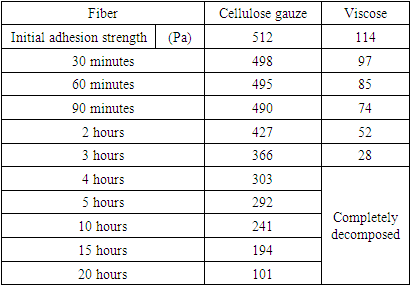
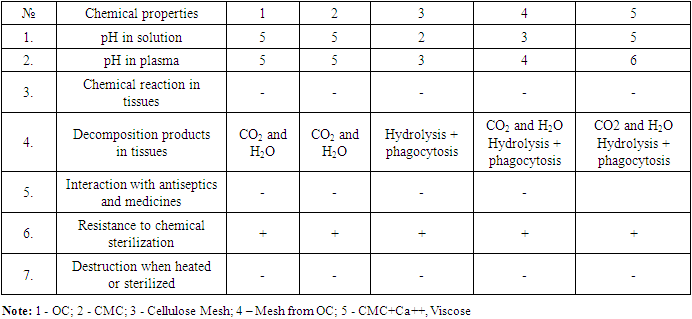
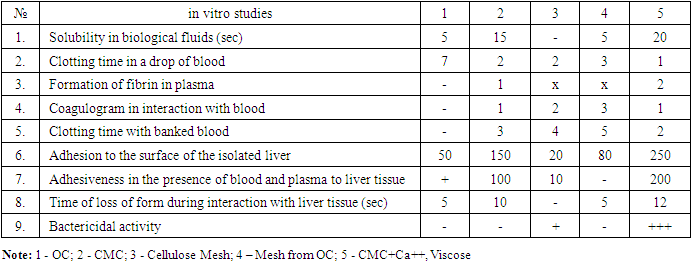
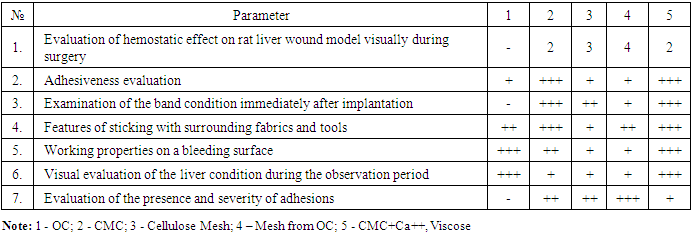
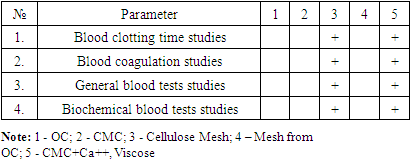
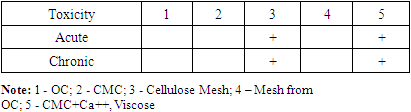
| [1] | Sadykov R.A., Ismailov B.A., Kim O.V. A new band coating from cellulose derivatives for local hemostasis. In Russian // News of surgery.2019. №3. URL: http://985.so/b0v0e. |
| [2] | Holcomb J.B., Moore E.E., Sperry J.L., Jansen J.O., Schreiber M.A., et al. Evidence-Based and Clinically Relevant Outcomes for Hemorrhage Control Trauma Trials. Ann. Surg. 2021; 273: 395. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000004563. |
| [3] | Kalkwarf K.J., Drake S.A., Yang Y. Bleeding to Death in a Big City: An Analysis of All Trauma Deaths from Hemorrhage in a Metropolitan Area during 1 Year. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020; 89: 716-722. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000002833. |
| [4] | Pourshahrestani, S., Kadri N. A., Zeimaran, E., Towler, M. R. Well-ordered mesoporous silica and bioactive glasses: promise for improved hemostasis. Biomaterials Sci, 7(1): 31-50 (2018). doi: 10.1039/c8bm 01041b. |
| [5] | Zhang S, Li J, Chen S, Zhang X, Ma J, He J. Oxidized cellulose-based hemostatic materials. Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Feb 15; 230: 115585. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115585. |
| [6] | Lipatov V.A., Kudryavtseva T.N., Severinov D.A. Application of carboxymethylcellulose in experimental surgery of parenchymal organs/ In Russian // Nauka molodykh (Eruditio Juvenium). -2020. -Vol. 8, №2.- P. 269-283. |
| [7] | Boerman MA, Roozen E, Sánchez-Fernández MJ, Keereweer AR, Félix Lanao RP, Bender JCME, Van Hest JCM. Next Generation Hemostatic Materials Based on NHS-Ester Functionalized Poly(2-oxazoline)s. Biomacromolecules. 2017 Aug 14; 18(8): 2529-2538. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00683. |
| [8] | Khan MA, Mujahid M. A review on recent advances in chitosan based composite for hemostatic dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 2019; 124: 138-47. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.045. |
| [9] | Li D, Chen J, Wang X, Zhang M, Li C, Zhou J. Recent Advances on Synthetic and Polysaccharide Adhesives for Biological Hemostatic Applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Aug 14; 8: 926. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00926. |
| [10] | Mndlovu H, du Toit LC, Kumar P, Choonara YE, Marimuthu T, Kondiah PPD, Pillay V. Bioplatform Fabrication Approaches Affecting Chitosan-Based Interpolymer Complex Properties and Performance as Wound Dressings. Molecules. 2020 Jan 6; 25(1): 222. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010222. |
| [11] | Yin M.L., Wang Y.F., Zhang Y., Ren X.H., Qiu Y.Y., Huang T.S. (2020). Novel quaternarized N-halamine chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol nanofibrous membranes as hemostatic materials with excellent antibacterial properties. Carbohyd. Polym. 232: 115823. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115823. |
| [12] | Belozerskaya G.G., Bychichko D.Yu., Kabak V.A. et al. Creation of new hemostatic coatings of local action based on sodium alginate. In Russian // Clinical physiology of blood circulation. - 2018. - Vol. 15. - № 3. - P. 222-229. |
| [13] | Kholturaev B.Zh., Atakhanov A.A., Sarymsakov A. A. Hemostatic films based on carboxymethylcellulose. In Russian // Universum: chemistry and biology: electron. scientific. Journal /. 2021. 9(87). |
| [14] | Gu BK, Park SJ, Kim MS, et al. Fabrication of sonicated chitosan nanofiber mat with enlarged porosity for use as hemostatic materials. Carbohydr Polym 2013; 97: 65-73. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.060. |
| [15] | Jiang X, Wang Y, Fan D, Zhu C, Liu L, Duan Z. A novel human-like collagen hemostatic sponge with uniform morphology, good biodegradability and biocompatibility. // J Biomater Appl. 2017 Mar; 31(8): 1099-1107. |
| [16] | Lan G., Lu B., Wang T., Wang L., Chen J., Yu K., et al. (2015). Chitosan/gelatin composite sponge is an absorbable surgical hemostatic agent. Colloids Surf. B 136 1026-1034. 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.10.039. |
| [17] | Nakielski P., Pierini F. Blood interactions with nano- and microfibers: Recent advances, challenges and applications in nano- and microfibrous hemostatic agents. Acta Biomaterialia, 84, 63–76 (2019). doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.029. |
| [18] | Sung YK, Lee DR, Chung DJ. Advances in the development of hemostatic biomaterials for medical application. Biomater Res. 2021; 25(1): 37. Published 2021 Nov 12. doi:10.1186/s40824-021-00239-1. |
| [19] | Budko E.V., Chernikova D.A., Yampolsky L.M., Yatsuk V.Ya. Local hemostatic means and ways of their improvement/ In Russian // Russian med.-biol. vestn. named after. akad. I.P. Pavlov. 2019. №2. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/mestnye-gemostaticheskie-sredstva-i-puti-ih-sovershenstvovaniya. |
| [20] | Lempert A.R., Belozerskaya G.G., Makarov V.A. et al. Hemostatic activity of a new compound based on fibrin monomer during intravenous administration in the experiment // Experimental and clinical pharmacology. - 2018. - Vol. 81. - № 11. - P. 14-17. |
| [21] | Chen Y, Qing J, Chang Q, Zhao Y, Jing Y, Ding J, Guo H. Preparation and evaluation of porous starch/chitosan composite crosslinking hemostatic. European Polym. J. 2019; 118: 17-26. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.039. |
| [22] | Hazra C., Kundu D., Chatterjee A. Stimuli-responsive nanocomposites for drug delivery. In: Inamuddin A.A.M., Mohammad A., editors. Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery. 1st ed. Elsevier Inc; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. pp. 823-841. |
| [23] | Jiang X, Wang Y, Fan D, Zhu C, Liu L, Duan Z. A novel human-like collagen hemostatic sponge with uniform morphology, good biodegradability and biocompatibility. // J Biomater Appl. 2017 Mar; 31(8): 1099-1107. |
| [24] | Xie Y, Gao P, He F, Zhang C. Application of Alginate-Based Hydrogels in Hemostasis. Gels. 2022 Feb 10; 8(2): 109. doi: 10.3390/gels8020109. |


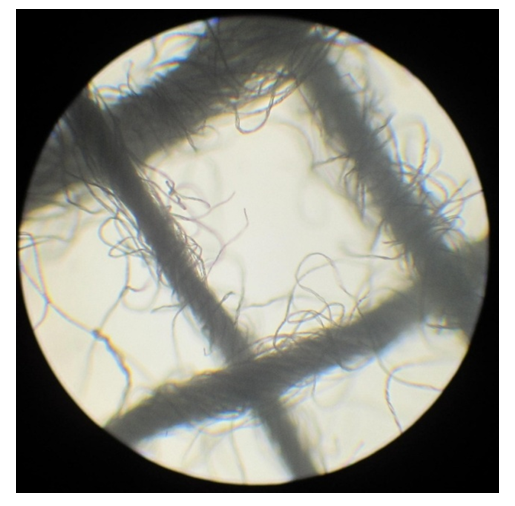

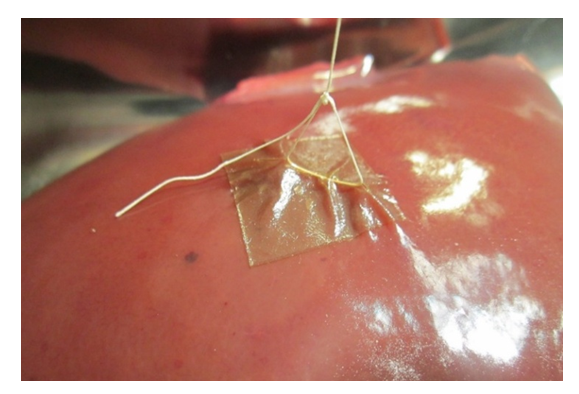
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML