-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2021; 11(11): 816-824
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20211111.16
Received: Nov. 4, 2021; Accepted: Nov. 23, 2021; Published: Nov. 28, 2021

Dynamic Patterns of Prescription Writing along with Private Practitioners in Sylhet City
Md. Mokbul Hossain 1, Nasrin Akter 1, Abul Khayer Chowdhury 1, Md Rahimullah Miah 2, Mohammad Basir Uddin 3, Miftahul Jannat Chowdhury 4, Parag Datta 5, Chowdhury Mizanur Rouf 6, Md Raihan Parvez 7, Tahmina Hossain Moni 8
1Department of Pharmacology, North East Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
2Department of IT in Health, North East Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
3Department of Paediatrics, North East Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
4Department of Pharmacology, Sylhet Women’s Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
5Medical Officer, Surgery Unit, Oasis Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
6Department of Pharmacology, Jalalabad Ragib Rabeya Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh
7Community Medicine, Aichi Medical College, Dhaka, Bangladesh
8Department of Pharmacology, Aichi Medical College, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Md. Mokbul Hossain , Department of Pharmacology, North East Medical College, Affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

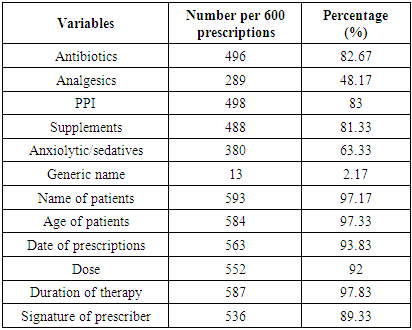
Prescription writing is an art and it is a written order to the pharmacist to supply drugs in particular form to a patient and the directions to the patient regarding the use of medicines. Therefore, Evaluation of drug prescription patterns is a significant aspect of patient care and it is an important therapeutic translation between the clinician as well as the patient and the central priority of the healthcare system is providing the right medicine to the right people at the right time. This study was conducted to observe the prescribing patterns of the practitioners in Sylhet city and analyzed by using INRUD indicators. In this study there were prescribed average numbers of 4.63% drugs per prescription A limited number of (2.17%) generic names containing prescriptions were observed. Antibiotics constituted 82.67% of prescriptions. Injectable drugs were prescribed in about 14.33% of prescriptions. About 41% drugs followed the essential drug list. Supplements prescribed for about 81.33%, PPI (Proton pump inhibitor) 83%, whilst analgesics comprised about 48.17%, and anxiolytics 63.33% of the prescribed drugs. 6.33% unclear handwriting prescriptions were observed in this study. Patient`s names were not mentioned in 1.17% and the age of the patients were absent in 2.67% of the prescriptions. 93.83% of prescriptions contained prescribing dates. Treatment duration was not mentioned in 2.17% of prescriptions and formulations of drug were not mentioned in 8% prescriptions. About 89.33% of prescriptions were signed whereas 10.67% were not signed. To that end, the study suggests future research trajectories of a new dynamic prescription pattern for physicians to provide patients with a specific form of medication that could save millions of lives.
Keywords: Prescription pattern, Private practitioners, Sylhet city
Cite this paper: Md. Mokbul Hossain , Nasrin Akter , Abul Khayer Chowdhury , Md Rahimullah Miah , Mohammad Basir Uddin , Miftahul Jannat Chowdhury , Parag Datta , Chowdhury Mizanur Rouf , Md Raihan Parvez , Tahmina Hossain Moni , Dynamic Patterns of Prescription Writing along with Private Practitioners in Sylhet City, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 11, 2021, pp. 816-824. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211111.16.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Healthcare facilities are the fundamental need for any country in the world and it is one of the basic rights in Bangladesh. So, it is very important to improve the healthcare systems so that patients can get proper medical benefits. For appropriate health service proper diagnosis of disease and rational prescription is very important. Therefore, Evaluation of drug prescription patterns is a significant aspect of patient care and It is an important therapeutic translation between the clinician and the patient [1] and the central priority of the healthcare system is providing the right medicine to the right people at the right time [2]. Prescription writing is an art and it is a written order to the pharmacist (who sells/supplies medicine from the pharmacy) to supply drugs in particular form to a patient and the directions to the patient regarding the use of medicines [1].However inappropriate use of medicines is a global problem, particularly in underdeveloped countries. In Countries like Bangladesh, irrational prescribing is common and frequently observed in polypharmacy (to prescribe more than two drugs in a prescription) as well as inappropriate use of antimicrobials, injectable drugs and vitamins [3]. Irrational drug use leads to reduction in the quality of drug therapy, excess treatment cost, increased risk for adverse reactions and emergence of resistance [4,86]. The prescribed drug costs huge money, causing problems in developing countries like Bangladesh. This problem can be solved by prescribing drugs by generic name and it could be prescribed from EDL (essential drug list). Generic drugs are substitutes of brand drugs without any patient protections having similar efficacy though 40-60% cheaper than brand drugs [5]. Doctors are bound to prescribe easily available, affordable and essential medicines to the patients; rather they are blamed to prescribe costly branded drugs [6]. Changing the bad practicing habits is a must. Prescription audit is another approach to avoid irrational prescribing. Periodic appreciation of prescribing habits leads to increased therapeutic efficacy, decreases adverse effects and provides feedback to prescribers [7,8,9]. So, with this view, this study was an attempt to find out the prescribing patterns of the private practitioners in Sylhet city.Prescription writing is a science and art, as it carries the message from the prescriber to the patient. A prescription order is a written instruction of doctors to pharmacists to supply drugs in particular form to a patient and the directions to the patients regarding the use of medicines. It is an important therapeutic translation between the clinician and the patient [1] and the central priority of the healthcare system is providing the right medicine to the right people at the right time [2]. Evaluation of drug prescription pattern is an important aspect of patient care, which also serves as a measure of the quality of care provided. A recent systematic analysis has ascertained that prescribing quality is a dimension requiring constant evaluation [3]. The rational use of drugs is imperative for an effective and efficient health-care system. However Irrational use of medicines is a global problem, particularly in developing and transitional countries. In Countries like Bangladesh, irrational prescribing is common. Frequently observed irrational use of medicines per patient (poly pharmacy), inappropriate use of antimicrobials, over use of injections and vitamins. On the other hand, aggressive drug marketing, lack of information on the use of drugs and inadequate drug supply has been suggested to be the main causes behind the irrational prescribing [4]. Irrational drug use leads to reduction in the quality of drug therapy, excess treatment cost, increased risk for adverse reactions and emergence of resistance [5]. The prescribed drug costs huge money, causing problems in developing countries like Bangladesh. This problem can be solved by prescribing drugs by generic name and it should be selected from the essential drug list. Generic drugs are substitutes of brand drugs without any patient protections having similar efficacy though 40-60% cheaper than brand drugs [6]. Doctors are bound to prescribe easily available, affordable and essential medicines to the patients; rather they are blamed to prescribe costly branded drugs [7]. Changing the bad practicing habits is a must. Prescription audit is another approach to avoid irrational prescribing. Periodic evaluation of prescribing patterns leads to increased therapeutic efficacy, decreases adverse effects and provides feedback to prescribers [8,9,10]. Irrational and inappropriate use of drugs is very common in Bangladesh. The International network of Rational Use of Drugs (INRUD) has developed a list of indicators of rational prescribing [11]. Thus, this study was an attempt to evaluate the prescribing patterns of the private practitioners in Sylhet city.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Design
- A retrospective cross-sectional study in Sylhet, Bangladesh was used to analyse the relationship between initiating factors and prescription quality indicators. This cross-sectional descriptive study was carried out at Sylhet city in Bangladesh in the month from April to September, 2019 during this period those who had visited a medical practitioner and were desirous to respond were included in this study tool. Several initiating factors included on gender, age, academic degree, work experience, daily outpatient number, training, specialty, research and publications, rational drug use, acquisition of medical knowledge [88], attitude towards national jurisprudence for medical practitioners and patient-related factors and history.
2.2. Sample Size and Mode of Data Collection
- The sampling technique was purposive. The sample size was 600. Samples of patients’ prescription were collected randomly. Mode of collection was copying prescriptions by photocopy or by digital or mobile camera. Patients consent was taken. All prescriptions were analyzed according to INRUD indicators. Following parameters were analyzed-1. Average number of drugs per prescription2. Percentage of generic name related prescriptions.3. Percentage of antibiotics containing prescription.4. Percentage of injectable drugs containing prescriptions.5. Percentage of drug prescribed from essential drug list6. Whether prescription is complete with relation to-a. Formatb. Doses and durationc. Patient medical informationThe sum total of average and percentages were calculated by using standard formulas in WHO’s manual on “How to investigate drug use in health facilities” [9]. The random sampling was used to investigate different prescriptions of general practitioners, surgeons, orthopaedists, obstetricians, gynaecologists and paediatricians at Sylhet city in Bangladesh.
2.3. Data Compilation and Analysis
- All surveyed data were collected and compiled according to research aims. These compiled data were checked for accuracy from different sources, are also verified for the preparation of master sheet for analysis and interpretation using update software like SPSS ver.27, MS Excel 2019, and R programming 3.6 version.
3. Results
- The prescriptions, which were randomly collected from the Sylhet city, counted a total of 600 prescriptions. From these prescriptions a sum of 2778 drugs were prescribed at an average of 4.63 drugs per prescription for patients by the physicians for treatment of diseases so as to improve the quality of life of the patient. Most of the prescriptions 95.4% were prescribed by hands whereas only a few numbers of 4.6% were written using a computerized software method. (Figure 1). Female patients were predominant in this study, 366 (61%) and 234 (39%) patients were male of them aged between 10-60 years. A limited number of (2.17%) generic names containing prescriptions were observed. Antibiotics constituted 82.67% of prescriptions. Injectable drugs were prescribed in about 14.33% of prescriptions. About 41% drugs followed the essential drug list (Figure-2). Supplements prescribed for about 81.33%, PPI (Proton pump inhibitor) 83%, whilst analgesics comprised about 48.17%, and anxiolytics 63.33% of the prescribed drugs. 6.33% unclear handwriting prescriptions were observed in this study (Figure 2).
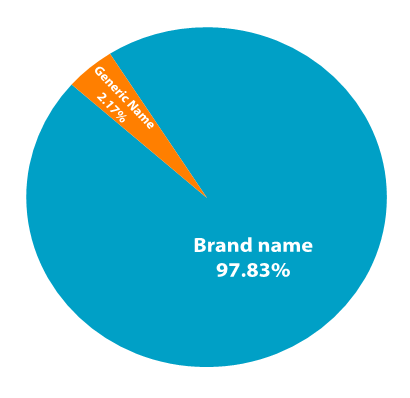 | Figure 1. Brand name and generic name |
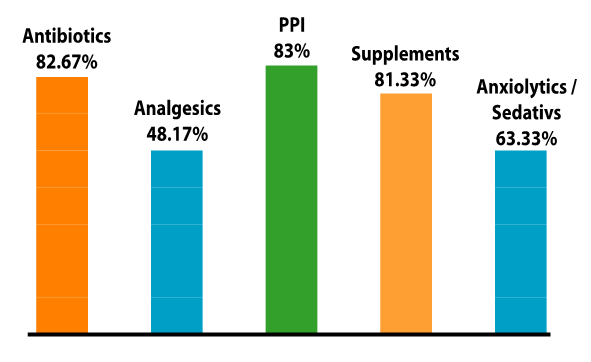 | Figure 2. Antibiotics and other status |
|
4. Discussion
- In this present study, Collection of 600 prescriptions (From BM&DC approved MBBS and postgraduate doctors) have been ready for analysis and tried to focus the pattern of prescription writing among private practitioners (who consults and to treat patients in their personal chamber) in Sylhet city. A sum of 2778 medications in 600 prescriptions and an average of 4.63 medicines were written in every prescription and it was 3.81 in a study conducted in 2009 and 3.24 in 2001 and 3.40 in 2012 [10,11,12]. Another study in Delhi Lucknow's district, Islamic republic of Iran, Goa, Sudan, Zimbabwe and Ethiopia showed every single prescription contained the average number of medicines respectively from 1.42 to 4.07 [13], 3.1 [14], 4.4 [15,16], 1.8,1.4,1.3, 1.9 [17]. Compared with other studies this present study showed a higher number of average medications were mentioned in every prescription and most of the private practitioners violated the criteria of rational prescribing.In a study showed in Nepal 44% [12] and in Jordan 5.1% [18] drugs were written in generic name and another exercise in northwest Ethiopia higher average number of generic names containing prescriptions were 83% in health stations and 75% in health centres [19], whereas in our study only 2.17% of medications were involved in generic name and this indicates that the prescribers were not conscious about the value of generic name. In this study, figure of 82.67% prescriptions having an antibiotic which was much higher than the studies conducted in Bangladesh [10,11,20,21,22], India [23], Lebanon [24], Nepal [25] and Tanzania [26] (17.5% to 39.6%), Iraq [27], Pakistan [28], Iran (61.9%) [29]. In another study by Biswas et al revealed that mostly prescribed medications were also antibiotics (49.22%) [30]. According to WHO 15-25% of prescriptions with antibiotics are expected, where infectious diseases are more prevalent [31]. So improper use of antibiotics is responsible for bacterial resistance and the antibiotic will lose its effectiveness if it is used without a culture sensitivity test [32,79,80,81,82]. So appropriate use of antibiotics is necessary. This trend implies that prescribers were more interested in prescribing antimicrobials as empirical therapy.
4.1. Pattern Model
- The WHO recommended target for injection exposure is 10% or less [33]. Injection-containing percentage of prescription encountered was 2.32% in this study which is less than in Nepal (3.1%) [34,81], Zimbabwe (13%) [35] and India (13.6%) [36,76,77,78,79,80]. In our study, 14.33% prescriptions contained injectable drugs. About 10% prescriptions contained an injection which was almost similar with the study done by Saurabh et al (8.0) [5] and 8.35% in the study done by Begum F et al, [37]. But in comparison it was more (12.1%) in the study of Rahman Z et al [10]. In this study, the percentage of drugs prescribed from EDL of Bangladesh was 41% and it was lower than studies performed in another part in Bangladesh 48.35% [11] and 49% [22]. 43.16% 40.48% [21], in India (99.6%), Tanzania (96%), and South Ethiopia (96.6%), whereas higher in comparison to that in countries like Nepal (88%) [38,83]. In this current study supplements containing prescriptions were prescribed more frequently and it was 81.33% and it was much and much higher than another study conducted in Bangladesh 40.80% [39], 15.95% [40] and also in Iraq 44.2% [27], In Rajasthan16.22% [41].This current study, 83% prescriptions contained antiulcerants drugs and it was much higher than another study carried out in Bangladesh 69% [39], 20.86% [40,74,75,76]. It was observed that a higher percentage of NSAIDs and anxiolytics drugs were also prescribed in this study.
4.2. Innovative Idea
- In this study the name of the patients was mentioned in 97.17% prescriptions, while the age was written in 97.33% of prescriptions. To mention the age of the patient in prescription is necessary because different doses are required for children, adults and neonates for proper action of the drugs and to avoid adverse drug reaction because the risk of toxicity is increased by decreasing the drug clearance (Cl) in these age groups [42]. Duration of therapy was written in 97.83% of prescriptions. Absence of duration of therapy in drug prescription is regarded as irrational and can result in drug abuse as the patient may take the drug for shorter or longer duration and affect the efficacy of therapy as well as having a chance of treatment failure and adverse effects [46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,65,66]. The dose of drugs was mentioned in 92% of prescriptions and it is very beneficial for proper action of drugs and 93.83% of prescriptions revealed the date of prescription, which is necessary particularly for prescription of antibiotics and analgesics. In this study we observed that there were 6.33% prescriptions, where unclear handwriting could result in misinterpretation and mistakes [43,54,67,68,69,70,84,85]. We also observed 10.67% unsigned prescriptions.From this study it stated that the habit of prescription style of the private practitioners was irrational regarding polypharmacy [Appendix], generic name, use of antibiotics, drug selection from EDL. Irrational prescribing is tough to cure from the root. But it can be prevented with innovative ideas on dynamic pattern of practitioner’s prescription. Proper training in pharmacotherapy and workshops on proper use of drugs may improve prescription behaviour and skills [44,45,55,62,63,64,71,72,73]. Strict rules should be applied by the Government to ensure rational prescribing. The significance parameters of dynamic prescription patterns for practitioner included (i) local, national or global patient’s status, (ii) follow global health agency’s guideline, (iii) public health advocates, (iv) national government agency’s instruction, (v) health insurance company, (vi) pharmaceutical firm, (vii) medical ethics researchers, (viii) Patient consumers, and (ix) secure advanced wireless sensor technology [56,57,58,59,60,87]. The motto of dynamic prescription states as medicine is not enough to cure disease, it requires mental health awareness, nutritious food, proper use of new technologies and religious values. Your well-being also depends on your outlook, which as shown in Figure 3.
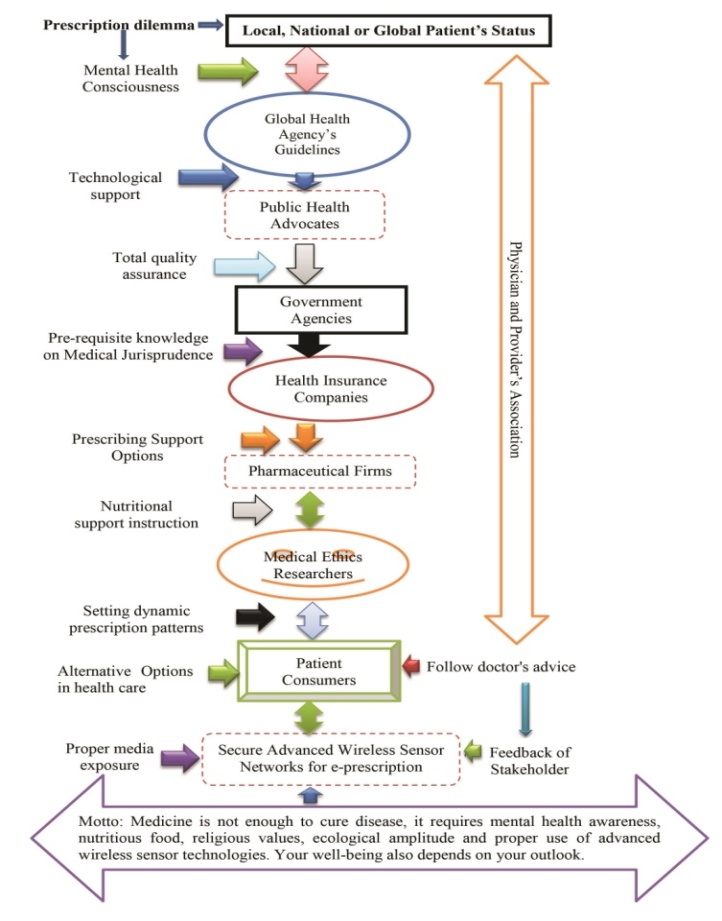 | Figure 3. Significance parameters of Dynamic Prescription Pattern |
5. Conclusions
- We observed from this current study that the physicians were prescribed unnecessary and overuse of drugs which is irrational and harmful for the patients and thus may be caused drug resistance, adverse drug reaction as well as economical loss of the patients and the nation. Proper training, workshop, strict rules by the government can improve prescription behaviour and efficiency of the prescriber and to ensure rational prescribing. Lastly, the study suggests future research trajectories of a new alternative prescription pattern for doctors to provide patients with a positive form of medication that could save millions of lives.
6. Declarations
- FundingThis research work is done by self-funding.Data AvailabilityThe data being used to support the findings of this research work are available from the corresponding author upon request. Competing InterestsThe authors declare no potential conflict of interests in this research work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledged the authority of North East Medical College, affiliated with Sylhet Medical University, Sylhet, Bangladesh for kind supports.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML