-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(4): 418-423
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221204.10
Received: Mar. 26, 2022; Accepted: Apr. 13, 2022; Published: Apr. 16, 2022

Kallidinogenase (Tissue Kallikrien) in Complex Therapy in Patients with Isolated Closed Traumatic Brain Injury
Аvakov V. E., Ibragimov N. K., Murotov TM. N., Kenjaev L. T., Naubetova S. D., Juraqulov A. Q., Durdiev H. U.
Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Closed isolated traumatic brain injury (ТBI) is a major medical and social problem due to its high prevalence, high rates of mortality and disability, as well as the economic costs of treatment, rehabilitation and social assistance to victims [1]. Considering the severity of this disease and the insufficient effectiveness of conventional methods of treatment, we studied the effectiveness of the drug Kallidinogenase (tissue kallikrein) in complex therapy in patients with closed isolated traumatic brain injury.
Keywords: CTBI, Tissue kallikrein (kallidinogenase), ICP, CPP, GLASGOW scale, SAPS II, APACHE II
Cite this paper: Аvakov V. E., Ibragimov N. K., Murotov TM. N., Kenjaev L. T., Naubetova S. D., Juraqulov A. Q., Durdiev H. U., Kallidinogenase (Tissue Kallikrien) in Complex Therapy in Patients with Isolated Closed Traumatic Brain Injury, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 4, 2022, pp. 418-423. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221204.10.
1. Introduction
- СTBI is a traumatic brain injury, which is a primary and secondary damage to the brain tissue and an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP), which leads to a temporary or permanent impairment of brain function. [2]. Over the past 15 years, the world has seen an increase in natural disasters, man-made disasters, road traffic accidents (RTA), terrorism and military conflicts, accompanied by traumatic injuries in particular to the brain. In particular, injuries to the skull and brain account for more than 1/3 of all injuries [4,6], increasing by an average of 2% annually [5]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), every year in the world 1.5 million people die from CBI, and 2.4 million become disabled. In different countries, traumatism in the structure of mortality of the population follows cardiovascular and oncological diseases, but the economic and medical and social damage caused to society brings PTBI to the first place [1]. CTBI leads to the death of 30-50% of victims aged 20-40 years, causing severe disability with a frequency of 15-20 per 100,000 people per year [15,3] About 10,000,000 people in the world receive CTBI leading to hospitalization within one year [14]. According to the Research Institute of Emergency Medicine N.V. Sklifosovsky, the number of patients with CTBI in Moscow hospitalized in neurosurgical departments is 10,000–13,000 per year. In general, the incidence of CTBI in Moscow is 1.2–1.4 cases per 1000 people per year [16]. Treatment of victims with severe closed craniocerebral injury (CTBI) is an urgent task of modern medicine and is of great social and economic importance. [17].With CTBI, from the standpoint of pathophysiology, several phases of the development of brain damage can be distinguished. Negative outcomes of traumatic brain injury are mainly associated with the development of uncontrolled secondary tissue damage and neuroinflammation. The early phase of damage, as a rule, occurs in the first 24 hours after injury and is directly related to tissue damage and physiological dysfunction; the intermediate phase occurs in the first days after CTBI and entails the development of neuroinflammation; the late phase is associated primarily with cognitive impairment, convulsive syndrome and epileptogenesis and occurs within days to weeks after TBI. In each of the phases, there are appropriate treatments and interventions that directly target the pathophysiological mechanisms of each phase [18].The first phase of damage to the brain substance is characterized by various physical damage to the brain, depending on the localization and mechanism of CTBI. However, subsequent brain damage is primarily associated with the development of an ischemic cascade. Violation of energy processes leads to a decrease in glucose utilization, accumulation of lactate, a decrease in the amount of ATP and a decrease in the activity of ATP-dependent ion pumps, Ca2+ induced depolarization, excitotoxicity, and cell death. The ischemic cascade begins with impaired cerebral blood flow and oxygenation of the brain tissue [19]. It has been experimentally shown that these processes develop more intensively in the brains of older individuals compared to young ones [20]. Due to such a high importance of brain perfusion control for assessing the development of its ischemic damage, the Brain Trauma Foundation recommends the use of monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) and cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) in all patients with СTBI [21]. However, there is evidence that the control of ICP and CPP does not replace the assessment of true oxygenation of the brain tissue [7]. A decrease in blood flow and oxygen metabolism in the brain contributes to the restructuring of metabolism from an aerobic to an anaerobic pathway. Lactate is a marker of anaerobic respiration and accumulates in oxygen-deprived tissue. In severe traumatic brain injury, impaired ability of glucose to penetrate into brain cells is noted, and glucose deficiency correlates with worsening of long-term results [8,11]. Metabolic dysregulation occurs in the brain even when other vital parameters are well controlled [9]. Thus, among 76 successfully resuscitated patients with CTBI and successful control of ICP, 76% had a decrease in the level of glycemia and 93% had an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio [10]. Deregulation of cerebral metabolism leads to a deficit in energy production in the brain. Subsequently, a decrease in ATP leads to a deficiency of ATP-dependent ion channels and proteins [12]. Ischemia, reduced cerebral blood flow, and metabolic disorders can eventually lead to excitotoxicity and cell death, including apoptosis and necrosis [13].It has been shown that patients with isolated CTBI were characterized by higher levels of D-dimer and lower concentrations of protein C [22], by performing a multiple logistic regression analysis, it showed that D-dimer levels >400 ng/ml. Thus, the authors conclude, D-dimer levels can be used to assess disease severity and predict outcome.There is no specific therapy for isolated CTBI that would reduce the inflammatory cascade, prevent coagulation disorders and inhibit apoptosis, which is the most important trigger of isolated CTBI, so far does not exist [13].As a therapy that could stop the ongoing damage in the form of glutamate excitotoxicity and cell death, including apoptosis and necrosis, reduce the inflammation cascade, the use of tissue kallikrein is being considered, one of which is kallidinogenase (serine proteinase extracted from human urine) [32].Kallidinogenase - tissue kallikrein, a component of the kallikrein-kinin system (KKS), has a protective effect against cerebral ischemia. Tissue kallikrein is a serine proteinase (protein) extracted from human urine, which plays an important role in the regulation of local blood flow and vasodilation, which reduces total vascular resistance, in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, and in stimulating angiogenesis and neurogenesis [23].Tissue kallikrein is able to cleave low molecular weight kininogen to release vasoactive kinins, which in turn activate bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors on vascular endothelial cells, promoting the release of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandins (PGL2) regulatory T cells, suppression of the death of apoptotic cells [24]. Numerous lines of evidence indicate that KKS is important for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system and KKS deficiency is associated with cardiovascular and endogenous pathology [25]. Kallidinogenase has a relaxing effect on the arteries and inhibits platelet aggregation, increases the elasticity of red blood cells and the ability to dissociate oxygen. Kallidinogenase, a KKS regulator and a kallikrein producer, exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, angiogenesis, and neurogenesis effects [26]. Several studies have shown that kallidinogenase improves functional deficiency promotes angiogenesis and improves cerebral blood flow [27-29]. The main mechanism is upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and activation of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors [30]. In addition, kallidinogenesis has been shown to improve cognition [31].On the general data of the literature, we can say that urinary kallidinogenesis (kalgen), acting on the kallikrein-kinin system, improves cerebral hemodynamics, eliminating spasm of cerebral blood vessels, prevents vascular restenosis, promotes postischemic angiogenesis, improves cerebral perfusion, and also has a neuroprotective effect. action, contributing to the formation of a neuronal synapse, the protection of nerve cells, the growth of neurons and suppressing their apoptosis.The above characteristic of human urinary kallidinogenase was the reason for our study.We examined 6 patients with severe isolated closed craniocerebral injury in surgical intensive care unit No. 1 of the TMA multidisciplinary clinic.All patients were admitted through the ambulance line in the period from 12.24.2021 to 01.04.2022. after an accident in critical condition.The average age of the victims was 45.0 ± 5.4 years.Gender distribution: 2 women and 4 men.The level of impairment of consciousness on the Glasgow scale from 5 to 10 points.All patients were admitted in a state of traumatic shock.In order to determine the effectiveness of Kalgen, patients who died in the first 2-5 days were excluded from this study.Due to the absence of significant intracerebral hemorrhages, all of these patients did not undergo surgical intervention. In order to combat shock, pain syndrome and respiratory disorders, the victims were transferred to prolonged mechanical ventilation with a multimodal scheme of anesthesia with infusion-transfusion therapy carried out into the central vein (v.Subclavia).After stabilization of vital parameters on the 5th day, intravenous excretion of colladinogenase 0.15 ED intravenously per 100 ml of saline at a rate of 1.7 ml/hour was started. All patients underwent complex therapy according to the protocol adopted in our clinic, which included:Cranio-cerebral hypothermia (CCH), Na channel blockers (lidocaine at a rate of 10 mg/kg body weight), Ca ++ channel blockers (nimodipine, nemotan), antioxidant therapy (edaravone 20 ml per 100 ml saline at a rate 1.6 ml/hour, ascorbic acid), drug loading (ketamine, Natrii oxybutirat, propofol, droperidol). All were treated with antibiotics. For the first 2 days, patients received hemostatic therapy (etamsylate), and from the 4th day low molecular weight heparins (enoxaparin 01 mg/kg) were prescribed.
2. Patient Research Methods
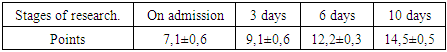
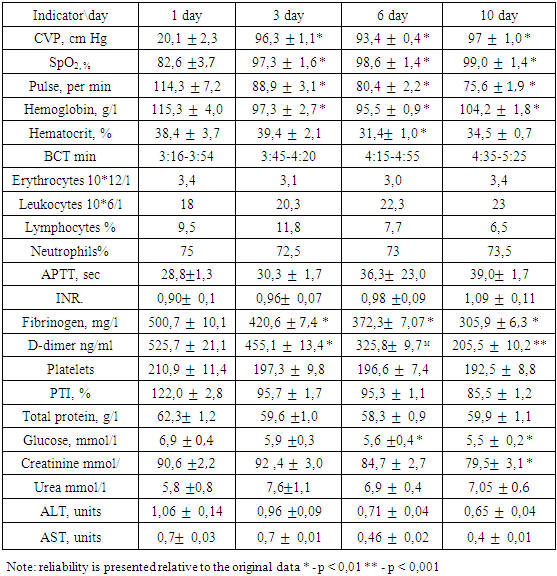
- In addition to general clinical and biochemical studies, the following indicators were studied in dynamics:1. Coagulogram (fibrinogen, platelets, PTI, APTT, INR, D-dimers)2. ICP (invasively - if possible - lumbar punctures with monometry and non-invasively (qualitatively) using a portable diagnostic ultrasound machine (Complexmed, Russia) by M-echo pulsation of the 3rd ventricle of the brain (normal, moderate and pronounced increase in ICP)3. Mean arterial pressure (SBP) according to the formula: SBP, mm Hg = (System. BP + 2 Diast. BP): 3.4. Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) according to the formula: CPP, mm Hg = SBP - ICP5. MSCT according to indicationsThe prediction and severity of the patients' condition at admission and during therapy was carried out using the APACHE II and SAPS scales. The level of consciousness and the dynamics of its recovery were judged according to the Glasgow scale.Stages of the study: initial data, after the introduction of kalgen on the III day, VI, X day.Study design: single center prospective study.
3. Research Results
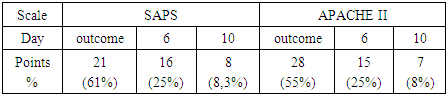
- Average data for predicting the severity of functional disorders (APACHE II and SAPS scales) are shown in Table 1.
|
|
|
|
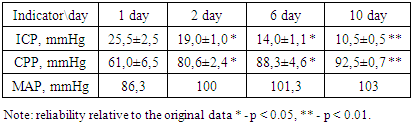
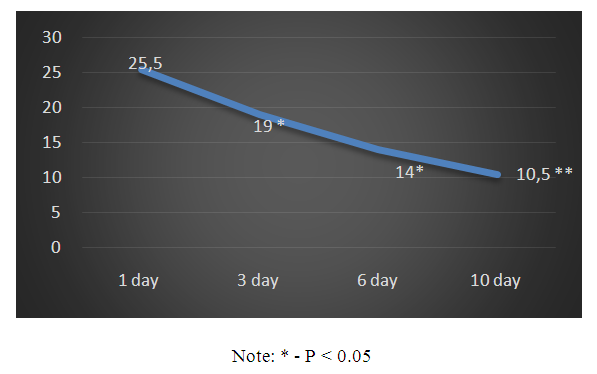 | Schedule 1. Dynamics of changes in ICP (mm Hg) |
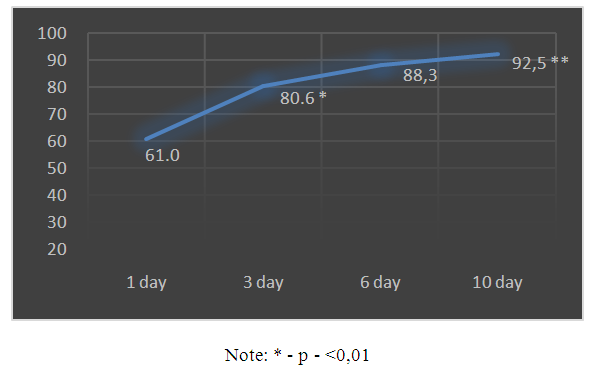 | Schedule 2. Dynamics of CPP values |
4. Conclusions
- 1. Based on the foregoing, it must be assumed that the drug Kallidinogenase (tissue kallikrein) showed a pronounced effect on the survival of patients with isolated CTBI. In addition, a clear shortening of the length of stay of patients in the intensive care unit was noted.2. The use of Kallidinogenase (tissue kallikrin) in isolated CTBI improves the general condition of patients and clinical and biochemical laboratory data.3. After the application of the drug Kallidinogenase, a decrease in ICP was noted and, in parallel, an increase in the CPP index, as well as an improvement in the level of consciousness.The obtained immediate positive results of the complex therapy of patients with closed isolated TBI with the inclusion of calidinogenase formed the basis for an ongoing study in this direction with the study of long-term results.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML