-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(4): 396-398
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221204.06
Received: Mar. 27, 2022; Accepted: Apr. 10, 2022; Published: Apr. 15, 2022

Diagnostics of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis
Khaydar Kamilov, Farangiz Bakhramova, Lazzat Usmanova
Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry Department, Tashkent State Dental Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Khaydar Kamilov, Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry Department, Tashkent State Dental Institute, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Recently, there has been an increase in the number of patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Due to the unclear etiology of the disease, the issue of diagnostics of aphthous stomatitis remains relevant for dentists. Often, clinicians pay attention to the lesion itself, forgetting about general somatic changes, which leads to frequent relapses. Clinical studies were conducted on the basis of the Department of Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry of the Tashkent State Dental Institute for the period from 2018 to 2021. The interdependence of antistreptolysin-O indicators with the development of RAS in gastroduodenitis has been proven, which can serve as confirmation of the direct involvement of streptococcal infection, which in turn affects the course of treatment of the disease.
Keywords: Recurrent aphthous stomatitis, Oral mucosa, Markers of inflammation, Oral mucosa
Cite this paper: Khaydar Kamilov, Farangiz Bakhramova, Lazzat Usmanova, Diagnostics of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 4, 2022, pp. 396-398. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221204.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS; recurrent aphthous ulcers) applies to group chronic inflammatory diseases mucous shells cavities mouth (Field and Allan, 2003; McCullough et al., 2007; Rogers, 1997; Scully and Porter, 2008). The most characteristic symptom of the disease is the recurring onset of single or multiple painful erosions and ulcers that appear mainly on the loose mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, cheeks and tongue [1-5].According to the results of an epidemiological dental survey of the population, the proportion of diseases of oral mucosa in adults aged 35-44 years is 8.6%, among them recurrent aphthous stomatitis is in first place with an indicator of 3.67%. In patients older than 65 years, the proportion of OM pathologies increases to 11.6%, while the prevalence of CRAS also increases - 4.38% [6-10].
2. Object of Research
- Taking into account the urgency of the problem, the object of our research was to study the content of disperse luminescent particles (DLP) in precancerous processes in the oral mucosa, to improve early detection of precancerous processes, and to apply cytological examination of smears from the oral mucosa to determine the DLP in clinical practice.
3. Material and Methods of Research
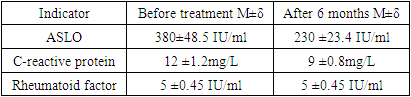
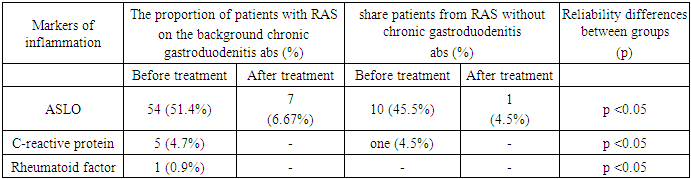
- Clinical studies were conducted on the basis of the Department of Hospital Therapeutic Dentistry of the Tashkent State Dental Institute for the period from 2018 to 2021.During the examination of the oral cavity, we identified and evaluated such parameters as the intensity of dental caries, the level of oral hygiene, the state of the periodontium according to the papillary-marginal-alveolar and complex periodontal indices, the presence of anomalies of the dentoalveolar system and the state of the oral mucosa, were detailed pathological elements are described, as well as the collection of data from additional laboratory examinations with the recording of the information obtained in specially designed tables of the clinical study. Markers of inflammation in the blood test, the so-called "acute phase proteins" are involved in the body's inflammatory response to various injuries. They are used in clinical practice as markers of inflammation and damage, as well as to monitor the course of diseases and control the effectiveness of treatment. A comprehensive study consists of the following laboratory parameters:- C-reactive protein (CRP) - a protein that determines the presence of an inflammatory process in the body in the acute phase.- Antistreptolysin- O (ASLO) - a marker of acute streptococcal infection.- Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a human immunoglobulin that forms complexes that cause an inflammatory reaction, leading to the destruction of bone and cartilage tissue. Used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis.Material for research: Blood serumResearch method: Latex agglutinationAntistreptolysin O (ASL-O) is an antibody to streptolysin, an antigen of group A β-hemolytic streptococcus. It is a marker of streptococcal infection in the body. Its level rises 1 week after infection and decreases after 6-12 months.
4. The Results of the Study
- For the purpose to estimate intensity teeth caries index DMF (Decayed, Missed, Filled teeth) was used. Analyzing structure given indicator at patients before treatment, we found that the average value index was 5.47, while the indicator "D" was detected in 54.3% (absolute average meaning was 2.75), indicator "F" was in 42.1% (absolute average meaning was 2.34), indicator "|M" - in 2.9% (absolute average meaning was 0.11).Before treatment, on the day of treatment, we registered the following values of the PMA index: in the 1st group of patients it was 14.8 ± 2.1%, in the 2nd group it was 12.1± 3.3% in the 3rd group it was 13.9 ± 2.5%. Differences between groups were statistically significant.Majority of patients examined in first day treatment complained of burning (30%), soreness in the oral cavity, aggravated by eating, talking and breathing (25%), appearance painful "ulcer" on the oral mucosa (50%), burning, tingling in areas foci defeat. From anamnesis it was revealed, what average duration clinical demonstrations RAS at patients having chronic gastroduodenitis in history, amounted to 7.3 day. Least duration was registered in 6 patients (5.8%): the duration of relapses in them was less 6 days after what aphthae healed on one's own. The longest duration was found in 4 patients (4.3%) and was more 12 days. At majority patients - in 56 cases, there were 58.2% of the total number of examined, - the duration of relapse diseases was 7 days. At patients not having in history chronic gastroduodenitis, the average duration of the disease was 4.8 days.Antistreptolysin (ASLO) is antibodies against streptococcal hemolysin - O. ASLO is a marker of acute streptococcal infection. The ASLO level rises during the acute period of infection (7-14th day) and decreases during the period of convalescence and recovery. The absence of a decrease in the activity of antistreptolysin- O by the 6th month of the disease suggests the possibility of a relapse. Detection ASLO in RAS may indicate the participation of streptococcal infection in the development of the disease, which changes the approach to complex treatment tactics, forcing us to use antibacterial agents (Table 1).
|
|
5. Conclusions
- Recurrent aphthous stomatitis in patients suffering chronic gastroduodenitis in comparative aspect from patients who do not have this comorbid pathology, has more expressed character. It is determined heavier clinical course: enlarged number relapses in a year, big duration of clinical manifestation of the disease, an increased incidence of patients having from five lesion elements in cavities mouth, more extensive area of the affected oral mucosa. The prevailing complaints were severe pain syndrome, dry mouth.The interdependence of ASLO indicators with the development of RAS in gastroduodenitis had been proven, which could serve as confirmation of the direct involvement of streptococcal infection, which in turn affects the course of treatment of the disease. Detection ASLO in RAS may indicate the participation of streptococcal infection in the development of the disease, which changes the approach to complex treatment tactics, forcing us to use antibacterial agents.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML