-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2021; 11(11): 769-773
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20211111.05
Received: Oct. 20, 2021; Accepted: Nov. 3, 2021; Published: Nov. 15, 2021

Combined Antinociceptive Effects of α-Tocopherol and Ketorolac in Acetic Acid Induced Writhing Test
Mahadi Abdur Rouf, Md. Mizanur Rahman
Department of Physiology, Ad-din Akij Medical College, Boyra, Khulna, Bangladesh
Correspondence to: Mahadi Abdur Rouf, Department of Physiology, Ad-din Akij Medical College, Boyra, Khulna, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Studies on animals and humans have demonstrated that alpha-tocopherol (αT) has antinociceptive effects whether used alone or in conjunction with other analgesics to treat a wide range of painful and inflammatory conditions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ketorolac tromethamine (KT), are used to treat pain and inflammation, but they frequently induce gastrointestinal problems. The goal of this study is to see if combining αT with ketorolac is a superior anti-nociceptive drug than ketorolac alone. A prospective experimental study was conducted in the Department of Physiology at Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University (BSMMU) in Dhaka from March 2015 to February 2016 to examine how efficient a combination of ketorolac and α-tocopherol is at reducing nociceptive discomfort. 15 (fifteen) Long Evans rats (215±35 gm) of either sex were used in this study. The rats were separated into three (3) groups based on vitamin and medication treatments (5 rats in each). One group received 10mg/kg of ketorolac tromethamine (KT), whereas the other received a combination of KT and αT at 10mg/kg and 500mg/kg body weight, respectively. 1 hour before the test, each group got a single dosage of the same volume (1ml) administered intraperitoneally. They were put through an acetic acid-induced writhing test just one hour after receiving the drugs. For statistical analysis, ANOVA was employed, followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. The significance level for interpreting the results was set at p≤0.05. The variables for visceral nociceptive pain and inflammatory pain were significantly reduced (p≤0.05) when KT and αT were given combinedly than when KT was given alone. This study suggests that combining αT and KT in a single dose may be more beneficial than administering KT alone in reducing nociceptive and inflammatory pain.
Keywords: Analgesic, Nociceptive pain, α-tocopherol, Ketorolac, Writhing Test
Cite this paper: Mahadi Abdur Rouf, Md. Mizanur Rahman, Combined Antinociceptive Effects of α-Tocopherol and Ketorolac in Acetic Acid Induced Writhing Test, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 11, 2021, pp. 769-773. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211111.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction and Background
- Pain is a distressing sensory and emotional sensation that is associated with or defined by tissue damage that has occurred or may occur [1]. As a result, pain and suffering are common, making it the most common reason for a doctor's appointment [2,3]. Pain associated with acute tissue damage, disease, or intervention is a symptom, and it is a common presenting sign in a range of medical conditions [3]. Furthermore, peripheral nerve fiber stimulation causes nociceptive pain, which is an essential physiologic sensation. The thresholds or sensitivities of nociceptor receptors are distinct [4]. Which serves as an important early warning system for tissue harm [5]. Mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical types of nociceptive pain exist [5,6]. "Pain caused by injury activating nociceptors in peripheral tissue [1,7]" is one way to describe it. To establish the severity of the illness, pain must be measured. It's also important for choosing the proper analgesics. Another acceptable method for evaluating nociceptive and inflammatory pain behaviors in animal models is the acetic acid induced writhing test, which is sensitive to several analgesic medicines. Abdominal muscle contractions and hind limb stretching is part of the writhing reaction in this test. Both opiates and non-opiate analgesics are detected by this test [8]. Ketorolac tromethamine (KT) is a potent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is commonly used to treat severe acute pain caused by inflammation that requires immediate analgesia, such as postoperative pain, renal colic, arthritis, lumbago, headache, and cancer pain [9,10]. Studies have been conducted around the world to find analgesic alternatives that can replace or at the very least shorten the duration of drug therapy, to minimize any negative effects of the medicine [11,12]. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, and among its eight naturally active forms, α-tocopherol is the most physiologically active [13,14]. Antinociceptive properties of α-tocopherol, a relatively straightforward ROS scavenger, have been demonstrated in several animal experiment trials [15]. αT's antinociceptive action is assumed to be due to a mechanism that inhibits anti-inflammatory effects, and it is expected to be beneficial in both acute and chronic pain management. Furthermore, it has been proposed that αT may work in conjunction with NSAIDs to lower gastrointestinal inflammation and pain in patients with peptic ulcer disease [15-17]. However, a single dose of 10 mg/kg KT has been reported to be sub-effective in the treatment of nociceptive pain [18]. It has also been suggested that in the treatment of pain, combining analgesics with antioxidants may be used to reduce analgesic doses [19]. However, the available knowledge on this subject is insufficient to draw any firm conclusions. The combination analgesic effects of αT and KT were not reported to be comparable to the effects of their solo administration on nociceptive pain.
2. Objectives
- Taking all of this into consideration, the current study aims to compare the combined analgesic effects of Ketorolac and αT administration in Long Evans rats with their separate analgesic effects in order to determine their analgesic efficacy.
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Study Design
- From March 2015 to February 2016, this prospective experimental study was done in the Pain Laboratory of the Department of Physiology at Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University (BSMMU), Shahbag, Dhaka. All experiments and animal care were conducted under the guidelines established in the 'Manual for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals' by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee (AEEC) of the International Centre for Diarrheal Disease Research, Bangladesh (icddr,b 2002) [20] and was approved by the BSMMU's institutional review board (IRB).
3.2. Procurement and Maintenance of Animals
- Fifteen (15) apparently healthy adult Long Evans rats weighing 180-250 g [11] of either sex [18,21] were provided by the Bangladesh University of Health Sciences (BUHS) in Dhaka. It was 12/12 light/dark for the rats [22]. The rats' thermo-neutral zone was regulated between 27 and 28°C [23]. All rats had free access to a conventional laboratory diet and cooled boiled water [11]. They were held there for seven (7) days before the trial to acclimate. To avoid circadian effects, all trials were conducted between 08:00 and 16:00 hours [24].
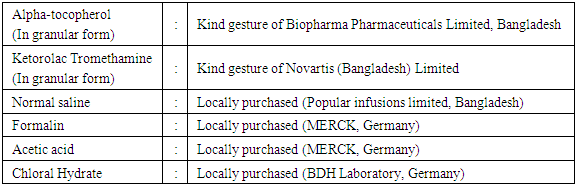
3.3. Vitamins and Drugs Collection
3.4. Grouping and Dose Schedule
- The rats were separated into three (3) groups based on vitamin and medication delivery (5 rats in each). The control group received normal saline at a dose of 5ml/kg body weight [24], one experimental group received ketorolac tromethamine (KT) at a dose of 10mg/kg body weight [18], and another experimental group received KT and αT at doses of 10mg/kg body weight and 500mg/kg body weight, respectively. 1 hour before the test, each group got a single dosage of the same volume (1ml) administered intraperitoneally. They were treated to an acetic acid induced writhing test just one (1) hour after injection [25].
3.5. Writhing Test
- Before the test, all rats were marked for the writhing test and placed in the plexiglass observation chamber for 30 minutes daily for seven (7) consecutive days. On the day of the experiment, the rats were initially placed in a Plexiglass observation room and given 30 minutes to acclimate to the chamber atmosphere. They were then intraperitoneally injected with normal saline, KT, or a combination of αT and KT, as appropriate for the paradigm of the experiment. One (1) hour later, using a 25-gauge syringe needle, one (1) cc of 2% acetic acid was administered intraperitoneally. The latency of the first writhe and the number of writhes were counted immediately following the injection and up to 60 minutes into the observation period. Finally, we estimated the proportion of analgesic action using the formula below [26-29]:

3.5.1. Latency Time
- Period between acetic acid administration and the onset of the first writhing.
3.5.2. Writhing
- Abdominal muscle contraction followed by hind limb extension. The results are expressed as mean standard error of the mean, and the data were evaluated statistically using ANOVA and the Bonferroni's post hoc test. The level of significance for interpreting the results was determined to be p≤0.05.
4. Results
4.1. Antinociceptive Effects
- The writhing test was used to assess the effects of intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of KT and its combination with αT. The latency time and percentage of analgesic activity were evaluated in this test to determine nociceptive pain behavior.
4.2. Nociceptive Pain
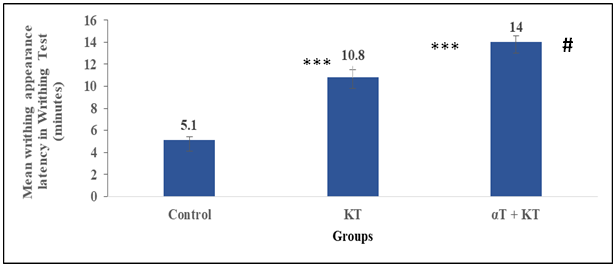
- The mean values of this measure in the study groups were significantly (p≤0.001) lower than the mean values of this measure in the control group in the writhing test. It was shown that this variable was significantly (p≤0.05) lower in the combined administered group as compared to that of the ketorolac administered group. (See Figure 1A.)
5. Discussion
- For as long as humans have been experiencing pain, they have attempted to explain it. It is essentially a biological protective device [30], which is required for an organism's existence and integrity. It notifies a man of actual or possible tissue damage and initiates defensive actions, but it also causes him anguish and distress, making it the most common reason for a physician visit [4]. Numerous compensatory mechanisms exist in the human body for limiting the initiation of pain and blocking the channel of pain transmission. Additionally, there are other analgesics available to alleviate pain, but they all have a variety of negative effects. Thus, the hunt for innovative medications with fewer adverse effects for the treatment of pain is a critical area of research today. With this in mind, the current study examined the analgesic effects of the conventional analgesic ketorolac in conjunction with α-Tocopherol and compared them to the effects of ketorolac alone.
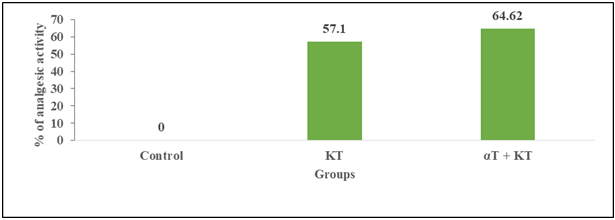 | Figure 1B. The percentages (%) of analgesic activity were more in combined treatment of αT and KT (64.62%) than single administration of KT (57.10%) |
- The standard test for detecting visceral nociceptive and inflammatory pain is writhing in reaction to acetic acid. It is an outward manifestation of pain caused by irritating substances. This test is capable of detecting opiates as well as non-opiate analgesics. The writhing test delivers a signal to the central nervous system in response to irritation-induced pain and the synthesis of endogenous mediators such as bradykinin and prostaglandin, both of which contribute to increased receptor sensitivity [8]. In our current study, the combination of ketorolac and vitamin significantly (p≤0.05) lowered the variable for nociceptive response compared to a single injection of ketorolac. Though the particular mechanisms underlying these effects were not revealed in this study, other investigators from various countries postulated numerous pathways for nociceptive pain reduction. α-tocopherol may alleviate nociceptive pain by raising the central nervous system's GABA activity, which suppresses central nociceptors [7,31]. On the other hand, KT's antinociceptive impact may be attributable to its stimulation of the NO–cyclic GMP pathway, which results in the opening of ATP-sensitive K+ channels at the peripheral level [32]. The K+ channels open, allowing this ion to seep out of the postsynaptic neurons and hyperpolarize it, reducing pain conduction [7]. Additionally, ketorolac may exert a modulatory effect on central opioid pharmacology [33]. Though the exact method by which the combination administration enhanced effectiveness could not be determined directly from this experiment, concurrent activation of numerous pain-relieving pathways may be a feasible explanation.
6. Conclusions
- As a result of this study, it may be inferred that combining αT and KT may be more successful at reducing nociceptive pain than administering KT alone. This evidence may persuade doctors and the general community to use αT in conjunction with KT to improve pain treatment. Although additional experimental studies are necessary to establish the precise component and mechanism underlying these effects.
7. Limitations
- The acute antinociceptive effects were seen using a single-dose test rather than a multi-dose test. Due to time and funding constraints, we were unable to finish the chronic antinociceptive and histological changes in the liver and inflamed paws.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are grateful to Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University and Physiology Department, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University.
Conflicts of Interest
- The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML