-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(9): 863-868
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221209.02
Received: Aug. 21, 2022; Accepted: Sep. 6, 2022; Published: Sep. 9, 2022

Relatival Description of Kidney Morphometric Parameters in Polypharmacy of Anti-Inflammatory Pills
Mustafoev Z. M. 1, Teshaev Sh. J. 2
1Department of Human Anatomy, Samarkand State Medical University, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The urinary system is the first to respond to various internal and external influences. Therefore, scientific studies are being conducted to study the reaction of the kidneys to various internal influences. Although they are held less frequently today, they remain relevant to this day. The main task of the urinary system is to protect the body from foreign factors and chemical influences and to control the stability of the body's internal environment. This function is performed by natural and adaptive mechanisms.The urinary system can be considered a complex of organs, which is responsible for the stability of the internal environment of the body, and also protects the body from pathogenic factors. The kidney is an organ that ensures adaptation of the body under the influence of various damaging exogenous factors during human life.
Keywords: Urinary system, Pathogenic factors, Protective functions, Exogenous and endogenous influences
Cite this paper: Mustafoev Z. M. , Teshaev Sh. J. , Relatival Description of Kidney Morphometric Parameters in Polypharmacy of Anti-Inflammatory Pills, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 9, 2022, pp. 863-868. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221209.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Kidneys are complex organs that remove waste products from the blood by producing urine. In addition, the kidneys perform other vital functions, including maintaining homeostasis, blood pressure, osmotic pressure, and acid-base balance.In connection with the rapid development of nephrology and kidney transplantation, the interest of morphologists to study the structure of the kidney as an important organ of the urinary system is constantly increasing.At the moment, diseases of the urinary system are increasing in the world, and many researchers point out that the main reason for the increase in the number of diseases is environmental pollution, which leads to the violation of the protective functions and adaptive reserves of the human body. The kidney is a very vulnerable organ to exogenous and endogenous influences. Morphological changes in this body as a result of exposure to various substances of a physical, chemical and biological nature, as well as the effects of stress and severe pathological conditions, hypergravity and ionizing radiation have been widely studied.Any disturbances resulting from one or another cell damage lead to the breakdown of the kidney protective barrier and, as a result, the development of toxemias, which leads to a violation of homeostasis.The high sensitivity of the kidney to the influence of various factors, its ability to be the first in the body to react positively with adaptive changes in cell architecture and morphological regeneration has already been proven in the experiment.Important results obtained in many studies devoted to the study of kidney structures expands its role and importance in every way.Despite the existence of publications on polypragmasy and their effects on the urinary organs, the unusual sensitivity of the kidneys to extreme factors has not been sufficiently defined and studied.All this, of course, complicates the correct interpretation of the functional significance of kidney elements in normal and pathological terms.There is no clear understanding of the rules of formation of the kidney structure at different ages, the structural basis of the reaction of the vascular-tissue structures of the kidney of animals when polypharmacy is used.The relevance and necessity of studying these problems is very clear, because revealing the adaptive mechanisms and morphological bases of the urinary system allows to determine very important points - morphological and functional characteristics at different ages, inter-organ and interactive periods.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are one of the most widely used drug groups in medicine. The advantage of these drugs is their complex effect (antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and pain reliever), as well as a wide range of possible indications. The drugs used in our experiment are 5 types of anti-inflammatory drugs that are common and frequently prescribed by doctors, and they belong to the same group according to their pharmacodynamic effects. However, the data available today on the results of treatment with these drugs do not allow us to make clear conclusions about their effectiveness or ineffectiveness, as well as the development of side effects in such combinations.The side effects of these agents are naturally associated primarily with damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and the urinary system. Not including polypragmasia, that is, long-term uncontrolled intake of any drugs with anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving, hormonal effects can lead to structural damage of kidney nephrons. At the same time, the information presented in the literature about the toxic effect of these drugs on the kidneys is somewhat contradictory. Thus, there are also cases where damage to the kidney nephrons caused by taking anti-inflammatory drugs leads to the development of life-threatening situations, poisoning of the body and a decrease in its adaptive response. Today, a large number of drugs are created and used in practical health care, which, on the one hand, improve the patient's condition to a certain extent, but on the other hand, seriously harm the health. The desire to increase the effectiveness of treatment, to help the patient get rid of all the diseases that have developed in him inevitably leads to prescribing a large number of drugs - polypharmacy. Currently, polypharmacy as a result of iatrogenicity is a serious health problem, as it is clinically manifested by a decrease in the effectiveness of pharmacotherapy and the development of serious adverse reactions to drugs, as well as a significant increase in health care costs.At the moment, in Uzbekistan, active work is being done to reduce the incidence of polyphragmosis in medical practice in the field of health care. Decision of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan No. PQ-4554 of December 30, 2019 "On additional measures to deepen reforms in the pharmaceutical sector of the Republic of Uzbekistan", Decree of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan No. 191 of June 18, 2010 "Prescription of drugs and treatment by the patient- Order "On approval of the regulation on the procedure for receiving, storing and using drugs in preventive institutions, as well as the procedure for providing drugs to the population by prescription in pharmacies" (registered in the Ministry of Justice on June 29, 2010 with No. 2118). among them.Our study was devoted to determining the morphometric characteristics of the kidney of 5-month-old white rats under the influence of anti-inflammatory drug (IAD) polypharmacy.During the years of independence, fundamental changes were made in the healthcare system of our country, special attention was paid to early diagnosis of diseases from various sources and reduction of negative consequences.The purpose of the study. Study of changes in kidney morphometric parameters in conditions of polypharmacy of anti-inflammatory drugs.Research tasks:1. To study changes in the morphological parameters of five-month-old white rat kidneys in the norm, as well as when using anti-inflammatory drugs separately.2. To determine the morphological parameters of the kidneys of five-month-old white rats and the changes in the morphometric parameters of the kidney structural structures when two, three, four and five types of anti-inflammatory drugs are used simultaneously.3. To study the morphometric parameters of kidney nephrons of five-month-old white rats in the norm, as well as the morphometric changes caused by the simultaneous use of two, three, four and five types of anti-inflammatory drugs.Research object. The study was conducted on 250 5-month-old inbred white rats. They were kept in normal vivarium conditions. According to the study, all experimental animals were divided into 5 comparable groups. 5 types of anti-inflammatory drugs were used in polypharmacy in different combinations.
2. Materials and Methods of Research
- Experimental, histological, morphological, morphometric, and statistical methods were used to conduct the research and achieve the goal.Scientific novelty of the research.- for the first time, it was found that polypharmacy of anti-inflammatory drugs in 5 combinations has different negative effects on the structural structure of the kidneys of white rats;- it was proved that these structural changes in the organs of the urinary system lead to deep disturbances in the processes of growth and formation of blood vessels and tubules of the kidney nephron, which revealed a decrease in the density of nephrons in the kidney tissue and a high variability of the diameter of nephron elements;- when using more than three anti-inflammatory drugs at the same time, the negative effects of polypharmacy increase significantly. The rate of formation of the structural and functional zones of the kidneys, the activity of their cells and the decrease in the morphological parameters of the studied nephron structures of the kidney were analyzed;- using modern morphological research methods (organometric, histological, histomorphometric, statistical), new information was obtained directly about the characteristics of the morphological reactions of the kidney cortex. The identified changes at the tissue, cellular and intercellular levels were characterized by hypotrophic and hypoplastic changes in rat kidney structures.Practical significance of research. The results of the study of macro- and microscopic changes in kidney formations against the background of polypharmacy help to choose the right number of drugs and to determine the interaction of drugs with similar pharmacodynamics.The study of the morphological structural changes of the kidney under the influence of two or more drugs allows to create the most important combinations of these drugs.The obtained information serves to develop scientific bases for improving the condition of patients suffering from pain syndrome, musculoskeletal system problems, and inflammatory diseases.
3. Research Results and Discussion
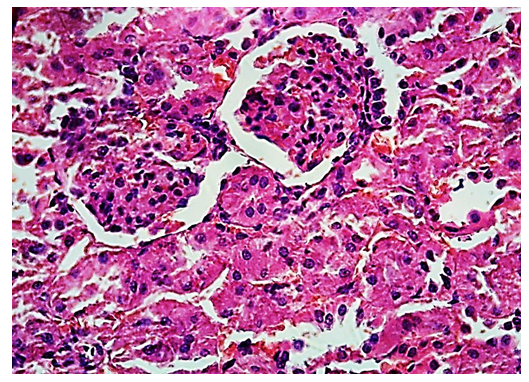
- The results of the research were introduced into the educational process of the departments of pharmacology and clinical pharmacology, pathological anatomy, and pathological physiology of the Samarkand State Medical Institute, as well as the work of doctors of polyclinics of the city of Samarkand.The kidney performs many functions. It participates in almost all types of metabolism and maintains body homeostasis. Thus, the kidney is an important link in the formation of adaptive reactions to various external influences or diseases caused by other organs and systems.The kidney and its structures have been studied by scientists for centuries. To date, many issues such as development of organ layers in interaction, development of vessels, innervation apparatus, topography, histogenesis and morpho-biological and morpho-biochemical changes of this organ have been studied.According to scientists, the kidney is not only a member of the urinary system, but also an active component of the endocrine system. Researchers have proven that many endocrine hormones are produced by the kidneys. In the kidneys, there are receptors in certain areas, the nature of their excitation affects the regulation and control of the body.In mammals, the kidney is a bean-shaped organ, covered with a smooth, shiny capsule, the gate is clearly visible on the medial surface, and no other pathological or altered macroscopic abnormalities are visible to the eye.Since all populations of nephrons have parallelism of age-related changes, the kidney body is represented by a vascular ball and is surrounded by a ball capsule. Proximal convoluted tubules are covered with cylindrical epithelium, located in a row on the basement membrane, and their apical and basal poles are clearly visible. The cavity of the canals is clearly visible, its shape and diameter depend on the flatness and thickness of the histological section. On the inner surface of the canals, in some cases, single-cell elements are identified. With a higher magnification method, the brush-like part on the apical surface of the epithelial cells and the blurring of the cytoplasm in their basal part are revealed.Distal tubules are composed of bundles of cuboidal epithelial cells, which lie on the basement membrane and do not have a brush-like part on the apical surface. Due to the absence of a brush-like part and the low thickness of the epithelium, the space of the distal tubules is larger than the space of the proximal tubules.It is known from ultrastructural examinations that the vascular ball of the kidneys is enclosed in a two-layered capsule with an outer and an inner part. The outer part of the capsule is covered from the inside with one-layer flat epithelial cells.The interior of the capsule of the ball is lined with podocytes, which are numerous branched-looking islets that resemble legs. Podocytes are located in the basement membrane of the capillary capillaries and are in constant contact with each other. There is an oval-shaped nucleus with fine granular chromatin, which protrudes from the large cell body into the capsule. The cytoplasm of podocytes is transparent. A large number of ribosomes are detected in the granular endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi complex is well developed and consists of a small number of small mitochondria. Several large protrusions-cytotrabeculae stand out from the cytoplasm. They contain high-density fibrils and microtubules. The outgrowths extend along the nearby small vessels, giving rise to numerous secondary small and slender pedicle-like outgrowths, known as cytopodia. The cytoplasm of the cytopodium is very dense. They have long fibrils attached to the basement membrane. The inner sheet of the capsule and the capillary wall of the ball have a common three-layer basement membrane and form a filtration barrier. There are filtration spaces between the cytopodia, which communicate with the capillaries of podocytes and cytotrabeculae and the narrow subpodocytic space between them. Proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells have a brush-like part represented by a large number of closely related cytoplasmic microvilli in the apical part. At the bottom of the microvilli, small-sized invasions containing medium-density substance penetrating into the cytoplasm to various depths are identified. In the basal part of the proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells of the nephron, there are many mitochondria located parallel to each other and perpendicular to the basal membrane of the cell in the recesses of the basement membrane.The conducted histomorphometric studies showed that the diameter of the proximal convoluted tubules in newborn white rats in the 1st (control) group of the experiment ranged from 9.50 μm to 12.36 μm, with an average of 10.75 ± 0.09 μm, and the diameter of their cavity - an average of 3.12 ± 0.05 μm to 5.68 ± 0.07 μm, 4.40 ± 0.05 μm.In the morphometric study of the parameters of the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys in newborn white rats of the 1st (control) group of the experiment, an increase in all studied parameters was observed.Accordingly, the diameters of the distal convoluted tubules ranged from 12.17 μm to 12.95 μm on average, with an average of 12.54 ± 0.13 μm, the diameter of the space of the distal convoluted tubules - from 6.14 ± 0.06 μm to 7, up to 28 ± 0.09 μm, with an average of 6.67 ± 0.06 μm.Renal cortical layer of nephrons is characterized by parenchyma of different structures, stroma represented by blood vessels and connective tissue elements.Renal nephrons (subcapsular, cortical and supraglomerular) have a typical structure and are represented by renal corpuscles, as well as convoluted and straight tubules.Since it has been proven that there are parallel age-related changes in all populations of nephrons, to describe in detail below, we dwelled more deeply on the study of the structure of a large number of nephrons in the cortical layer.The kidney body of the nephron is represented by a vascular ball and a ball capsule surrounding it (Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule) (Fig. 1).
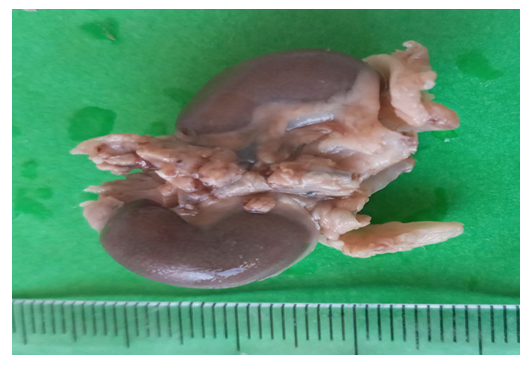 | Figure 1. Kidney length of 5-month-old rats of the control group. Magnified 2.5 times |
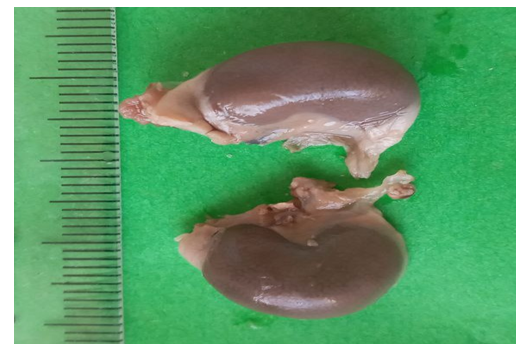 | Figure 2. Kidney width of 5-month-old control group rats. Magnified 2 times |
4. Conclusions
- 1. Polypharmacy of anti-inflammatory drugs had a negative effect on the parameters of kidney structures. It was found that the area of the renal corpuscle (up to 6.23%), the area of the renal capsule cavity (up to 12.36%), and the area of the renal corpuscle (up to 7.04%) decreased.2. Under the influence of polypragmasy, the renal nephron proximal convoluted tubules (up to 8.27%) and distal convoluted tubules (up to 8.77%), as well as the diameter of their cavities (up to 16.97% and 8.77%) decreased indicators were observed.3. In polypragmasy rats, the initial parameters describing the structural and functional state of nephrons underwent negative changes, and it was found that the diameter of the proximal and distal convoluted tubules and their spaces was smaller than the kidney elements of the control group of the experiment.4. Compared with the experimental groups under the influence of polypharmacy of YaQDV, it was observed that the area of kidney corpuscles, the area of the capsule space of the kidney ball, the diameter of proximal and distal convoluted tubules and their cavities decreased in different sizes. These changes in the parameters of the kidneys of experimental animals depended on the number of drugs that the rats received.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML