-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(5): 499-501
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221205.10
Received: April 13, 2022; Accepted: May 5, 2022; Published: May 10, 2022

Prediction of Respiratory Disorders Syndrome in Underweight Children from Mothers with Preeclampsia
Yuldasheva G. G., Mukhamedova Sh. T., Baratov S. S., Abdiyeva N. R., Boboyeva U. F.
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The authors conducted a study to study the cytokine status of underweight children born to mothers with preeclampsia in order to predict the syndrome of respiratory disorders. The main clinical manifestations, methods of respiratory support of RDS syndrome are considered.
Keywords: RDS syndrome, Respiratory therapy, Cytokine status, Preeclampsia, Gestation
Cite this paper: Yuldasheva G. G., Mukhamedova Sh. T., Baratov S. S., Abdiyeva N. R., Boboyeva U. F., Prediction of Respiratory Disorders Syndrome in Underweight Children from Mothers with Preeclampsia, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 5, 2022, pp. 499-501. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221205.10.
1. Introduction
- Preeclampsia still remains an extremely important problem, as it can often lead to an increase in maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality [3,4]. The frequency of preeclampsia ranges from 7 to 16% and has no tendency to decrease [1,5]. The risk of perinatal mortality in this complication of pregnancy increases 5-fold and ranges from 10.0 to 30.0%o, the perinatal morbidity is 463.0-780.0 per 1000 [2]. Perinatal morbidity and mortality in preeclampsia are caused by prematurity (30%), chronic hypoxia (40%), intrauterine fetal growth retardation (30%) [8,11]. Preeclampsia accounts for 15% of the causes of premature birth [12]. The most important criterion for the complicated course of preeclampsia is the multiple organ lesion. The disease is characterized by a pronounced violation of fetal-uterine blood flow as a result of insufficient depth of cytotrophoblast invasion and inadequate placentation against the background of a conflict between pressor and idepressor factors of vascular tone reduction, as well as increased platelet aggregation. The basis for the formation of pathological placental circulation is a violation of angiogenic, atrombogenic and other functions of endotheliocytes. At the same time, proinflammatory and prothrombogenic changes lead to the appearance of areas of ischemia /reperfusion of the placenta and, under the influence of hypoxia, form a whole complex of aggressive factors affecting the fetus. It has been proved that if the adaptive and compensatory reserves of the fetus are preserved before childbirth, then the outcome of childbirth for the fetus is physiological, but if there is a lack of these reserves, then losses in fetal health are unpredictable [6,10]. According to WHO, every fifth child born to a mother with preeclampsia has some degree of impairment of physical and psycho-emotional development, the incidence is significantly higher in infancy and early childhood. In this group of children, respiratory disorders are 10 times more likely to develop, intrauterine infections are 8 times more likely, asphyxia is 3.5 times more common.Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality (25%) of premature newborns. The frequency of RDS in children born prematurely ranges from 35 to 65% with a gestation period of 30-34 weeks, in premature infants with a gestation period of more than 34 weeks, the frequency is less than 5%. The syndrome of respiratory disorders (RDS) of a newborn presents respiratory disorders in children in the first days of life due to primary surfactant deficiency and immaturity of the lungs. The main causes of RDS in newborns are impaired synthesis and excretion of surfactant by type 2 alveolocytes associated with functional and structural immaturity of lung tissue, as well as congenital qualitative defect of the surfactant structure. Predisposing factors for the development of RDS that can be identified before the birth of a child or in the first minutes of life: the development of RDS in siblings, gestational diabetes and type 1 diabetes mellitus in the mother, hemolytic fetal disease, premature placental abruption, premature birth, male fetal sex during premature birth, caesarean section before the onset of labor, asphyxia of a newborn. DN is characterized by the following clinical signs: cyanosis, tachypnea, swelling of the wings of the nose, difficulty exhaling, sinking of the pliable places of the chest, weakening of breathing during auscultation of the lungs [7,9]. In addition to clinical signs, respiratory insufficiency is laboratory manifested by respiratory acidosis, hypoxemia and hypercapnia.The purpose of the study was to study the cytokine status in the first day after birth in the blood of premature newborns with respiratory disorders born from mothers with preeclampsia.
2. Materials and Methods
- On the basis of the Bukhara State Medical Institute in the department of neuro-resuscitation of the regional perinatal center, a comprehensive clinical and laboratory examination of 60 premature newborns born at gestation from 28-36 weeks was conducted. All the examined newborns were divided into the following groups: 1 group of 30 newborns born to mothers with preeclampsia, 2 group of 30 whose real pregnancy and childbirth proceeded physiologically. For immunological studies (IL-6, IL-8), venous blood was taken from the umbilical vein immediately after the birth of the child, urine was collected (IFNa, IFNy) during the first day.
3. The Results of the Study
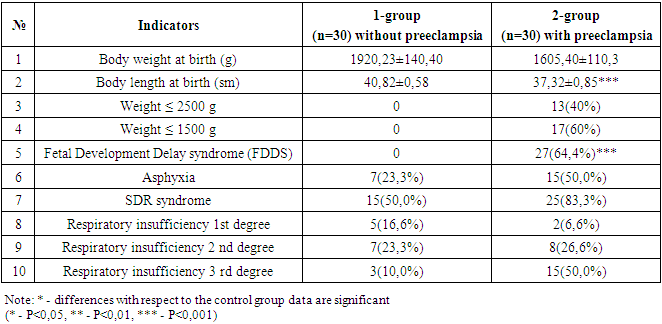
- Newborns born to women with preeclampsia and arterial hypertension had significantly lower birth weight and body length compared to children of the control group (p<0.0001) (table 1).
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
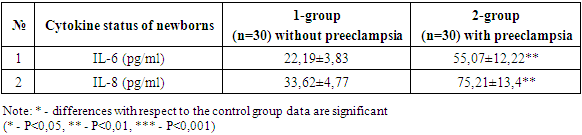
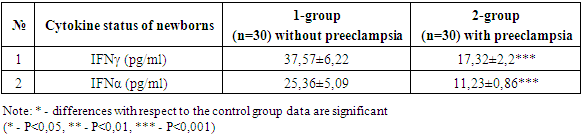
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) is more common in underweight children from mothers with preeclampsia. The need for respiratory support and the duration of its use are significantly higher in the group of premature infants with very low body weight born to women with preeclampsia. The need for surfactant administration depended not only on the degree of morpho-functional maturity of the lung tissue in a premature baby, but also on the presence of preeclampsia in the mother, so surfactant therapy was significantly more often used in newborns from women with preeclampsia. The functional state of underweight children depends not only on morpho-functional immaturity, but also on the presence of preeclampsia in the mother. The level of IL-6, IL-8 in the blood serum of newborns from mothers with preeclampsia was increased, indicating the presence of a systemic inflammatory response syndrome and a high risk of neonatal sepsis. A decrease in the level of IFNy and IFNa is associated with a low concentration capacity of the kidneys in preterm infants.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML