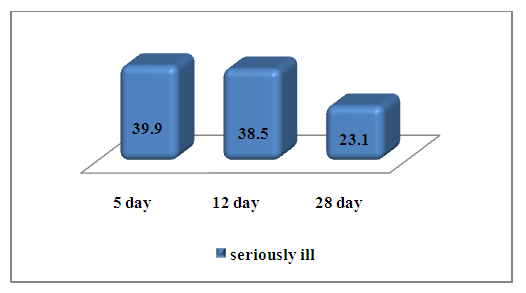 | Figure 5. The level of IL-6 in those examined in the group of severe patients |
Data analysis in the group with extremely severe covid 19, the level of IL-6 was30.8±9.7 pg/ml, in the middle of treatment there was a sharp increase in its synthesis by 1.96 times (60.5±6.6 pg/ml), and at the end of the treatment a significant decrease by 3.29 times. (Fig. 6.)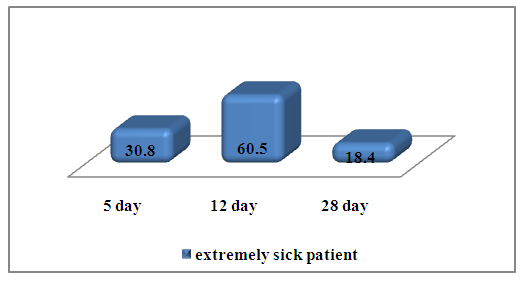 | Figure 6. The level of IL-6 in those examined in group of extremely severe patients |
Thus, in the group with a severe degree, a linear decrease in the level of IL-6 can be observed, and in the group with moderate and extremely severe, we observe an increase in its level in the middle of treatment, which is more pronounced in the group with an extremely severe degree of the disease. Perhaps it is for this reason that a cytokine storm occurs in patients with covid 19 in this category of patients, contributing to the development of irreversible consequences, including death.According to a number of authors, a particularly large number of Th17 cells are found in the peripheral blood of patients with severe COVID-19, which was associated with the development of a cytokine storm and excessive synthesis of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL -7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN-α, IFN-γ, IFN-γ-induced protein 10 (IP-10), MCP-1, macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIPs), and TNFα [3,5,7,20]. IL-17A is the most studied representative of the group of multifunctional cytokines IL-17. This cytokine is synthesized by Th17 cells, as well as by CD8+ -T-lymphocytes, γδT-lymphocytes, natural killer (NK-cells), NKT-lymphocytes, mast cells and neutrophils [6,8,10,14]. It has a wide range of biological features that include: activation of the production of chemokines - monocytic chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), which regulates the growth of the oncogene alpha (GRO-alpha / CXCL1) and IL-8, which enhances the attraction of neutrophils and monocytes; activation of production of IL-6 synthesized by macrophages, epithelial cells and T-cells in response to the introduction of extracellular microorganisms; activation of the production of hematopoietic cytokines - granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), which enhance the growth of myeloid precursors of hematopoiesis and the synthesis of other mediators, in particular IL-1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α and prostaglandin E2 [10]. IL-17 together with IL-22 regulates homeostasis and promotes the restoration of epithelial cells damaged by extracellular inflammatory stimuli. However, with excessive production of IL-17A, a shift towards increased pro-inflammatory pathological activity is possible [9,15,16,18]. IL-17A plays an important role in the pathogenesis of a number of immune-mediated diseases and is an effector cytokine. According to modern concepts, the cytokines IL-23 and IL-17A are key in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, while IL-17A is the main effector cytokine. IL-17 plays a protective role in the infection of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract by extracellular bacteria, fungi and viruses. In a review by WT Ma et al. (2019) noted that IL-17 plays an important role in various viral diseases, and treatment aimed at controlling IL-17 can be an effective alternative treatment for viral diseases [11,17]. IL-17A plays an important role in the pathogenesis of a number of immune-mediated diseases and is an effector cytokine. According to modern concepts, the cytokines IL-23 and IL-17A are key in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, while IL-17A is the main effector cytokine. IL-17 plays a protective role in the infection of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract by extracellular bacteria, fungi and viruses. In a review by WT Ma et al. (2019) noted that IL-17 plays an important role in various viral diseases, and treatment aimed at controlling IL-17 can be an effective alternative treatment for viral diseases [11,17]. IL-17A plays an important role in the pathogenesis of a number of immune-mediated diseases and is an effector cytokine. According to modern concepts, the cytokines IL-23 and IL-17A are key in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, while IL-17A is the main effector cytokine. IL-17 plays a protective role in the infection of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract by extracellular bacteria, fungi and viruses. In a review by WT Ma et al. (2019) noted that IL-17 plays an important role in various viral diseases, and treatment aimed at controlling IL-17 can be an effective alternative treatment for viral diseases [11,17]. IL-17 plays a protective role in the infection of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract by extracellular bacteria, fungi and viruses. In a review by WT Ma et al. (2019) noted that IL-17 plays an important role in various viral diseases, and treatment aimed at controlling IL-17 can be an effective alternative treatment for viral diseases [11,17]. IL-17 plays a protective role in the infection of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract by extracellular bacteria, fungi and viruses. In a review by WT Ma et al. (2019) noted that IL-17 plays an important role in various viral diseases, and treatment aimed at controlling IL-17 can be an effective alternative treatment for viral diseases [11,17].In this connection, we studied the synthesis of IL-17A in the dynamics of observation of the studied patients.Analysis of the obtained data on the severity of the disease revealed the following:In the group with moderate severity at the time of admission, the concentration of IL-17A was close to the control values, in the middle of treatment there was a significant increase in its level by 3.71 times, and at the end of the observation period there was a significant decrease did not reach the control group (12.8 ± 3.4 pg/ml). (Fig. 7.)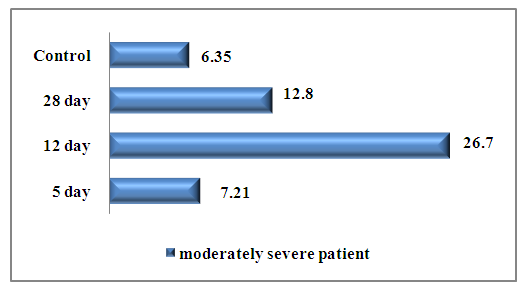 | Figure 7. The level of IL-17 in those examined in group of moderate patients |
In patients with a severe course, the synthesis of IL17A at the time of admission, i.e. on the 5th day of the disease was significantly higher than the control values by 2.97 times, in the middle (on the 7th day of hospitalization) and at the end of treatment, a linear decline in its concentration was observed, as was the synthesis of IL-6. (Fig. 8.)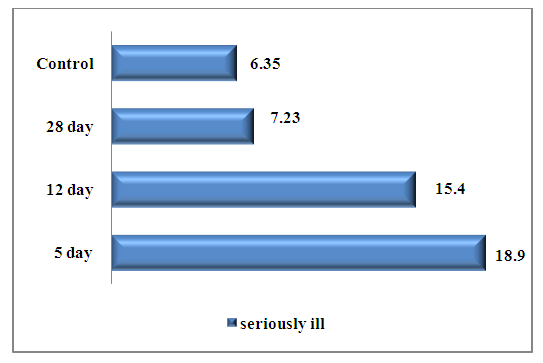 | Figure 8. The level of IL-17 in those examined in group of severe patients |
For an extremely severe degree of covid 19, a significant increase in the level of the studied cytokine at the time of admission was 5.05 (32.1 ± 4.61) times compared with the control group, in the middle of treatment this level increased by another 1.88 (60, 4±3.42) times. At the end of therapy, there was a slight decrease in its synthesis to 51.3 ± 7.4 pg/ml. (Fig. 9.)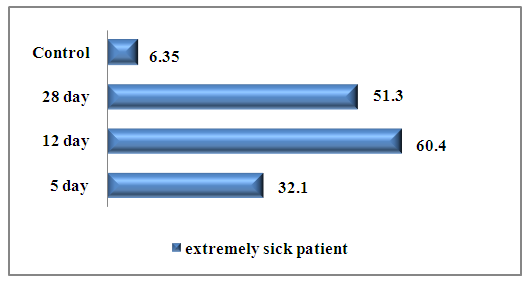 | Figure 9. The level of IL-17 in those examined in group of extremely severe patients |
IL-17 and IL-6 play an important role in the pathogenesis of many diseases and directly correlate with clinical activity.
4. Conclusions
Thus, the dynamics of the concentration of IL17A is similar to changes in the level of IL6, given that these two cytokines affect each other synergistically, it can be assumed that hyper cytokinemia is one of the causes of numerous complications in patients in the group with an extremely severe course of the disease. The role of the “cytokine storm” is not excluded, in which there is a large production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators, which lead to the activation of an aberrant innate and acquired immune response, leading to autoimmune inflammation.
References
| [1] | Gordeeva EK, Kade AH Korrekcija citokinovogo i hormonal'nogo disbalansa pri lechenii stabil'noj stenokardii naprjazhenija [Correction of cytokine and hormonal imbalances in the treatment of stable tension angina] // Kubanskij nauchnyj medicinskij vestnik [Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin]. 2018; 25(3): 51-55. |
| [2] | Il'nickij AN, Koroleva MV, Sharova AA, Kudashkina EV, Reznik AV, Borodulin AV, Belousova ON Gipomobil'nost' - factor snizhenija socializacii i kachestva zhizni u pacientov starshego vozrasta s serdechno-sosudistoj patologiej [Hypomobility is a factor in reducing socialization and quality of life in older patients with cardiovascular pathology] // Sovremennye problemy zdravoohranenija i medicinskoj statistiki [Current Health and Medical Statistics Issues]. 2019; 4:115-126. |
| [3] | Podobed IV, Proshhaev KI, Ahmedov TA, Rukavishnikov AS, Kovalenko O.Ju. Geriatricheskie aspekty techenija hronicheskoj serdechnoj nedostatochnosti [Geriatric aspects of chronic heart failure] // Sovremennye problemy zdravoohranenija i medicinskoj statistiki [Current Health and Medical Statistics Issues]. 2021:1:303-325. |
| [4] | Huang C. et al. Clinical features of patient infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Lancet. 2020; 395: 497-506. Doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. |
| [5] | Huang LH Interleukin-17 drives interstitial entrapment of tissue ipoproteins in experimental psoriasis // Cell Metabol. 2019; 29: 475-487. |
| [6] | Jong E., Oers JA, Beishuizen A., Vos P., Vermeijden WJ, Haas LE et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically IL-l patients: a randomised, controlled, openlabeltrial. Lancet I nfe ct D is 2016; 16: 819e27. |
| [7] | Rozhdestvenskaya OA, Korshun EI, Pochetaeva IP [and others]. Kletochnye hronoblokatory v mul'modal'nyh programmah profilaktiki prezhdevremennogo stareniya kardial'nogo tipa. [Cellular chronoblocks in mulmodal programs for the prevention of premature aging of the cardiac type. Sovremennye problemy zdravoohraneniya i medicinskoj statistiki. [Current health and medical statistics issues]. 2020; 4:234-247. (In Russian) |
| [8] | Zakharycheva T., Mаkhovskaya T., Shirokova A., Shikina I. Autonomic dysregulation syndrome in covid-19 convalescents: possible causes and approaches to its correction. (2022) Autonomic Dysregulation Syndrome in Covid-19 Convalescents: Possible Causes and Approaches to Its Correction. In: Antipova T. (eds) Comprehensible Science. ICCS 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 315. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-85799-8_34. |
| [9] | Zakharycheva T., Makhovskaya T., Shirokova A., Shikina I. The Nervous System Disorders in COVID-19: From Theory to Practice. (2021) In: Antipova T. (eds) 2021 International Conference on Advances in Digital Science (ICADS 2021), AISC 1352, pp.191-197 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71782- 7_17. |
| [10] | Stoyakov AM, Ilnitsky AN, Bessarabov VI [and others]. Signal'nye molekuly i ul'cerogenez v pozhilom vozraste. [Signaling molecules and ulcerogenesis in old age.] Fundamental'nye research. [Basic research]. 2012; 10(1): 122-125. (In Russian). |
| [11] | Annuziato F, Romagnani C, Romagnani S. The 3 major types ofinnate and adaptive cell-mediated effector immunity. J Allergy Clinic Immunol. 2015; 135: 626-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.11.001. |
| [12] | Isalovic N, Daigo K, Mantovani A, Selmi C. Interleukin-17 and innate immunity in infections and chronic inflammation. J Autoimmun. 2015;60:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.04.006. |
| [13] | Miossec P, Kolls JK. Targeting IL-17 and Th17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11:763-76. doi: 10.1038/nrd3794. |
| [14] | Beringer A, Miossec P. Systemic effects of IL-17 in inflammatory arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019 Jun 21. doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0243-5. |
| [15] | Beringer A, Noack M, Miossec P. IL-17 in chronic inflammation: from discovery to targeting. Trends Molec Med. 2016; 22: 230-41. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2016.01.001. |
| [16] | Benedetti G, Miossec P. Interleukin 17 contributes to the chronicity of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2014; 44: 339-47. doi:10.1002/eji.201344184. |
| [17] | Fragoulis GE, Siebert S, McInnes IB. Therapeutic targeting of IL-17 and IL-23 cytokines in immune-mediated disease. Ann Rev Med. 2016: 67: 337-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-051914-0219444. |
| [18] | Allam G, Abdel-Moneim A, Gaber AM. The pleiotropic role of interleukin-17 in atherosclerosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 106: 1412-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.110. |
| [19] | Robert M, Miossec P. Effects of Interleukin 17 on the cardiovascular system. Autoimmun Rev. 2017; 16(9): 984-91. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.07.009. |
| [20] | Cortvrindt C, Speeckaert R, Moerman A, et al. The role of interleukin-17A in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases. Pathology. 2017; 49(3): 247-58. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2017.01.003. |











 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML