Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Dehonov Aziz Toshpulatovich, Gaziev Karim Umarovich, Khamdamov Ilkhom Bakhtiyorovich, Khakimboyeva Kunduz Askar Kizi
Bukhara State Medical Institute, Republic of Uzbekistan, Bukhara
Correspondence to: Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Republic of Uzbekistan, Bukhara.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Comparative characteristics of the parameters of the immune system of T- and B-lymphocytes showed the presence of an imbalance and tension in the immune system of patients with wound infection on the background of diabetes mellitus, which indicates the development of a systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome and the occurrence of gross immunological rearrangements reflected in the significant activity of lymphocytes with markers of early activation (CD25+ cells) and the readiness of cells to apoptosis (CD95+ cells), as well as natural killers (CD16+ cells). In patients with wound infection on the background of DM, in comparison with healthy people, it was shown that the content of all studied immunocompetent cells was significantly increased. This fact indicates that all lymphocytes are activated and the immune system is tense, which is associated with a sufficiently high number of pathogens in the focus and the development of systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (SIRS) in patients, which in our opinion aggravates the course of the wound process.
Keywords:
Immune profile, Wound infection, Diabetes mellitus
Cite this paper: Khamdamov Bakhtiyor Zarifovich, Dehonov Aziz Toshpulatovich, Gaziev Karim Umarovich, Khamdamov Ilkhom Bakhtiyorovich, Khakimboyeva Kunduz Askar Kizi, Characteristics of the Immune Profile in Wound Infection in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 4, 2022, pp. 432-436. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221204.13.
1. Relevance
The development of purulent-inflammatory process in soft tissues is associated with the formation of hemorheological disorders. Their particular severity occurs in the presence of a systemic reaction syndrome to inflammation [1,6,8]. Correction of hemorheological deviations is realized through a complex effect, including surgical treatment of a purulent focus, as well as antibacterial and detoxification therapy.The systemic inflammatory response to infection or sepsis was probably similar to the systemic inflammatory response to a group of various injuries and injuries, such as burns, injuries, etc. Scientists' attention is focused on developing effective strategies to reduce excessive inflammatory response in patients and obtain improved results [2,3].Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) indicates inflammation outside the infected area that runs throughout the body. It is determined by comparing two or more of the four abnormal representations of body temperature, pulse rate, respiratory rate and the number of white blood cells. The SIRS presentation is defined as the most severe degree of infection of various sites, suggesting higher risks of shock or mortality [4,14,16].In patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, purulent-necrotic soft tissue diseases occur about five times more often. At the same time, they are characterized by a special severity of the course, unlike in patients who do not suffer from diabetes mellitus [5,7].It has been established that wound infection in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) leads to various complications, including the development of systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (SIRS), which negatively affect the results of treatment of this category of patients, often leading to organ dysfunction [5,12]. As is known, wound infection of various etiologies and localization is characterized by the presence of immunodeficiency in the T-link of immunity, an imbalance of humoral protection indicators, pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines [4,12,16]. At the same time, great importance is also attached in the literature to the study of the systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (SIRS), which is a universal generalized response of the body to various damaging effects, including systemic and local infection, and is caused by the release of inflammatory mediators into the circulatory channel [3,7,8,18]. The manifestations of CVD in patients with wound infection involving a large mass of muscle tissue, fascia, bone structure, in fact, determines the severity of the course of the disease, contributes to the occurrence of gross immunological rearrangements that lead to the development of CVD, while closing the vicious circle that arises [9,10,11,13,15].An integrated approach to assessing the immune status in such patients was carried out extremely rarely, therefore, we found it expedient to analyze the results obtained to determine the parameters of the immune system of sick and healthy individuals in a comparative aspect.
2. The Purpose of the Study
Study and evaluation of the immune system indicators of patients with wound infection on the background of diabetes mellitus in comparison with the data of healthy individuals.
3. Material and Methods
153 patients with purulent-necrotic soft tissue lesions (abscesses, phlegmons, beneficial phlegmons, carbuncles) on the background of diabetes mellitus were involved in the research, of which 97 men (63,3%) and 56 women (36,7%). At the same time, systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome was detected in all the studied patients. Of all the examined patients, 42 were urban residents (27,4%), and 111 people were villagers (72,6%). The average age of the examined patients was 54±17.5 years. The control group consisted of 30 healthy individuals, whose sex and age composition was almost the same as the patients. To carry out immunological parameters, blood was taken from the ulnar vein into a centrifuge tube treated with 5.0 ml heparin. We selected 10 µl for counting leukocytes and lymphocytes on the Goryaev chamber with the help of Zadorozhny S.I. and Dozmorov I.M. paint (1987).Mononuclear cells from peripheral blood were obtained by isolation on a density gradient of ficoll-verografin with a density of 1.077g/l according to Boyum (1968). The number of cells was counted in the Goryaev chamber by the conventional method under a microscope and the concentration of lymphocytes was adjusted to 2x106 in 1 ml, the viability of lymphocytes was determined in a test with 0.1% trypan blue.The assessment of the state of the immune system of the body of patients and healthy was carried out by the expression of CD-differentiation and activation antigens. The following markers of immunocompetent cells were determined: CD3+-, CD4+-, CD8+-, CD16+-, CD20+-, CD23+-, CD38+-, as well as CD25+-, CD95+-lymphocytes. CD receptor expression was carried out in the rosette formation reaction using monoclonal antibodies of the LT series manufactured by Sorbent LLC (RF) according to the method of Garib F.Yu. et al. (1995).Determination of the serum concentration of the examined immunoglobulins of the main three classes M, A and G was carried out by the method of radial immunodiffusion according to Mancini (1963).All studies were conducted in the Department of purulent surgery of the Bukhara Regional Multidisciplinary Medical Center and at the Institute of Human Immunology and Genomics of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan.The results of the studies were processed by the generally accepted method of variation statistics. A software package for biomedical research was used. The principles of evidence-based medicine were used in the organization and conduct of research.
4. Results and Discussion
The obtained results showed that if a 2.0-fold increase in the number of leukocytes in patients with wound infection (14300 ±50x109 /l) compared to healthy individuals (6300±75x109 /l) was a manifestation of the inflammatory process in the body, then a decrease in the relative and absolute number of lymphocytes (respectively 21,14 ± 1.50% and 2700 ± 170mcl) it indicated a decrease in the resistance of the body of these patients (table 1).Table 1. Comparative indicators of cellular immunity of patients with diabetic foot syndrome with signs of critical ischemia of the lower extremities and healthy individuals, М±m
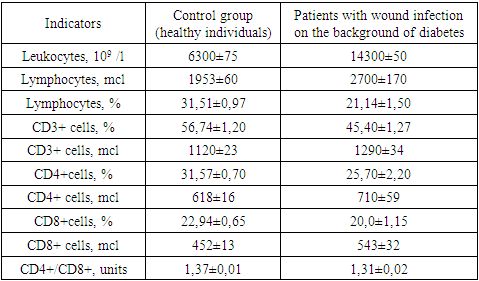 |
| |
|
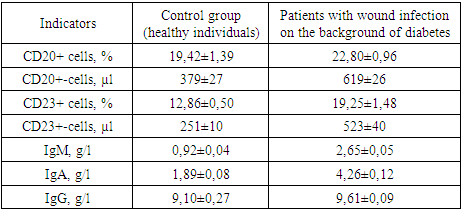
The study of the relative and absolute number of lymphocytes carrying differentiating CD3+ markers (T-lymphocytes) on their surface showed that they changed in different directions with respect to the control data. If the relative number of CD3+ cells is 1.3 times significantly reduced in relation to healthy data (respectively 56,74± 1.20% vs. 45,45± 1.27%, P<0.05), then the absolute number of these cells were significantly increased in relation to the norm by 1.1 times (respectively 1290 ±34 µl vs. 1120±23 µl). That is, T-immunodeficiency was established in patients with wound infection on the background of DM. Next, we studied the main subpopulations of T-lymphocytes - T-helper/inducers (CD4+ cells) and T-suppressors/cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD8+ cells).The trend and direction of changes in the relative and absolute number of these subpopulations were the same as in CD3+ lymphocytes, but with different intensity. The deficit of the relative number of CD4+ cells in patients was 1,25-fold in relation to this parameter of healthy individuals - respectively 25,70±2,20% vs. 31,57±0,70% (P<0.05), but the deficit of CD8+ cells was little noticeable - the decrease was 1,1 times (respectively 20,0±1,15% vs. 22,94±0,65%, P<0.05). In both cases, the absolute values, as in CD3+ lymphocytes, were significantly higher than the control values (P<0.05). Against this background, the immunoregulatory index (CD4+/CD8+) was also significantly reduced in patients with respect to the norm – 1,31±0,02 units, respectively, versus 1,37±0,01 units. (P<0.05).A comparative study of the relative and absolute number of T-lymphocytes (CD3+ cells) and their regulatory subpopulations - T-helpers/inducers (CD4+ cells) and T-suppressors/cytotoxic lymphocytes (CD8+ cells) showed that in patients with wound infection against the background of DM, the parameters changed with the same tendency and different directions. The absolute numbers of all cells in patients were significantly increased, but the relative values were significantly reduced in relation to the data of healthy individuals.Considering the fact that in clinical immunology, the activity of the immune system is evaluated by the functional states of the immunocompetent cells examined, the relative number of cells indicates the true state of the immune status. Based on this, we found that the studied patients with wound infection have T-immunodeficiency.At the next stage of the research, we studied the parameters of the B-system of lymphocytes, the results of which are shown in Table 2.Table 2. Comparative indicators of the B-lymphocyte system and humoral immunity in patients with diabetic foot syndrome with signs of critical lower limb ischemia and healthy individuals, М±m
 |
| |
|
The results obtained show that, in contrast to the T-system of lymphocytes, the relative and absolute number of B-lymphocytes (CD20+ cells) in patients was significantly higher than in healthy individuals, respectively, by an average of 1,2 and 1,6 times (P<0.05) – 22,80±0,96% and 619±26 µl in patients, versus 19,42±1,39% and 379±27 µl in healthy individuals.Almost the same results, but with greater intensity, were observed for the content of CD23+ lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients, the relative and absolute content of which were significantly higher than the same parameters of healthy individuals (P<0.001) - respectively, on average 19,25±1.48% versus 12,86±0.50% (the difference is 1.5 times, P<0.001) and an average of 523 ±40 µl versus 251±10 µl (a difference of 2,1 times, P<0.001).Indicators of humoral immunity (immunoglobulins of classes M, A and G - IgM, IgA and IgG) had the same tendency and direction of changes in the examined patients as CB20+ and CB23+ cells.The concentration of all studied serum immunoglobulins in patients was elevated relative to the control data, only with different intensity (Figure 1).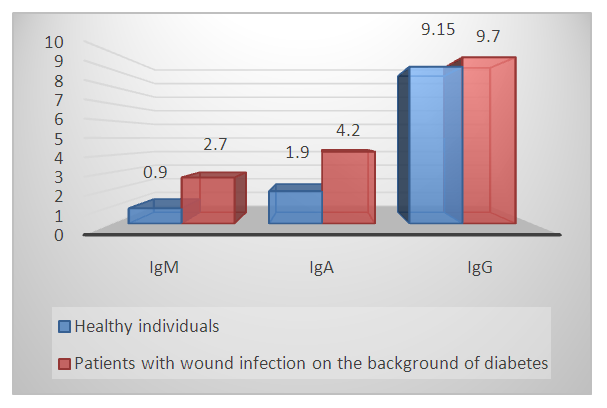 | Figure 1. Comparative parameters of the content of the main classes of immunoglobulins in the blood serum of patients with wound infection on the background of DM and healthy individuals, g/l |
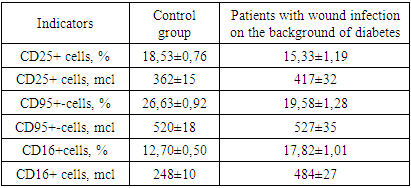
If the indicators of IdM in patients were increased in relation to the data of healthy individuals by an average of 2,9 times (respectively 2,70± 0,05 g/ l versus 0,90± 0,05 g/l, P<0.001), then almost the same trend was observed in the serum content of patients and healthy IdA, the difference was 2,2 times - respectively 4,20±0,11 g/l versus 1,99±0,07g/l (P<0,001). The intensity of differences between the content of IgG in the peripheral blood of the examined patients and healthy individuals was relatively low - on average 1,2 times increased in patients compared to healthy ones - respectively 9,70±0,08g/l versus 9,15±0,25 g/l (P<0.05).Thus, the study and evaluation of the parameters of the B-system of lymphocytes and humoral immunity in patients with wound infection on the background of DM compared with the data of healthy individuals showed that the relative and absolute content of CD20+ and CD23+ cells were significantly increased in patients by an average of 1,2-2,2 times relative to the control. The same trend and direction of changes were observed in the comparative analysis of the content of IdM, IdA and IgG in the blood serum of the examined patients. The greatest increase was in IdM, where the difference from healthy was 2,9 times (P<0.001), and the smallest increase in IgG, where the difference from the control data was 1,2 times (P<0.05).Comparative characteristics of the parameters of the immune system of T- and B-lymphocyte systems showed that in the examined patients with wound infection on the background of DM, these indicators changed in the opposite direction - a decrease in the content of T-lymphocytes and an increase in the concentration of B-lymphocytes. This indicates the following patterns that we have identified: firstly, the studied patients have an imbalance of T- and B-lymphocytes; secondly, this imbalance indicates the presence of tension in the immune system of patients; thirdly, a decrease in one component of the body's immune system causes an increase in another component of immunity, which complement each other's functions.At the next stage of the research, the expression of some activation markers on the surface of peripheral blood lymphocytes of the studied patients with wound infection on the background of DM and healthy individuals was analyzed in comparison. In the studies, the features of the expression of the marker of early activation of lymphocytes - CD25+ cells were evaluated, while the readiness of cells for apoptosis was assessed based on the determination of the expression content of CD95+ cells (Table 3).Table 3. Comparative parameters of lymphocytes with a marker of activation and apoptosis, natural killers in patients with DFS with signs of CILE and healthy individuals, М±m
 |
| |
|
The results showed that CD25+ cell lymphocyte markers were significantly reduced in the examined patients compared with the data of healthy individuals, respectively, by an average of 15,33±1,19% versus 18,53±0,76% (P<0.05). The obtained 1,2-fold difference indicates an increase in the content of lymphocytes with markers of early activation (CD25+ cells), the same pattern was observed when evaluating CD95+ cells responsible for the readiness of cells for apoptosis - respectively, on average 19,58± 1,28% versus 26,63± 0,92% (difference 1,4 times, p<0.05).It is known that Natural killer cells (NK cells) contain a CD16+ marker on their surface and are responsible for the detection and destruction of tumor cells. Activation of these CD16+ cells indicated the presence of tension in the immune system. Studies have found that, as well as lymphocytes with markers of activation of lymphocytes with readiness for cell apoptosis (CD25+ and CD95+ cells) and CD16+ lymphocytes were characterized by increased functional activity, that is, their content was significantly increased relative to normal values - respectively, on average 17,82± 1,01% versus 12,70±0,50% (the difference is 1,4 times, P<0.05).Thus, the study of lymphocytes with markers of early activation (CD25+ cells) and the readiness of cells for apoptosis (CD95+ cells), as well as natural killers (CD16+ cells) in patients with wound infection on the background of DM in comparison with healthy people showed that the content of all studied cells was significantly increased. This fact indicates that all lymphocytes are activated and the immune system is tense.This fact confirms that in the examined patients, the inflammatory process was strongly developed, associated with a sufficient number of pathogens in the infected focus and the development of systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome (SIRS) in patients, which in our opinion aggravates the course of the pathological process, and the inflammatory process in turn leads to an aggravation of the course of wound infection. Thus, there is a vicious circle with the mutual aggravation of wound infection and the syndrome of systemic inflammatory reaction SIRS.
5. Conclusions
1. The study of the relative and absolute number of CD3+ cells and their regulatory subpopulations of CD4+ and CD8+ cells showed that in patients with wound infection on the background of DM, these parameters changed with the same tendency and multidirection, while the absolute number of cells were increased and the relative significantly decreased relative to the control. 2. It was found that the relative and absolute content of CD20+ and CD23+ cells significantly increased in patients by an average of 1,2-2,2 times in relation to the control.3. The tendency and direction of changes to increase is observed when analyzing the content of IdM, IdA and IgG in the blood serum, while the greatest increase is subject to IdM, where their difference from healthy ones is 2,9 times.4. Comparative characteristics of the parameters of the immune system of T- and B-lymphocyte systems showed that in the examined patients with wound infection on the background of diabetes mellitus, these indicators changed in opposite directions - a decrease in the content of T-lymphocytes and an increase in the concentration of B-lymphocytes.5. In the course of research, the following patterns were revealed: patients have an imbalance, indicators of T- and B-lymphocytes; which indicates the presence of tension in the immune system of patients, while a decrease in one component of the body's immune system causes an increase in another component of immunity, which complement each other's functions.6. The study of lymphocytes with markers of early activation (CD25+ cells) and the readiness of cells for apoptosis (CD95+ cells), as well as natural killers (CD16+ cells) in patients with wound infection on the background of DM in comparison with healthy people showed that the content of all studied cells were significantly increased in patients. This fact indicates the development of a systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome.
References
| [1] | Alhaik, Sari, Huda A. Anshasi, Ja’far Alkhawaldeh, Kim Lam Soh, and Aseel Mazen Naji. 2019. “An Assessment of Self-Care Knowledge among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus.” Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2018.10.010. |
| [2] | Chen R., Ovbiagele B., Feng W. Diabetes and stroke: epidemiology, pathophysiology, pharmaceuticals and outcomes // The American journal of the medical sciences. – 2016. – Т. 351. – №. 4. – P. 380-386. |
| [3] | Choe, Sung Sik, Jin Young Huh, In Jae Hwang, Jong In Kim, and Jae Bum Kim. 2016. “Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders.” Frontiers in Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2016.00030. |
| [4] | Draxler D. F. et al. Tranexamic acid modulates the immune response and reduces postsurgical infection rates // Blood advances. – 2019. – Т. 3. – №. 10. – P. 1598-1609. |
| [5] | Hlinkova, Edita, Jana Nemcova, and Katarína Ziakova. 2017. “Educational Assessment of Diabetics Requiring Vascular Surgery.” Central European Journal of Nursing and Midwifery. https://doi.org/10.15452/CEJNM.2017.08.0023. |
| [6] | Khamdamov B.Z. Indicators of immunocitocine status in purulent-necrotic lesions of the lover extremities in patients with diabetes mellitus. // American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 2020, 10 (7). -Р 473-478. DOI: 10.5923/j.ajmm.20201007.08. |
| [7] | Khamdamov B.Z., Akhmedov R.M., Khamdamov A.B. The use of laser photodynamic therapy in the prevention of purulent-necrotic complications after high amputations of the lower limbs at the level of the lower leg in patients with diabetes mellitus. Scopus Preview. International journal of Pharmaceutical Research. July-Sep. Volume 11, Issue 3, 2019. https://doi.org/10.31838/ijpr/2019.11.03.089. |
| [8] | Khamdamov B. Z. et al. The role and place laser photodynamic therapy in prevention postoperative complication at treatment of diabetic foot syndrome // Applied Sciences: challenges and solutions. – 2015. – Р. 27-31. |
| [9] | Khamdamov B.Z., Dekhkonov A.T. Prospects for the use of silver preparations for local treatment of wound infection // Journal. New day in medicine. 2021, No. 2 (34) P. -141-146. |
| [10] | Khamdamov B. Z. et al. Prospects of application the use of perfluorocarbons at complex treatment of diabetic foot syndrome with critical lower limb ischemia // Applied Sciences: challenges and solutions. – 2015. – Р. 31-36. |
| [11] | Khamdamov B.Z., Nuraliev N.A. Pathogenetic approach in complex treatment of diabetic foot syndrome with critical lower limb ischemia. //American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, 2020 10 (1) 17-24. DOI: 10.5923/j.20201001.05. |
| [12] | Mooventhan A., Nivethitha L. Scientific evidence-based effects of hydrotherapy on various systems of the body // North American journal of medical sciences. – 2014. – Т. 6. – №. 5. – P. 199. |
| [13] | Nuraliev N.A., Khamdamov B.Z. Comparative assessment of the immune status of patients with diabetic foot syndrome with critical ischemia of the lower extremities. // Bulletin of the Tashkent Medical Academy. Tashkent, No. 1.- 2020. - Р. 132-138. |
| [14] | Ruhullaevich T. O. et al. Improved results of treatment of purulent wounds with complex use of photodynamic therapy and CO2 laser in the experiment //European science review. – 2016. – №. 3-4. – С. 185-189. |
| [15] | Świątoniowska, Natalia, Mariusz Chabowski, and Beata Jankowska-Polańska. 2020. “Quality of Foot Care Among Patients With Diabetes: A Study Using a Polish Version of the Diabetes Foot Disease and Foot Care Questionnaire.” Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2019.07.020. |
| [16] | Shettigar K., Murali T. S. Virulence factors and clonal diversity of Staphylococcus aureus in colonization and wound infection with emphasis on diabetic foot infection // European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. – 2020. – Т. 39. – №. 12. – С. 2235-2246. |
| [17] | Zarifovich K. B. et al. Method of prevention of postoperative complications of surgical treatment of diabetic foot syndrome // European science review. – 2018. – №. 9-10-2. – P. 194-196. |
| [18] | Zemskov V.M., Alekseev A.A., Kozlova M.N., Shiskina N.S. Changes in the immune system depending on the stage of burn disease and the area of thermal destruction. // Immunoglobin replacement therapy with gabriglobin. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res., 2017, Vol. 8, Iss. 2, p. 15653-15662. |




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

