-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(10): 1068-1073
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221210.13
Received: Sep. 25, 2022; Accepted: Oct. 8, 2022; Published: Oct. 21, 2022

The Analysis of Surgical Treatment Results of Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhages
L. B. Maksudova1, B. G. Gafurov2, M. K. Makhkamov1
1Republican Research Center of Emergency Medicine, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Center for the Development of Professional Qualifications of Medical Employees, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The authors carried out a comparative analysis of surgical treatment results of 80 patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). There were 22 females and 58 males. The mean age was 58.8±14.0 years. The results of the study showed that a comprehensive analysis of MSCT morphometric parameters were necessary in order to achieve high rates of 30- and 90-day survival in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. This, in turn, allows the surgeon to choose the optimal and adequate method of surgical intervention in each specific case.
Keywords: Intracerebral hemorrhage, Intraventricular hemorrhage, Surgical treatment
Cite this paper: L. B. Maksudova, B. G. Gafurov, M. K. Makhkamov, The Analysis of Surgical Treatment Results of Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhages, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 10, 2022, pp. 1068-1073. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221210.13.
1. Introduction
- There has been an increase in the prevalence of intracerebral hemorrhages (ICH) in recent years which rank second according to the World Health Organization. The frequency of ICH is on average 20 cases per 100,000 population, the fatal outcome exceeds 40% [27]. There are discussions about the surgical treatment of ICH to this day. Most specialists in this field offer a lot of different types of techniques of surgical treatment. Despite the existing various methods of surgical interventions on improving the treatment results and survival of patients with ICH, the mortality and disability rates with this formidable pathology still remain high [1-6,28]. There are still no clear standards or algorithms for surgical interventions in relation to hemorrhagic stroke. Postoperative mortality in the world's leading ICH surgery clinics reaches 48 – 50% [2,11,15,26]. The high mortality rate is justified by the fact that hemorrhagic stroke is a consequence not only of an isolated cerebral lesion, but also a complication of medically uncontrolled hypertension [16,21,32]. High mortality and disability of patients determine the relevance and detailed study of this issue in the field of ICH surgery.The aim of this research is to study the 30- and 90-day survival in patients with ICH after surgery depending on MSCT morphometric parameters.
2. Material and Methods
- We conducted a retrospective analysis of 80 patients with brain ICH. There were 22 females and 58 (72,5%) males aged 15 to 88 years The mean age was 58.8±14.0 years. All patients were performed neurological examination and assessment of the condition severity according to the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) and the modified Rankin scale (mRs). Evaluation of the consciousness level violation was carried out using the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). After studying the anamnesis and physical examination, all patients were performed a multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT). MSCT-morphometry included the assessment of the following indicators: localization and volume of the hematoma, the presence of a breakthrough of blood into the ventricular system, the condition of the bypass cistern, deformation or expansion of the ventricular system and its sizes, displacement of the median structures of the brain, perifocal edema around the hematoma at its presence and secondary brain changes. We used a modified Graeb scale (mGS) when assessing the spread of intraventricular hemorrhage. The 30- and 90-day survival of patients using the Kaplan-Mayer method was estimated based on the analysis of MSCT-morphometric parameters.
3. Results
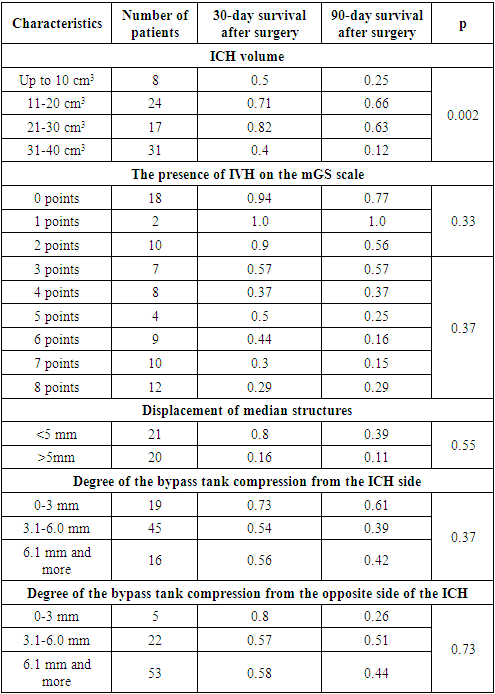
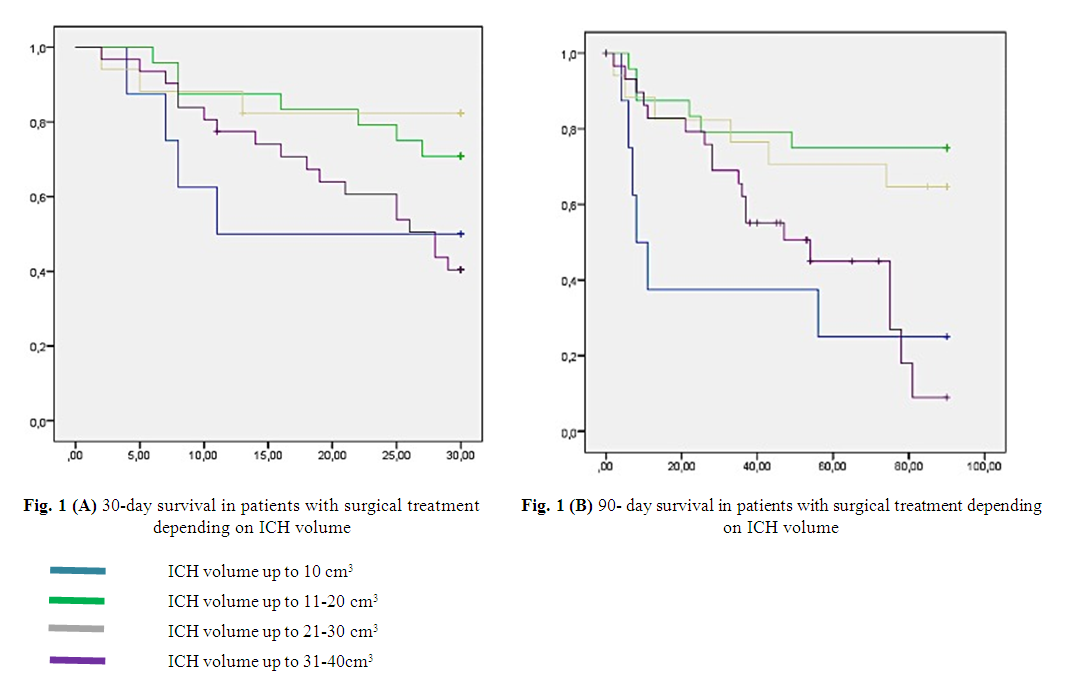
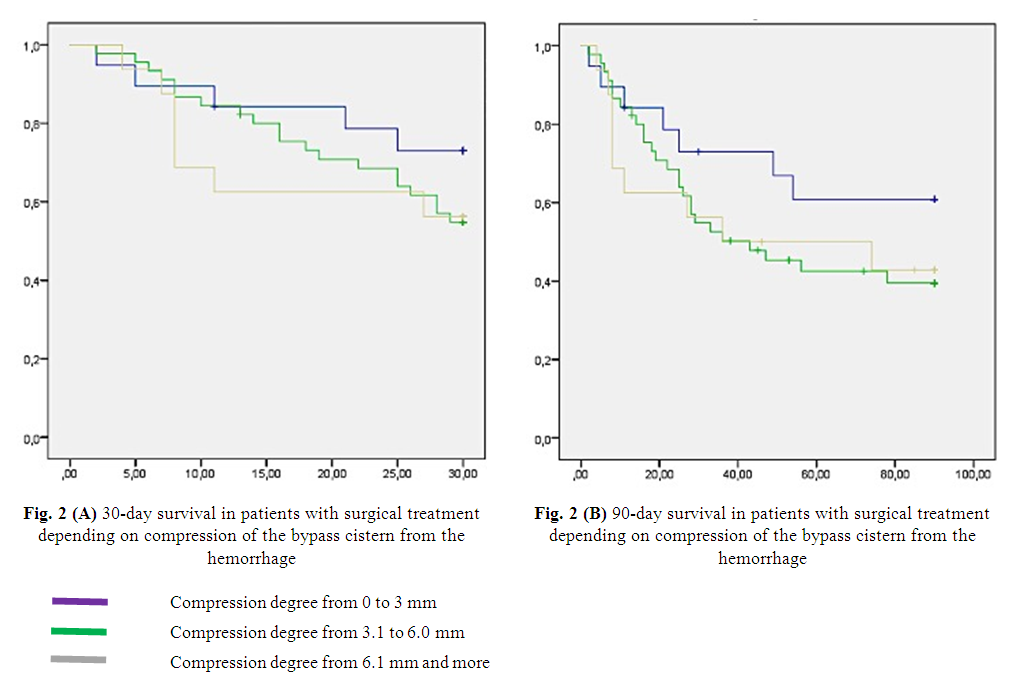
- An analysis of the results of 80 patients showed the following: in 22.5% (n=18) cases, lobar localization of ICH took place, in 13.8% (n=11) cases - medial localization, 15% (n=12) cases - lateral localization, in 10% (n=8) cases - localization in the thalamic area, in 27.5% (n=22) cases - mixed localization and in 11.2% (n=9) cases hemorrhage was diagnosed in the posterior cranial fossa. The analysis of 30- and 90-day survival of patients with ICH showed the following results: in 10% (n=8) cases the ICH volume was up to 10 cm3 (breakthrough into the ventricular system with a high gradation on the mGS scale), in 30% (n=24) cases, the volume of ICH ranged from 11 to 20 cm3: in 9 of them hemorrhage was localized in the posterior cranial fossa, and in the remaining 11 cases there was a medial localization with a breakthrough of blood into the ventricular system with occlusion of the liquor pathways. Endoscopic removal of the ICH was performed in 4 cases with lateral hemorrhage with an ICH volume of 20 cm3. In 21.2% (n=17) cases the volume of ICH ranged from 21 to 30 cm3 and in 51.7% (n=31) cases it varied from 31 to 40 cm3 (Table 1).
|
 | Figure 1 |
 | Figure 2 |
4. Discussion
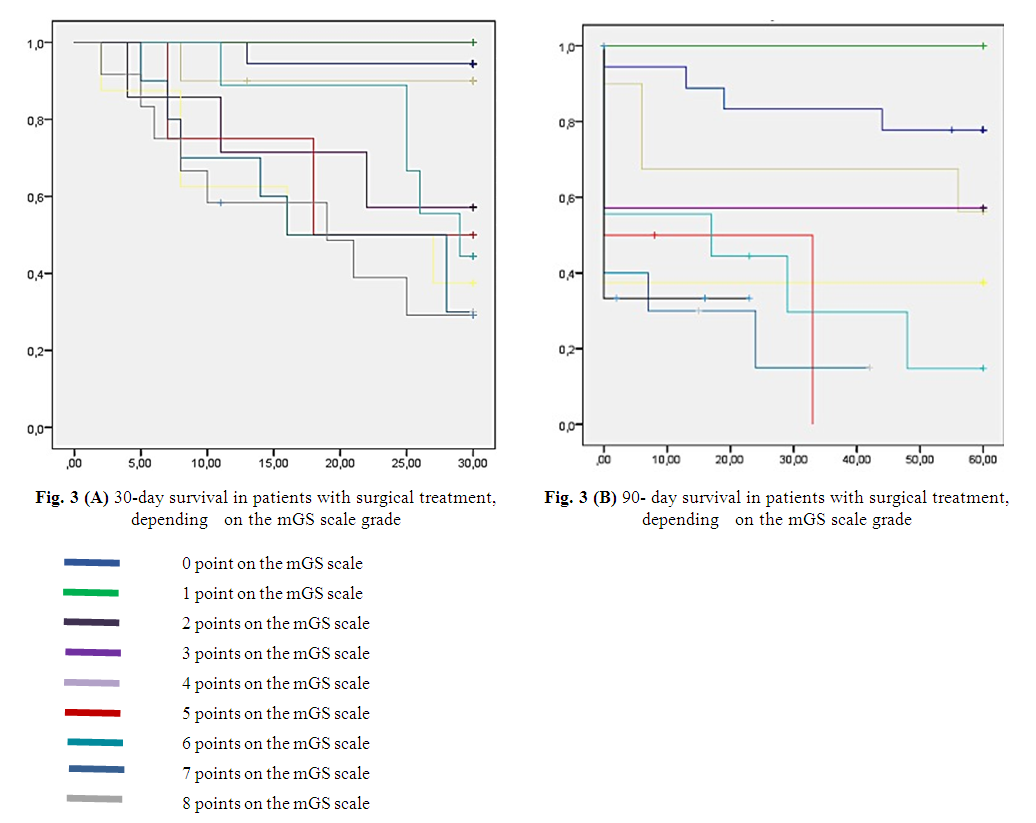
- When analyzing the world literature on the basis of multiple large-scale studies conducted by leading experts in this field, it was noted that one of the main predictors of an unfavorable outcome was IVH as a result of the breakthrough of ICH into the ventricular system of the brain [7,13,20]. It was proved in the STICH study, that intraventricular hemorrhage due to an ICH breakthrough reduced the frequency of favorable outcomes from 31% to 15% [9]. Trifan G et al. in his researches proved that the indicators of the mGS scale were the most important predictors of the treatment outcome in patients with ICH complicated by a breakthrough of blood into the ventricular system. Thus, it was noted in this study that in patients with mGS >5 points, the probability of an unfavorable outcome was high. In patients with mGS <5 points, the probability of a favorable outcome was high [24]. Tuhrim et al. showed in his studies that IVH volume was associated with lower 30-day survival rates [25]. Also Young et al. determined in their studies that an IVH volume >20 ml was a poor prognostic factor [31]. Analysis of the results of 30- and 90-day survival of patients with surgical treatment, depending on the degree of grade according to the mGS scale, showed the following: with zero grade by the mGS scale, 12.8% (n=18) cases were observed (the 30-day survival rate was 0.94); with the first grade by the mGS scale, there was 1.4% (n=2) - the 30-day survival rate was 1.0; with the second grade - (7.1% (n=10)) – 0.9; at the third grade - (5% (n=7)) – 0.57; with the fourth one - (5.7% (n=8)) – 0.37; with the fifth grade - (2.8% (n=4)) – 0.5; with the sixth one - (6.4% (n=9)) – 0.44; with the seventh grade - (7.1% (n=10)) – 0.3; 8.6% (n=12) cases were observed with the eighth grade (30-day survival was 0.29) (Figure 3 A and B).
 | Figure 3 |
5. Conclusions
- Thus, we can conclude based on our study that 30- and 90-day survival rates in patients with ICH who were performed surgery depend on MSCT morphometric parameters: localization of ICH, volume of hemorrhage, degree of intraventricular hemorrhage grade on the mGS scale and the degree of compression of the bypass cistern of the brain. A comprehensive analysis of MSCT morphometric parameters in patients with ICH allows the surgeon to choose the optimal and adequate method of surgical intervention in each case, which in turn increases the survival rates of ICH patients and thereby reduces the degree of mortality. The authors declare no conflict of interest. This study does not include the involvement of any budgetary, grant or other funds. The article is published for the first time and is part of a scientific work.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML