-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2021; 11(10): 722-724
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.12
Received: Sep. 25, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 23, 2021; Published: Oct. 30, 2021

Microalbuminuria as Early Diagnosis in Diabetic Kidney Diseases
Zulfiya Amangaldiyevna Sapaeva
Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Zulfiya Amangaldiyevna Sapaeva, Urgench Branch of Tashkent Medical Academy, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Timely diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy in the early stages in patients with diabetes mellitus diabetes is a very important task. There were 60 patients under observation type 2 diabetes mellitus. The functional state of the kidneys was assessed by the level of creatinen urine, as well as the level of microalbuminuria in the morning urine portion. According to the results of the research. The amount of albumin in the urine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the level of the studied parameter in urine was 102.8 ± 6.1 mg/l, which in both cases exceeded the average value of the norm. Timely detection of microalbuminuria can help diagnose diabetic nephropathy already in the early stages of its development. Formation of a risk group for developing diabetic nephropathy based on the timely determination of microalbuminuria will improve the effectiveness of therapeutic and prophylactic measures in patients with diabetes mellitus and the development of diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, Diabetic nephropathy, Microalbuminuria, Macrovascular complication, Microvascular complication, Proteinuria
Cite this paper: Zulfiya Amangaldiyevna Sapaeva, Microalbuminuria as Early Diagnosis in Diabetic Kidney Diseases, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 10, 2021, pp. 722-724. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.12.
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic human diseases, it causes the development of micro- and macrovascular complications, which are the main cause death of patients [5,8]. Among microvascular complications, the most important is the diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic nephropathy that manifests itself persistent proteinuria, arterial hypertension and a decrease renal function, is the cause of end-stage renal failure efficiency [2,4,7].At the present stage of development of medical science, reliableny and early preclinical criterion of glomerular damage of the kidney apparatus in diabetes mellitus is a microalbuminuria - highly selective urinary protein excretion, in which only low molecular weight protein is detected in the urine - albumin. The main mechanisms of development of microalbuminuria are glomerular hyperfiltration and damage vessels. In diabetes mellitus, microalbuminuria is not is only a predictor of diabetic nephropathy, but and is associated with a high risk of developing cardiovascular complications associated with increased general and cardiac but-vascular mortality [4,8,9].According to various researchers, microalbuminuria occurs in 25-40% of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The frequency of detection microalbuminuria increases with increasing duration of the disease [1,3,6].The aim of the study was to assess microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
2. Materials and Methods
- In this work, 120 patients were examined, of which 60 (83.3%) - patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and 20 (16.7%) - persons without disorders of diabetes mellitus. For research two observation groups were formed: the 1st group - patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 (60 patient); 2nd group - control (20 people).Diabetes mellitus was diagnosed based on complaints: history of the disease, the nature of the clinical course, results of objective and laboratory-instrumental examinations in accordance with diagnostic criteria. Functions the general state of the kidneys was assessed by the level of urine creatinine, as well as the level of microalbuminuria in the morning portion of urine and, if necessary, proteinuria in urine collected per day.Results were subjected to analysis of variance with the calculation of the average ariphmetic and its errors for each group. As the threshold level of statistical significance was adopted p-value<0.05.
3. Results
- Clinical examination data showed that, in the group of patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 disease duration up to 5 years was noted in 26 (43.4%) patients, from 6 to 10 years old - in 21 (35%) and more than 10 years – in 13 (21.6%) patients. In our study, the diagnosis of diabetes nephropathy at the stage of microalbuminuria was established new in 32 (53.4%) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Have of all examined persons of the control group noted the normalbuminuria. The urine creatinine level was determined in all patients. In microalbuminuria and albumin/creatinine ratio.The research results are presented in diagram 1.
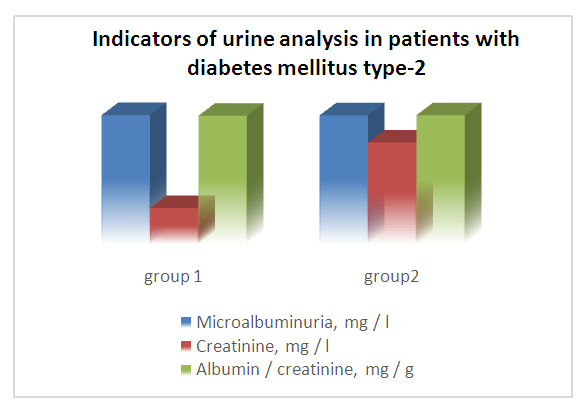 | Diagramm 1. Indicators of urine analysis in patients with diabetes mellitus type-2 |
4. Conclusions
- Thus the detection of microalbuminuria can help diagnose diabetic nephropathy early their stages of development. Formation of a risk group for development diabetic nephropathy based on timely determination division of microalbuminuria will improve the efficiency therapeutic and prophylactic measures in patients with diabetes mellitius and prevent the development of diabetic nephropathy.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML