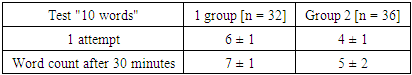-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2022; 12(2): 93-95
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20221202.05
Received: Jan. 8, 2022; Accepted: Jan. 30, 2022; Published: Feb. 15, 2022

The Nature of Cognitive Changes and Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Taking into Account the Therapy
Djurabekova Aziza Takhirovna, Fatullaeva Dildora Sayfullaevna, Shaimatov Rakhmonberdi Uktamovich, Gaibiev Akmaljon Akhmatovich
Department of Neurology Samarkand Medical Institute, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Achievements in the field of diagnosis and treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) are very high at the moment. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease that requires adherence to certain lifestyle rules, slowly progressing, leading to disability due to long-term complications. Damage to the CSF is complicated by retinopathy, renal failure, diabetic encephalopathy and diabetic polyneuropathy [1,3]. It has been proven that timely and early diagnosis and glucose control can reduce both the aggressiveness of the disease itself and the risk of complications.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, Diabetic encephalopathy, Diabetic polyneuropathy, Glucose control
Cite this paper: Djurabekova Aziza Takhirovna, Fatullaeva Dildora Sayfullaevna, Shaimatov Rakhmonberdi Uktamovich, Gaibiev Akmaljon Akhmatovich, The Nature of Cognitive Changes and Quality of Life in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Taking into Account the Therapy, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 12 No. 2, 2022, pp. 93-95. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20221202.05.
1. Introduction
- There is a reliable diagnostic study for the definition of diabetes - this is the detection of glucose in the blood (glycemic control), and an important reliable method of replacement therapy for diabetes is insulin therapy, but despite the advances in this direction, there are no clear standard recommendations, patients are looking for an easier way of treatment, according to their considered more acceptable, the use of tabularized forms of stabilization of blood sugar [2,4]. In this regard, it is necessary to analyze patients with Diabetes mellitus for the presence of cognitive and psycho-emotional complications that affect the quality of life of patients, depending on the duration of the disease and the therapy they use, to improve and stabilize glycemia.To study the nature of cognitive, psych emotional changes and the quality of life in patients with diabetes, taking into account the therapy used to correct glycemia.
2. Material and Research Methods
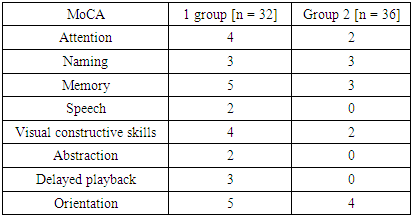
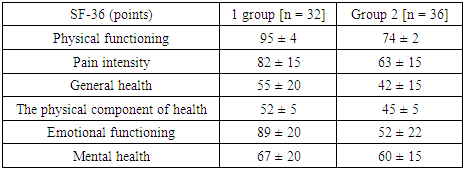
- Based on the goal, the recruitment of patients was carried out on the basis of the 1st clinic of the Samarkand Medical institute Department of Therapy, Cardiology, Neurology for the period 2020-2021. In accordance with the criteria for the inclusion of patients, 68 people aged 20-50 years were studied. The inclusion criteria for the study were the presence of type 2 diabetes mellitus with a disease duration of more than 5 years. An agreement was drawn up with the patients to participate in the study of their clinical, neurological and emotional state. The patients were divided into two groups, depending on the therapy received, to stabilize blood glucose. The study included collection of anamneses, detailed description of complaints, clinical, neurological and somatic status at the time of hospitalization. An important point was the identification of cognitive changes, for this a neuropsychological survey was meticulously conducted using the MMSE, MOCA, “10 words” tests, the HADS scale (excluding anxiety and depression). In the process of studying patients, it became necessary to determine the quality of life, using the standard SF-36 questionnaire, with an assessment of physical and mental health. Statistical analysis of the results obtained in the course of the work was recorded on an individual computer, using the standard Student's criteria and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient; p <0.05 was taken as the level of statistical significance.
3. Research Results
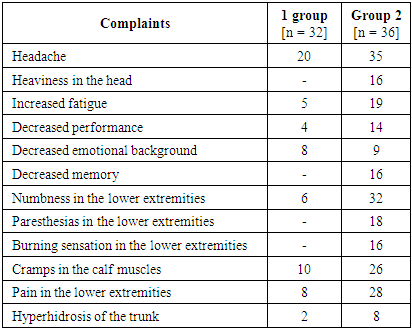
- The examination included patients from among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, divided into two groups depending on the type of therapy used, which improves blood sugar levels, 68 total number of patients, group 1 - 32 of whom took insulin therapy in the form of subcutaneous injections, group 2 - 36, received per os the drug "Metformin" 1 g (2 tab.) 2-3 times a day after meals. The ratio of men is 39%, women are 61%, respectively. The average age of the patients was 33.5 years. The duration of diabetes mellitus is from 5 to 10 years. The main complaints presented by patients are headache, a feeling of heaviness in the head; dizziness, decreased memory and attention, emotional lability, anxiety for their health. As for the complaints of polyneuritis disorders, this is numbness or burning sensation in the extremities, especially in the legs, cramps in the calf muscles, the extremities were cold to the touch, swelling in the legs by the end of the day (Table 1).
|
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
- 1. Examination of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus for the presence of cognitive and psycho-emotional changes as factors affecting the quality of life can serve as the basis for larger clinical trials.2. A comparative analysis of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, depending on the therapy they used to correct blood glucose, showed the effective use of insulin therapy, since patients who used Metformin were in a worse position in terms of cognitive, psych emotional and quality of life, since the drug they was used in violation of the regimen, sometimes at a lower concentration (patients artificially reduced the amount of drug intake), while patients using insulin therapy strictly adhered to the schedule of receiving therapy.3. From the questionnaires used, in our opinion, testing according to MOCA and SF-36 showed a sufficiently high and effective diagnostic sensitivity for screening the severity of "Diabetic encephalopathy".
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML