L. G. Sabirzyanova1, N. Ya. Fayzullaeva1, M. R. Ruzibakieva1, T. A. Askarov2
1Institute of Immunology and Human Genomics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Research aimed to study the local production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in women of childbearing age with grade 2 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia before and after combination therapy.CIN2 was used to examine the results of 75 women's immunological studies. ELISA was used to measure the levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cervical mucus. The statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out using Statistica 6.0. The significance of differences in the mean values (P) of the compared indicators was assessed by a Student's t-test (t).In women with CIN2 before treatment, an imbalance in the local production of pro-inflammatory (IL-6, IL-17A, and TNF) cytokines was established. After combination therapy, a decrease in the synthesis of the studied cytokines was observed, which indicates the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
Keywords:
Women, Immunity, Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, Interleukin, Papillomavirus infection
Cite this paper: L. G. Sabirzyanova, N. Ya. Fayzullaeva, M. R. Ruzibakieva, T. A. Askarov, Features of Local Cytokine Production in Women with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2-Stage before and after Treatment, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 12, 2022, pp. 1235-1238. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221212.13.
1. Introduction
Human papillomavirus infection (PVI) is recognized as one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. According to the WHO, more than 500,000 new cases of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection are registered annually in the world. Interest in the study of this pathology continues to grow, as it is a socially significant problem due to the oncogenic effects of the virus. So, in 95% of women of reproductive age with background, precancerous diseases, and cervical cancer, HPV is detected in biopsy specimens [2,3]. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in the cervix causes cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Transient HPV infections cause low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions/CIN1, while persistent HPV infection results in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions/CIN2–3, which are precursors of cervical cancer [4].The generally recognized trigger mechanism for neoplastic transformation of the cervical epithelium is infection with highly oncogenic strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) [6,7]. The emergence of a neoplastic process, as a rule, is facilitated by several stages:1. HPV infection.2. Finding the genome of the virus in episomal form with the reproduction of viral particles.3. Polyclonal introduction of viral DNA into the host cell genome.4. Induction of mutations in cellular DNA, which causes instability of the genome.5. Reproduction of a clone of cells with altered DNA containing viral DNA.However, this only contributes to the initiation of the tumor process but is not a sufficient condition for its further progression [11,12]. Only women with long-term persistence of high carcinogenic risk HPV (HRV HPV) are at risk of developing cervical precancer and cancer [9].Currently, the relevance of scientific research in the field of immunology in viral lesions is aimed at studying the type of immune response. Although some viral infections elicit a strong host immune response and are therefore eliminated by the host, HPV effectively evades such immune recognition, allowing persistent viral infection to be established [14]. However, in some patients, due to the activation of cellular and humoral immunity, HPV infection does not lead to changes in the organs of the genital area and passes as an asymptomatic carriage or is eliminated on its own. [4].A certain role in the persistence of human papillomavirus infection (PVI) and the development of these processes is played by local immune mechanisms, in particular, cytokine regulation of the local immune response to HPV [16,17].As is known, the algorithm for managing patients with CIN I requires active monitoring using cytology and colposcopy due to the high level of spontaneous regression and the low level of progression of these lesions. Particular difficulties arise when examining patients with CIN II since this lesion has a high degree and is most often associated with the long-term persistence of PVI [3,5].Thus, infection with the subsequent development of HPV-associated diseases occurs in immunocompromised people.In connection with the above, the purpose of this study was to study the local production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in women of childbearing age with grade 2 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia before and after combination therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
To perform the work, the materials of women who applied to the diagnostic center "De factum" were used. The results of a comprehensive examination of 75 women were studied aged 20 to 45 years with an established diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 (CIN2). The examined women are represented by 2 groups. The main group consisted of 50 women who underwent the following examination methods: liquid cytology, advanced HPV-PCR, femoflor screening, and microscopy. The control (comparison) group consisted of 25 practically healthy women of the same age.Immunological studies of the examined were carried out in the laboratory of reproduction immunology of the Institute of Immunology and Human Genomics of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.The concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-17A (IL-17A), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα)in cervical mucus was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using test systems of VECTOR-BEST JSC (Russia, Novosibirsk), following the manufacturer's recommendations.Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out using the computer program Statistica 6.0. The significance of differences in the mean values (p) of the compared indicators was assessed by Student's t-test (t).
3. Results and Discussion
One of the main functions of cervical mucus is to prevent infection by microorganisms. This mucus includes cytokines that mediate many of the activities of innate and adaptive immunity. However, the relationship between cervical neoplasia and mucosal cytokines is controversial and poorly understood [9,12].In the course of studying the results of the local cytokine status before the start of treatment, multidirectional values were established, which are shown in Fig. 1. below.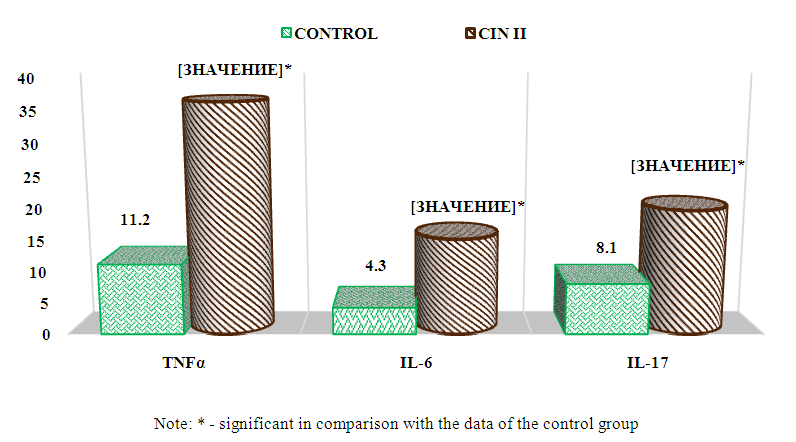 | Figure 1. The content of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the cervical fluid of the examined women before treatment |
Interleukin - 6 multifunctional cytokine, Th2-humoral immune response, regulates acute phase reactions and hematopoiesis. Formed by activated monocytes / macrophages, T-cells, endotheliocytes, fibroblasts, and a number of non-immunocyte cells. The main action of IL-6 (as well as IL-4) is associated with its participation in the maturation of B-lymphocytes into plasma cells that secrete immunoglobulins [6].Analysis of the content of IL-6 before the start of treatment is shown in Fig. 1. found that in women with CIN2 in the cervical mucus, the synthesis was significantly increased by 3,5 times, which averaged 15,1 ± 1.8 pg / ml, while in the group of healthy women this figure was 4,3 ± 0, 9 pg/ml (P<0.01).According to the mechanisms, IL-6 is involved in the induction of almost the entire complex of local manifestations of inflammation. It is likely that increased rates in women with CIN2 indicate stimulation of the immune response by attracting IIC to the focus of inflammation. But in the studies of Lin-Hung Wei et al. (2001) found that high levels of IL-6 in the microenvironment promote tumor angiogenesis and the development of cervical cancer [10].Interleukin - 17 refers to pro-inflammatory cytokines and is involved in many stages of the immune response.IL-17triggers an extensive tissue reaction, leading to the migration of neutrophils to the area of inflammation, followed by elimination of the pathogen. It can be produced by many cells, but the most pronounced production is provided by Th17-type [13,15].As shown in Fig. 1, the assessment of the content of IL-17A revealed an increased level in the cervical mucus of women with CIN2 by 24 times, which averaged 19.7±1.5 pg/ml, compared with those of the control group. 8,1±1,2pg/ml (P<0.001). Based on physiological functions, the results indicate that IL-17A may also play a role in enhancing immunity in high-risk HPV infection, especially in the cervical microenvironment, which contributes to disease progression of associated cervical lesions.The completeness of the body's response to a viral infection is also determined by sufficient production of TNFα by Th1-lymphocytes [8].TNFα is one of the main proinflammatory cytokines [6,8]. Produced by monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils and mast cells. TNF-α stimulates the adhesion of granulocytes to the endothelium and their emigration to the focus of inflammation from the vascular bed, enhances phagocytosis and the production of superoxide anion radicals by phagocytes, and the expression of receptors for the components of the complement system [2].Analysis of the local production of TNF-α found that the content of cachexin in the cervical mucus was increased by 3,2 times, with an average value of 36,4±2,7 pg/ml, while in the group of healthy women the average value was 11,1±1,3 pg/ml (P<0.001). Since the expression of TNF-α is an "indicator" of inflammation activity and correlates with the severity of the infectious process. It is likely that nOur results are consistent and confirm the earlier studies of Abramovskikh O.S. et al. (2011) thatTNF-αcan inhibit the proliferation of healthy epithelial cells of the cervix, however, in the case of infection of the epithelium with HPV types 16 and 18, the sameTNF-αstimulates the proliferation of affected cells [1].Thus, an increase in the concentrations of the studied cytokines in the cervical mucus in women with CIN2 indicated the activation of local immunity to pathogen activation. At this stage of the pathological process, an imbalance in the production of the Th1/Th2/Th17 system was established, as evidenced by hypercytokinemia.The choice of treatment tactics depends on the results of the examination, the nature and localization of HPV foci, immune status, the presence of urogenital infections, and concomitant somatic pathology.In order to identify the effectiveness of combined treatment in women with CIN2, the following drugs were used according to the above scheme: Allokin-alpha (injections) - 6 injections subcutaneously every other day and Pavisin (vaginal suppositories) - 12 days.ALLOKIN-ALFA (BRAND-PHARM, Russia) is an original selective stimulator of the activity of natural immunity factors, developed by an international team of scientists. The active substance - cytokine-like peptide alloferon - has a pronounced antiviral activity.Recently, the combined use of Pavisin suppositories in the treatment of moderate and severe cervical erosion has a much greater effect in clinical use. Pavisin has a wide spectrum of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory action, improves blood circulation in the area of erosion, improves phagocytic activity and stimulates local immunity.To establish the effectiveness of treatment with the above drugs, we monitored the dynamics of the studied cytokines in the cervical fluid 21 days after the end of treatment. The results obtained are shown below in Fig. 2.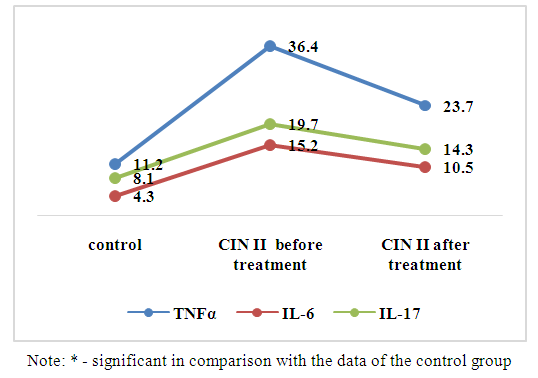 | Figure 2. Dynamics of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the cervical fluid of the examined women after treatment |
It should be noted that throughout the study, no side effects and allergic reactions were observed in women with combination therapy.The study of the level of IL-6 displayed in Fig. 2 revealed a significant decrease in synthesis by 30.9% compared with both the initial data (15.2±1.8 pg/ml) (P<0.05) and standard values (4.3±0.9 pg/ml), with an average of 10.5±1.4 pg/ml (P<0.001).In the study of the content of IL-17A in the cervical mucus in women with CIN2 after 3 weeks after treatment, a decrease trend of 27.4% was established. Thus, the concentration of this mediator averaged 14.3±1.4 pg/ml, which was significantly compared with those before treatment (19.7±1.5 pg/ml) (P<0.05) and with indicators of healthy women (8.1±1.2 pg/ml) (P<0.01).Analysis of the local level of TNF-α in women with CIN2 after 21 days of treatment also revealed a decrease in synthesis by 34.9%, which averaged 23.7 ± 2.2 pg / ml and was significant compared with the values before treatment 36.4 ±2.7 pg/ml (P<0.01) and with those of the control group of women 11.2±1.3 pg/ml (P<0.001).According to numerous studies, adequate therapy contributes to a more complete elimination of pathogens and complete epithelialization of the cervix, which reduces the frequency of relapses and increases the effectiveness of therapy for HPV-associated diseases of the cervix [3]. The data we obtained after treatment indicate the effectiveness of the combined therapy and, as a result, a decrease in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, indicating positive dynamics in the localTh-system. Thus, according to our observation, the use of Allokin-alpha and Pavisin in the complex treatment of women with CIN2 is effective and acceptable. Further research is required.
4. Conclusions
An immunological study was carried out to study local cytokine regulation in women with grade 2 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia before and after combination therapy. The results obtained before treatment indicate hyperactivation of local immunity to PVI, expressed by suppression of the immune response associated with an imbalance in the Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokine systems. After the therapy, a decrease in the synthesis of the studied pro-inflammatory cytokines is observed, which indicates the effectiveness of the chosen therapy.
References
| [1] | Abramovskikh O.S., Dolgushina V.F., Telesheva L.F. Cytokines in neoplastic processes of the cervix associated with the human papillomavirus of high carcinogenic risk. Russian immunological journal. 2011; 5/14(1): 66-68. |
| [2] | Briko N.I., Lopukhov A.D. The need to control HPV-associated diseases // Epidemiology and vaccine prevention. 2017. V. 16, No. 2. S. 10–15. |
| [3] | Dubensky V.V., Kuznetsov V.P., Belyaev D.L., Slyusar N.N. The effectiveness of immunocorrection with cytokines in the treatment of human papillomavirus infection. Journal. microbiology, epidemiology and immunobiology. 2001; 5: 54–8. |
| [4] | Svidinskaya E.A., Dzhibladze T.A., Zuev V.M. The role of the determination of molecular genetic markers in the diagnosis and prognosis of the course of diseases of the cervix. Tumors of the female reproductive system. 2010; #2: 93-98. |
| [5] | Shipitsyna E. V., Martikainen Z. M., Vorobieva N. E. et al. Application of the Femoflor test to assess microbiocenosis // Journal of Obstetrics and Women's Diseases, Vol. LVIII, Issue 3/2009. |
| [6] | Jay A. Lieberman, Anna-Barbara Moscicki, Jan L. Sumerel, Yifei Ma, Mark E. Scott. Determination of cytokine protein levels in cervical mucus samples from young women by a multiplex immunoassay method and assessment of correlates. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2008; 15(1): 49-54. https://doi.org/10.1128/cvi.00216-07. |
| [7] | Fahey JV, Schaefer TM, Channon JY, Wira CR. Secretion of cytokines and chemokines by polarized human epithelial cells from the female reproductive tract. Hum reproduction. 2005; 20(6): 1439-1446. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deh806. |
| [8] | Herbein, H. Tumor necrosis factor and TNF receptors and viral pathogenesis. H. Herbein, W.A. O'Brien // Proc. soc. Exp. Biol. Med. - 2000. - Vol. 223. –P.241–257. |
| [9] | Iwata T., Fujii T., K. Morii, M. Saito, J. Sugiyama, H. Nishio, T. Morisada, K. Tanaka, T. Yaguchi, Y. Kawakami, D. Aoki Cytokine profile in cervical mucosa of Japanese patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia Int. J.Clin. Oncol., 20 (1) (2015), pp. 126-133. |
| [10] | Lin-Hung Wei., Min-LiangKuo., Chi-An Chen., Wen-Fang Cheng., Shao-PeiCheng., Fon-JouHsieh., Chang-YaoHsieh. // Interleukin-6 in Cervical Cancer: The Relationship with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor - Gynecologic Oncology Volume 82, Issue 1, July 2001, Pages 49-56. |
| [11] | Lieberman JA, AB Moscicki, JL Sumerel, Y. Ma, ME Scott Determination of cytokine protein levels in cervical mucus samples from young women by a multiplex immunoassay method and assessment of correlates Clin. Vaccine Immunol., 15 (1) (2008), pp. 49-54. |
| [12] | Marks MA, Eby Y., R. Howard, PE Gravitt Comparison of normalization methods for measuring immune markers in cervical secretion specimens J. Immunol. Methods, 382 (1–2) (2012), pp. 211-215. |
| [13] | Patel DD Effect of IL-17A blockade with secukinumab in autoimmune diseases / Lee DM, Kolbinger F. // Ann Rheum Dis. – 2013. –No.2. – P.116–23. |
| [14] | Stanley MA, Sterling JC Host responses to infection with human papillomavirus Curr. Probl. Dermatol., 45 (2014), pp.58-74. |
| [15] | Yamada H. Current perspectives on the role of IL-17 in autoimmune disease. // J Inflam Res. – 2010. –No.3. – P.33–44. |
| [16] | Zur HH. Papillomaviruses causing cancer: evasion from host-cell control in carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; No. 92: 690-698. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/92.9.690. |
| [17] | Zur HH. Papillomaviruses causing cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nature Rev Cancer. 2002; 2: 342-350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc798. |




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML