-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(2): 183-188
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221202.27
Received: Jan. 20, 2022; Accepted: Feb. 19, 2022; Published: Feb. 24, 2022

The Course of Freund's Adjuvant Induced Chronic Arthritis under the Influence of Calcium Channel Blockers
Khakimov Z. Z.1, Bekova N. B.2, Rakhmanov A. Kh.1, Zaitseva O. A.1
1Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
2Urgench Branch of the Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Rakhmanov A. Kh., Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The therapeutic and preventative effects of calcium channel blockers on the course of adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis and hematological blood parameters were studied in sexually mature male rats weighing 140-160 g. The aim of this work was to study the effects of amlodipine, diltiazem and cinnarizine on the course of adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in comparison with diclofenac sodium. The AIA model in experiments is reproduced by injecting 0.1 ml of complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA), which contains dead mycobacteria suspended in oil, into the hind right paw. Animals were intragastrically administered amlodipine, diltiazem, cinnarizine and diclofenac sodium at doses of 20 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, respectively, once a day for 14 days. Similar studies were carried out in the second series of experiments for assessment of the therapeutic effects of the medicines. Treatment with the above medicines was carried out in similar doses from 15 to 28 days of experiment. It was found that calcium channel blockers have an inhibitory effect on the development of adjuvant-induced arthritis, especially diltiazem and cinnarizine, which effect was almost identical to diclofenac sodium. A more expressed correction of disturbances of hematological parameters was observed in animals treated with diltiazem in a therapeutic and preventative regimen.
Keywords: Adjuvant-induced arthritis, Calcium channel blockers, Hematology
Cite this paper: Khakimov Z. Z., Bekova N. B., Rakhmanov A. Kh., Zaitseva O. A., The Course of Freund's Adjuvant Induced Chronic Arthritis under the Influence of Calcium Channel Blockers, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 2, 2022, pp. 183-188. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221202.27.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common immune-inflammatory diseases, which is characterized not only by chronic erosive arthritis, but also by systemic damage of internal organs. It usually leads to disability and, as a consequence, a deterioration of the quality of life and a decrease in the life expectancy of patients [1]. In the treatment of this pathology, a significant breakthrough is associated with the introduction of glucocorticoid and cytostatic therapy. However, it is proved that treatment with these pharmacological drugs is insufficiently effective and accompanied by the development of a wide range of side effects. Due to the deciphering of the leading mechanisms of RA immunopathogenesis, a wide range of innovative drugs have been developed, such as genetically engineered biological drugs, monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and others [2]. Lack of effectiveness and high cost of these drugs were the most common reasons for discontinuing of pharmacotherapy [3]. In view of the wide range of pharmacological effects, NSAIDs are one of the most commonly used group of drugs in medical practice, including in the treatment of RA. However, this group of drugs is characterized by the development of a line of specific side effects from the cardiovascular system, organs of the gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys [4,5,6,7]. The foregoing confronts tasks for medical science and pharmacology, in particular, the development of effective drugs for the treatment of this pathology. As the literature data show that RA is quite often diagnosed in elderly patients, in whom, along with the main diseases, pathology of the cardiovascular system is accompanied, in particular, hypertension, arrhythmias, angina pectoris, etc., and calcium channel blockers are often used for treatment them [8,9]. However, the effect of calcium channel blockers (CCBs) on the course of the chronic inflammatory process of the joints has been insufficiently studied. Therefore, an assessment of the effect of calcium channel blockers on the course of RA would open up new possibilities for increasing the effectiveness of pharmacotherapy of this pathology.The aim of this work was to study the effect of amlodipine, diltiazem and cinnarizine on the course of adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in comparison with diclofenac sodium. We chose the last drug due to the fact that NSAIDs have not lost their positions in the treatment of arthritis [10].
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experiments
- The experiments were carried out on sexually mature white rats - males with an initial weight of 140-160 g, kept under standard vivarium conditions, quarantined for at least two weeks (with a natural light regime, at a temperature of 22-24°C and a relative humidity of 40-50%) using a standard diet. Experimental groups of animals were formed by 6 animals in each, taking into account the body weight. These experiments were carried out in accordance with the rules of good laboratory practice (GLP) for preclinical studies, as well as the rules and the International Recommendations of the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used in Experimental Research (1986). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan Protocol No. 6 dated September 23, 2021.Adjuvant arthritis is one of the first experimental model used to test pharmaceuticals specialized for the treatment of RA. The experiment is implemented on white outbred white rats and the duration of the study is approximately 30 days. The similarity of AIA with human RA lies in the presence of edema of the extremities, degradation of cartilage, lymphocytic infiltration of the inflamed joint tissue, loss of their function, resorption of bone and periosteum [11]. The AIA model in experiments is reproduced by injection 0.1 ml of complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA), which contains dead mycobacteria suspended in oil, into the hind right paw [12,13,14]. The AIA model was reproduced by intradermal injection of 0.1 ml of CFA (Chondrex, Inc., USA) into the dorsum of the hind paw, which contains killed mycobacterium H37RA at a concentration of 2 mg/ml suspended in oil, designed to reproduce AIA in rats [13]. AIA allows to induce an acute inflammatory reaction at the point of injection and an immunological reaction that develops after 9 days in the contralateral paw and other organs. The edema of the hind paw was observed from the very first to 15 days or more, depending on the duration of the experiment.Due to study the preventative effect of medicines the animals were divided into several groups after the injection of CFA. Animals were intragastrically administered amlodipine, diltiazem, cinnarizine and diclofenac sodium at doses of 20 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, respectively, once a day for 14 days. The similar studies were carried out in the second series of experiments for assesement the therapeutic effect of medicines. Treatment with the above medicines was carried out in similar doses from 15 to 28 days of experiment. After 3, 7, 10 and 14 days (preventative treatment), as well as after 21 and 28 days (treatment) of experiment, oncometric measurements of the affected paws were made by using a plethysmometer in all groups of animals [15]. Blood samples were taken from the tail vein and the formula of blood indexes was determined on a hematological analyzer BC-3000 (Mindray, China). Then the animals were decapitated under general anesthesia and blood was collected for biochemical studies.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
- The data obtained were processed by the method of variation statistics using the paired Student's test and one-way analysis of variance using the standard software package BIOSTAT 2009 with an assessment of the significance of indicators (Mean±Std error). Differences in the compared groups were considered significant at a significance level of 95% p <0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
- In the first series of experiments, we investigated the effect of the preventive action of CCBs on the course of chronic arthritis induced by CFA. The results of the experimental studies showed that the injection of CFA provoked a pronounced inflammatory process in rats. Already on the 3rd day after immunization, the rats became lethargic, aggressive, inactive, the coat became dull, tousled, and food consumption decreased. At the same time, after 3,7,10 and 14 days from the beginning of the experiment, there was a significant increase in the volume of the rat paws in comparison with the initial volumes by 256.4%; 269.0%; 283.6% and 290.9%, respectively. It was characteristic that there was some increase in the volume of other joints of the legs. All of these testified the development of chronic progressive, generalized, immune-dependent inflammation of the joints. In contrast, there was a less expressed increase in the volume of the paw in the group of rats preemptively treated with CCBs. So, under the influence of amlodipine, the increase in the volume of the paws was respectively 200.0%; 205.2%; 208.8% and 210.5%, compared with the initial value of paws in the indicated periods of observation. The index of inhibition of inflammation was 19.1%; 20.9%; 23.7% and 25.0% under the influence of medicine. A more pronounced pharmacotherapeutic effect was observed in the group of rats treated with diltiazem and cinnarizine. From the data in Figure 1, it is clear that the index of inhibition of inflammation by these medicines was 28.4 and 26.2% on the third day of the experiment, and after seven days, it was 29.7% and 27.7%, respectively. Continued administration of diltiazem and cinnarizine led to an increase in the noted effect, and on the 14th day of observation, the index of inhibition of inflammation was 33.1 and 30%, respectively. Similar in direction, but somewhat expressed action was stated in the group of animals receiving diclofenac sodium preventativly. In the indicated periods of observation, the index of inhibition of inflammation was 31.9%; 33.8%; 35.2% and 37.5%, respectively. As can be seen from the above data, calcium channel blockers have an inhibitory effect on the development of RA, which especially diltiazem and cinnarizine have a preventive effect almost identical to diclofenac sodium.
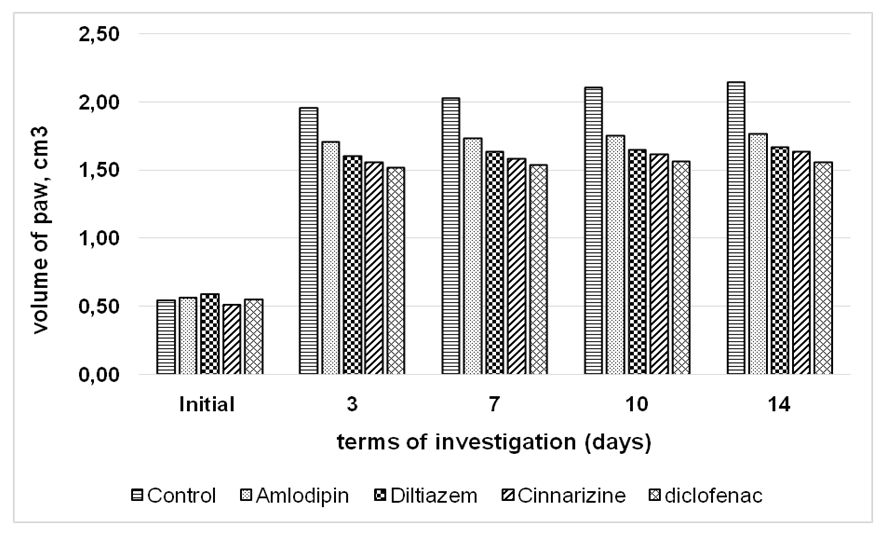 | Figure 1. Influence of CCB and diclofenac sodium on the course of adjuvant-induced arthritis in preventive administration |
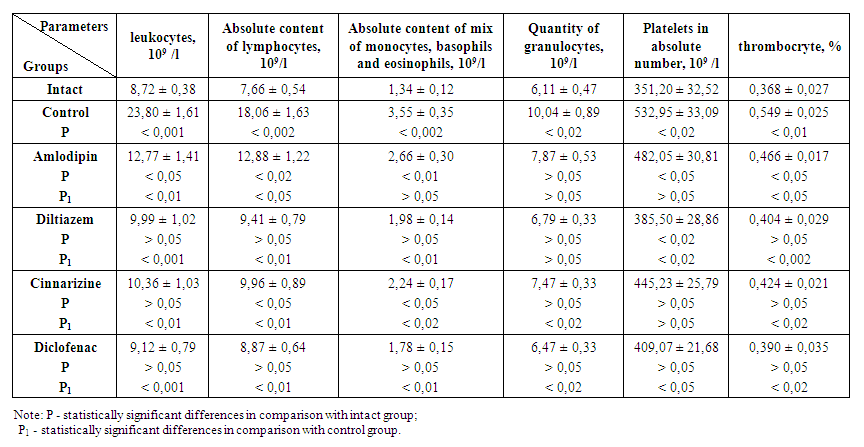 | Table 1. To study the effect of the preventative action of calcium channel blockers and sodium diclofenac on hematological parameters in adjuvant arthritis (M ± std error, n = 6) |
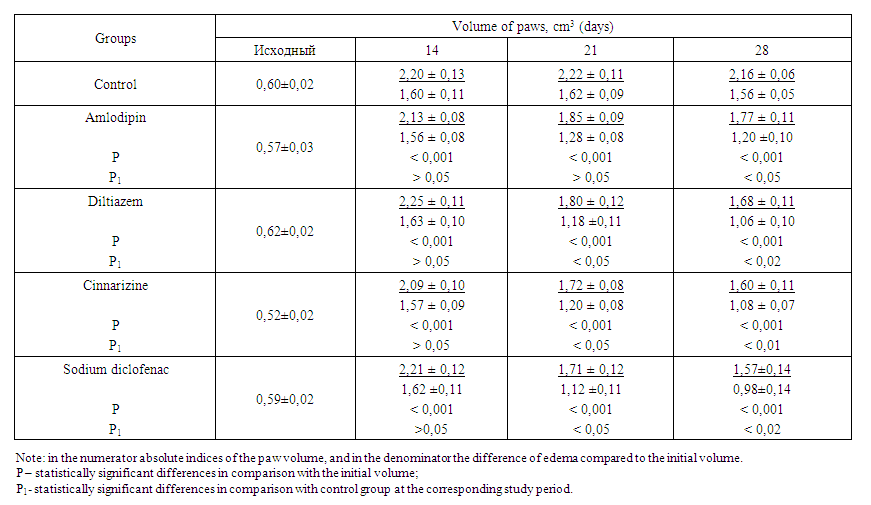 | Table 2. Study of the therapeutic effect of calcium channel blockers and sodium diclofenac on the course of adjuvant-induced arthritis (M ± m, n = 6) |
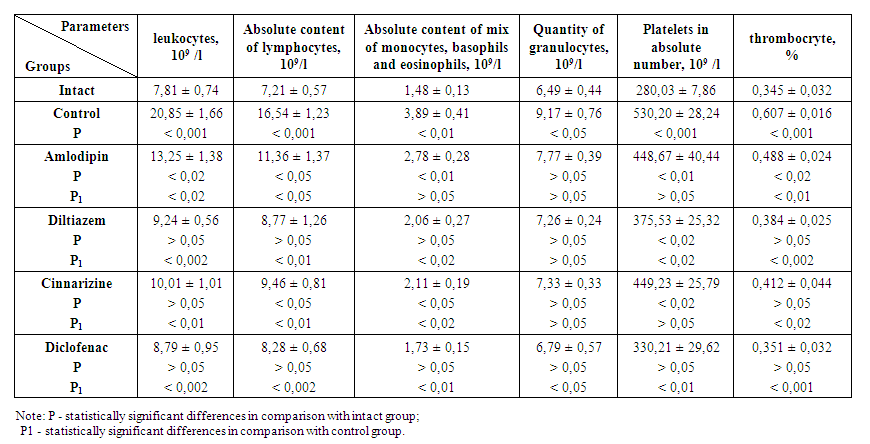 | Table 3. To study the influence of the therapeutic effect of calcium channel blockers and sodium diclofenac on hematological parameters in adjuvant arthritis (M ± m, n = 6) |
4. Conclusions
- 1. Calcium channel blockers clearly suppress the development of chronic autoimmune inflammation in experimental animals with adjuvant-induced arthritis.2. The pharmacological effects of calcium channel blockers are convincingly confirmed in the elimination of disturbances of hematological parameters.3. The results of these experimental studies can be the basis for introducing changes in the pharmacotherapy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who are simultaneously taking calcium channel blockers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML