-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(9): 894-896
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221209.08
Received: Aug. 14, 2022; Accepted: Aug. 30, 2022; Published: Sep. 15, 2022

Comparative Study of Lesbochol, Misoprostol, Mukagen on the Intensity of Free Radical Processes of the Gastric Mucosa in Indometacin Gastropathies
Djanaev Yu. Gayrat, Khakimov Z. Ziyovuddin, Allaeva J. Munira, Makhsumov M. Sharofiddin, Zaytseva A. Olga, Mamadjanova A. Munira
Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Djanaev Yu. Gayrat, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The content of acylhydroperoxides and malondialdehyde, as well as the activity of catalase and superoxide dismutase enzymes in the gastric mucosa, were comparatively studied in the model of indomethacin gastropathy in adult rats. It has been established that the mixture of extracts of medicinal plants Lesbohol has a unidirectional effect as misoprostol and mucogen on the intensity of lipid peroxidation and the activity of the antioxidant system in the gastric mucosa when it is damaged by indomethacin and in its activity it is not inferior to the known cytoprotector.
Keywords: Antioxidant system, Gastric mucosa, Gastropathy, Lipid peroxidation
Cite this paper: Djanaev Yu. Gayrat, Khakimov Z. Ziyovuddin, Allaeva J. Munira, Makhsumov M. Sharofiddin, Zaytseva A. Olga, Mamadjanova A. Munira, Comparative Study of Lesbochol, Misoprostol, Mukagen on the Intensity of Free Radical Processes of the Gastric Mucosa in Indometacin Gastropathies, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 9, 2022, pp. 894-896. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221209.08.
1. Introduction
- Gastropathy induced, especially NSAIDs, is an urgent problem due to the frequent, unreasonable use of these drugs, not only as anti-inflammatory drugs, but also as anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics [1,3,4,7,14]. It is considered proven that after a week of using NSAIDs, acute gastritis develops in almost 100% of cases [2,8,13]. Considering the insufficient effectiveness of gastropathy prevention measures, the creation of new means of preventing the stomach is an urgent problem. At the same time, it should be taken into account that damage to the gastric mucosa is quite common under the influence of stress factors [11]. It is considered established that the settlement of free radical oxidation - oxidative stress, is one of the main links in the pathogenesis of the development of most human pathologies, including gastropathy. The formed free radicals damage the biological membranes of cells, from subcellular structures, as a result of which dysfunction of organs and systems is noted. In this regard, it is necessary to use substances with antioxidant properties in order to prevent gastropathy.
2. Materials and Methods
- Experimental studies were carried out on mature male rats with an initial weight of 165-185 g. Five groups of animals were composed, six in each. One day and 2 hours before the reproduction of the gastropathy model, the animals of the first, second and third groups were intragastrically injected with drugs in doses: Misoprostol - 0.2 mg/kg, Lesbochol - 50 mg/kg, Mucogen (rebamipide) - 100 mg/kg, the fourth adequate amount water (control), and the fifth group consisted of healthy animals and served as a control for all the rest (intact). The destruction of the gastric mucosa was reproduced by a single intragastric injection of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) - indomethacin at a dose of 60 mg/kg in saline [8]. When playing "indomethacin" ulcers, rats were deprived of food 24 hours before exposure to the ulcerogen.24 hours after the administration of drugs over the sedimentary part of the gastric homogenate, the products of lipid peroxidation (LPO) and the activity of enzymes of the antioxidant system (AOS) were determined.For biochemical studies, the animals were decapitated under light ether anesthesia in a cold room at a temperature of 0 ± 4°C. The stomach was removed, the proventriculus was removed, the mucous membrane was separated, weighed, then washed with cold saline, crushed and homogenized in a glass homogenizer with a Teflon pestle in 3-4 times the volume of the isolation medium, consisting of 0.25 M sucrose, 0.15 M potassium chloride in 0 ,05M solution of Tris HCl - buffer, pH-8.6 with the addition of 15 units/ml of contrical and 3 units/ml of heparin, which is necessary for the inhibition of proteases and stabilization of the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. In order to precipitate nuclei, mitochondria, and particles of destroyed cells, homogenates were centrifuged at 9000 g for 30 minutes.It is known that increased LPO processes in the cell membrane and subcellular structures contribute to the degradation of membrane phospholipids, and this, in turn, leads to disruption of intracellular homeostasis and inhibition of complex metabolic and synthetic processes inside the cell. The main powerful protective mechanism in the cell, which ensures the regulation of LPO activity, is the antioxidant system. The vital activity of the cell directly depends on the degree of activity of factors that enhance lipid peroxidation and the activity of AOS enzymes. Taking into account the above, to assess the state of lipid peroxidation, we determined the products of lipid peroxidation [acyl hydroperoxide (AcHP), malondialdehyde (MDA)] and the activity of enzymes AOS [catalase (CT), superoxide dismutase (SOD)] in the supersedimentary fraction of the homogenate of the gastric mucosa.The content of ACGP was determined by the method of V.B. Gavrilov et al. [6]. The method is based on the extraction of lipid hydroperoxide with a mixture of heptane-isopropanol in an acid medium, followed by measurement of the optical density with a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 233 nm. The content of ACGP was expressed in relative units per mg of protein. The content of MDA was determined by the method of L.I. Andreeva [5]. The products reacting with thiobarbituric acid were calculated using the molar extinction coefficient of MDA equal to 1.56x105 mol cm and recalculated per mg of protein. QD activity was determined by the method of M.A. Korolyuk [9]. The method is based on the ability of H2O2 to form a stable color with molybdenum salts. The intensity of staining was measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 410 nm. The obtained data were expressed in mmol H2O2/min.mg of protein. SOD activity was determined by the percentage of reduction of nitrotetrazolium blue in an alkaline medium and expressed in arbitrary units (U) per mg of protein [12]. The results of the studies were subjected to statistical processing using the Biostat 2009 software package according to the method of variation statistics with an assessment of the significance of the characteristics M ± m and differences in the considered samples according to the Student's t-test. Differences in the compared groups were considered significant at a significance level of 95% (p<0.05).
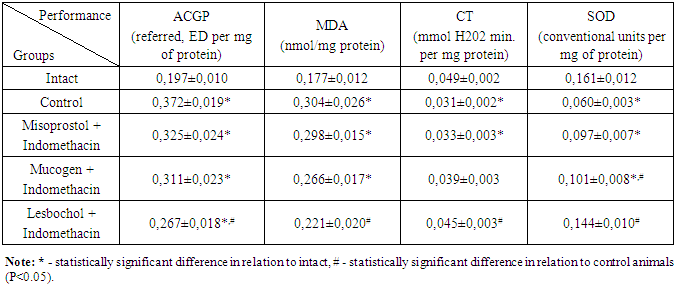
3. Results and Discussion
- The results of the biochemical studies showed that in the gastric mucosa of control animals, compared with healthy ones, the level of ACGP increased by 89.0%, and MDA - 71.7%, which were accompanied by a decrease in CT activity by 36.8%, and SOD - 62.7%. Consequently, the damage to the GM by indomethacin is based on the development of oxidative stress, as indicated by an increase in the level of lipid peroxidation products and a decrease in the activity of AOS protection enzymes.We revealed a different picture of changes in the group of animals that received gastroprotectors preventively. The concentration of ACGP and MDA in the GM under the influence of mesoprostol did not undergo statistically significant changes, although it decreased by 12.6% and 2.0% compared to the control. As can be seen from the data in Table 1, in animals treated with mucogen, these data were 16.4 and 12.5%, respectively, and in animals treated with lesbochol: 28.2 and 27.3%, respectively.
4. Conclusions
- 1. Strengthening of the processes of lipid peroxidation as a result of a decrease in the activity of antioxidant system enzymes is one of the leading causes of the development of gastropathy, under the influence of indomethacin.2. Synthetic analogue of prostaglandin E1 - misoprostol has a distinct antioxidant effect in gastropathy induced by indomethacin.3. Mucogen - stimulating the synthesis of prostaglandins E2 and G1 2 in the gastric mucosa, has a statically significant suppression of LPO processes and increases the activity of AOS, which is the main one in its cytoprotective effect.4. A mixture of extracts of medicinal plants Lesbochol has a unidirectional effect, like misoprostol and mucogen, on the intensity of lipid peroxidation and the activity of AOS in the gastric mucosa when it is damaged by indomethacin, and in terms of its activity it is not inferior to the known cytoprotector.
References
| [1] | Djanayev G. et al. Immobilizаtsiya stressi fonida oq kalamushlarda me’da shilliq qаvatining shikastlanishiga "lesboxol" o‘simlik vositаsining ta'siri: dis. – Tibbiyotning dolzarb muammolariga innovatsion yondashuv C. 20-22, 2022. |
| [2] | Kamada T. et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for peptic ulcer disease 2020 // Journal of gastroenterology. - 2021. - T. 56. - No. 4. - S. 303-322. |
| [3] | Khakimov Z. Z. Effect of Derivatives of Glycyrrhetic Acid on the Intensity of Free Radical Processes During Immobilization Stress // Pioneer: Journal of Advanced Research and Scientific Progress. - 2022. - Vol. 1. - No. 1. - S. 7-12. |
| [4] | Omatsu T. et al. Reactive oxygen species-quenching and anti-apoptotic effect of polaprezinc on indomethacin-induced small intestinal epithelial cell injury // Journal of gastroenterology. - 2010. - T. 45. - No. 7. - S. 692-702. |
| [5] | Andreeva L.I., Kozhemyakin L.A., Kishkun A.A. Modification of the method for determining lipid peroxides in the test with thiobarbituric acid. // Laboratory business. - 1988. - No. 11.- P.41-43. |
| [6] | Gavrilov V.B., Mishkorudnaya M.I. Spectrophotometric determination of the content of lipid hydroperoxides in blood plasma. // Laboratory business. - 1983. - No. 3. - P.33-35. |
| [7] | Dzhanaev G. Yu., Allaeva M. Zh., Kholmatov Zh. A. Immobilization stress yuli bilan chaqirilgan meda yarasi-da ўsimliklar kuruқ extracts yiғmasining samaradorligini ўrganish: dis. – ‘‘Uzbekistonda Milliy Tadqiqotlar: Davriy Anzhumanlar:’’, 2022. |
| [8] | Drozdov VN Gastropathy caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: pathogenesis, prevention and treatment // Gastroenterology. Supplement to Consilium Medicum. - 2005. - no. 1. - P. 3-6. |
| [9] | Korolyuk M.A., Ivanova L.I., Maiorova I.G., Tokarev V.E. Method for the determination of catalase. // Laboratory business. - 1988.- No. 1.- P.12-15. |
| [10] | Lorents S.E., Zharikov A.Yu., Bobrov I.P. et al. Gastroprotective effect of the peptide complex from porcine kidney tissues in experimental "indomethacin" ulcer in rats. // Siberian scientific medical journal. -2017. -No. 6. -C. 5-9. |
| [11] | Morozova O. Yu. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: damaging effect on the gastric mucosa and methods of protection against their ulcerogenic effects // Integrative Physiology. - 2021. - Vol. 2. - No. 4. - S. 390-398. |
| [12] | Mkhitaryan V.G., Badalyan G.E. Determination of superoxide dismutase activity. // Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. - 1978. - No. 6. - S.7-11. |
| [13] | Samodelkin E. I. et al. Modeling of NSAID gastropathy in an animal experiment // Agrarian Bulletin of the Urals. – 2010. – no. 11-1(77). - S. 36-38. |
| [14] | Usmanova Sh. Influence of some α-APF, omeprazole, Cytotec and their combinations on the processes of oxidative stress in the gastric mucosa in indomethacin-induced gastropathy // Journal of Problems of Biology and Medicine. – 2018. – no. 2.1 (101). - S. 118-120. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML