-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2021; 11(10): 718-721
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.11
Received: Sep. 25, 2021; Accepted: Oct. 20, 2021; Published: Oct. 30, 2021

Improving the Effectiveness of Medical and Social Assistance to the Population of Secondary Medical Staff
V. N. Turakulov, N. A. Narmukhamedova
Center for the Development of Professional Qualifications of Medical Workers, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In each country, health care services are provided through the health care system. This system is made up of various organizations, institutions, institutes, resources and people whose purpose is to promote, restore and maintain health. According to a report by the World Health Organization, everyone applies to the primary health care system. Primary health care system refers to the institutions that provide basic health services: multidisciplinary central polyclinics, family clinics and family doctor's offices. They must provide the population with quality medical services. The population applies to such institutions of the health care system located in the area where they live and work.
Keywords: Health services, Patronage, Pediatrician, Primary care
Cite this paper: V. N. Turakulov, N. A. Narmukhamedova, Improving the Effectiveness of Medical and Social Assistance to the Population of Secondary Medical Staff, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 10, 2021, pp. 718-721. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Everyone is forced to visit these facilities several times in their lifetime and consult a midwife during the visit. The nurse listens to their problems and decides what to do. That is, it directs you to the necessary specialist examination and doctor's appointment. The socio-psychological condition of the visiting patient depends on the impression he received from the first meeting and the interaction with the staff working in the primary system. This means that the activities of secondary health employees play an important role in the quality and efficiency of health care services provided to the population [3].Secondary medical staff face a variety of situations during their activities. They have to deal with a variety of patients throughout the day. This, in turn, requires them to withstand stress and adhere strictly to medical ethics and deontology. But, unfortunately, sometimes the problems in the personal life of nurses and socio-economic difficulties make the staff of this field very tired [4].Every unresolved problem of a paramedic over time causes them to change psychologically (nervousness, lack of attention, indifference to what is happening around them). If this is not addressed in a timely manner, the employee will face serious changes in health. Because human health is affected by personal, economic, social, environmental and many other factors. They are usually called health determinants. Such factors include the following.• Human behavior and lifestyle: quality of food consumed, daily activities, tobacco products, alcoholism, level of stress management; • Income and social status: rich and poor, place in society; • Employment and working conditions; • Education: level of knowledge, level of knowledge of medical culture; • Social assistance branches: family environment, level of assistance provided by the community;• Culture: traditions, family and social traditions, beliefs; • Gender: what gender (male, female); • Environmental conditions: water, air purity, living and working conditions; Some of the above factors can be controlled: for example, this or that person can choose a healthy or unhealthy lifestyle [5].Various strategies and actions are also aimed at developing certain skills in individuals, changing social, economic, and environmental conditions for the positively, thereby reducing the negative impact of these factors on nurse health.
2. Purpose
- Development of targeted measures to improve the psychological environment in primary care facilities, identify and eliminate factors that negatively affect the work of secondary health workers, as well as the quality of work and services.
3. Materials and Methods
- In order to improve the quality of work of secondary medical staff in Navoi region, research was conducted and a medical examination and social survey were conducted among employees of primary health care. The event was attended by about 1,200 secondary medical staff. The survey was designed for three main purposes:1) to study the extent to which the above factors affect the health of the nurse;2) job satisfaction and the correct organization of the work process and work ethic are assessed; 3) the employee's level of knowledge, professional skills and work experience are studied; serves to develop measures based on the results obtained.The questionnaire consists of 100 questions, mainly in the areas of social status, level of education, work ethic, professional potential, attitude to issues in the system. Of the 1,200 respondents, 1,144 (95.7%) were female and 51 (4.3%) were male. The majority of respondents are community nurses - 77.3%, nurses working in other positions - 17.2%, midwives - 2.2% and senior nurses - 3.4%. The average age of those surveyed was 34 years.
4. Results and Their Discussion
- While most nurses work 6 days a week (92.5%), 7.5% of participants reported working 5 days a week. 3.6% of respondents have 1 to 5 years of experience, 19.9% have 6 to 10 years of experience, 1.3% have 11 to 15 years of work experience, 52.9% have 16 to 20 years of work experience, and 0.2% have 21 to 25 years of work experience. 22.4% were found to be 26 to 30 years old, while 0.7% indicated work experience higher than 31 years. The figures show that more than half of the respondents have up to 30 years of work experience, while low-skilled employees are very scarce. This means that the contingent of primary health care facilities is more stable.Among the nurses who answered the questionnaire, the category was 49.6%, the highest category - 22.6%, the first category - 11.1%, the second category - 16.2%, the category (category). Due to the lack of a category, the majority of employees said that 41.1% still have a term of 1-2 years, and 8.5% said that the term comes in 3-5 years. 53.1% of respondents said that professional skills would increase if the category increased, 28.4% said that self-confidence would increase, 16.4% of respondents chose to increase their salary, and only 0.6% of respondents chose the option of prestige in front of employees. It can be concluded that in this system, the midwife does not have a special status and the classification can lead to an increase in prestige. Those who are financially interested in this are in short supply (Figure 1).
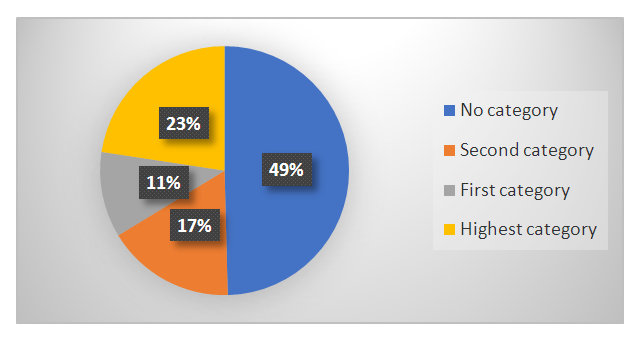 | Figure 1. Distribution by categories |
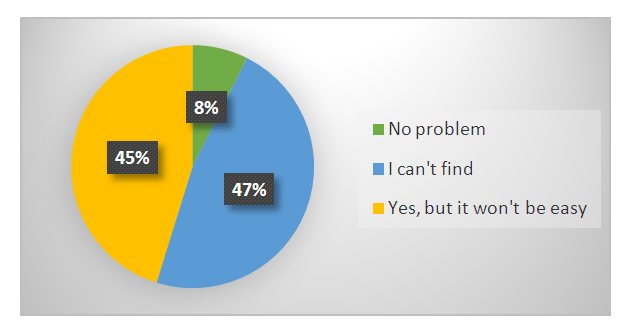 | Figure 2. Risk of losing your job and being able to find another job |
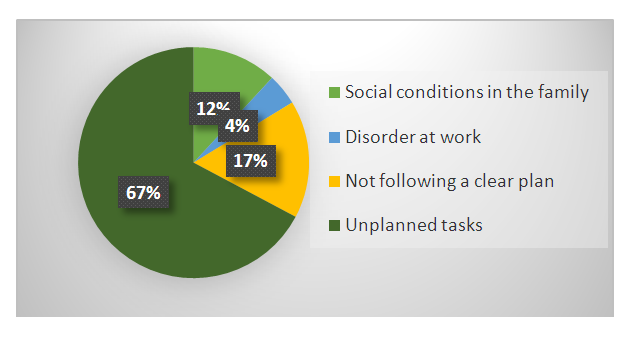 | Figure 3. Negative factors affecting an employee’s life |
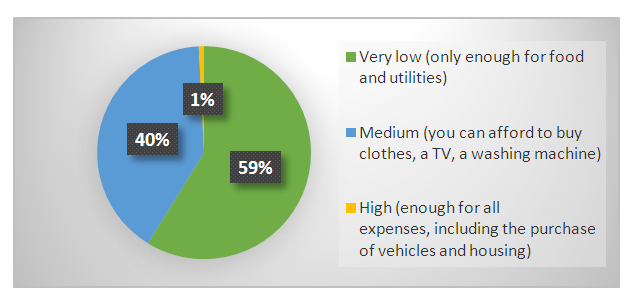 | Figure 4. Amount of salary received |
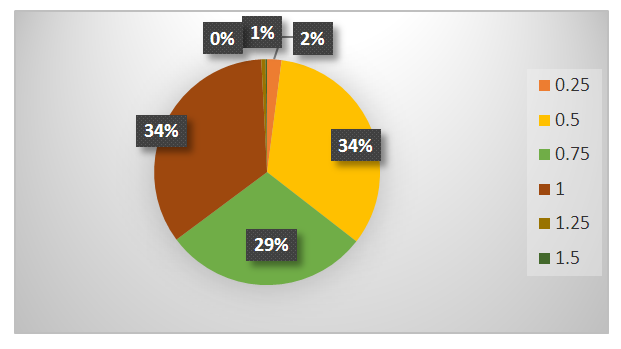 | Figure 5. Distribution by work rate |
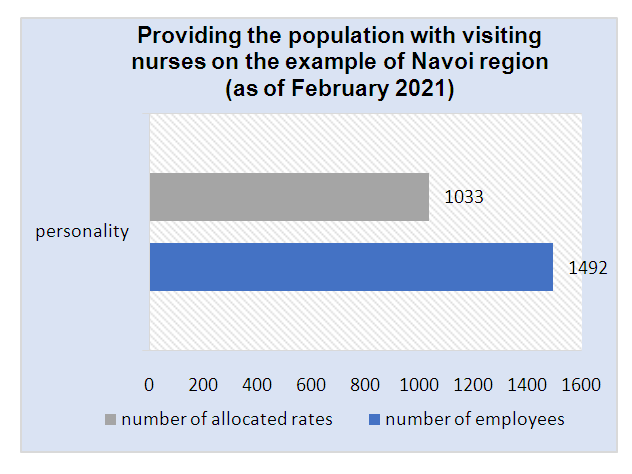 | Figure 6. Status of provision of patronage nurses |
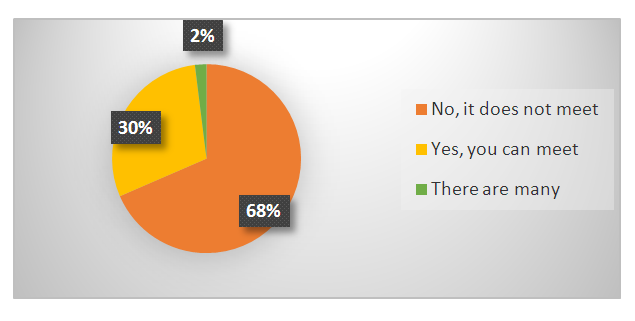 | Figure 7. Teamwork perception of employees with low level of professional training and knowledge |
5. Conclusions
- The times are rapidly evolving, and the medical sector and health care system are in need of reform in recent years, including the need to raise the efficiency and quality of primary health care and adapt to the medical system of the world's leading countries.It is necessary to protect the work of medical employees and increase their social status, as well as to implement measures to identify the factors of stress and occupational fatigue in these employees.Primary health care facilities need to train secondary health employees as physician assistants in training and to perform a wide range of practical skills.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML