Ziyavidenova S. S., Vypova N. L., Enikeeva Z. M., Agzamova N. A., Nishanov D. A., Madaliev A. A., Alimkhodjaeva L. T.
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
Aim of the study was evaluation of the new drug Dekoglitz safety in the study of acute and chronic toxicity in rats after oral administration.Material and methods: The study of chronic toxicity was performed on 40 rats with 30-fold oral administration of the drug at doses of 13.0, 26.0 and 68 mg/kg. Hematological and biochemical studies were performed 10 and 30 days after the start of the experiment, and in some animals - after 1 month of the recovery period. Changes in the clotting process under the influence of drugs were judged by the records of thromboelastograms performed on the thromboelastograph “Thromb-2”. Morphological studies of the obtained organs were carried out. The differences were considered significant at p<0.05.Results: With repeated oral administration to rats, the drug does not affect the behavior and weight dynamics of animals, does not have a toxic effect on the composition of peripheral blood, kidney function. But it increases alanine aminotransferase in the liver which indicates that the drug has a toxic effect on liver function in rats. There is a multidirectional effect on the blood clotting process. However, after 1 month of the recovery period, all these indicators changed within the physiological norm. Pathomorphological examination of the rats internal organs showed that isolated dystrophic changes were noted when using doses of 13 and 26 mg / kg - at these doses, the drug does not show toxicity when it affects the internal parenchymal organs. At a dose of 68 mg / kg the drug shows low toxicity. Conclusion. All the above mentioned data allow us to conclude that the drug does not have a pronounced toxic effect on the animal body.
Keywords:
Drug "Decoglitz", Oral administration, Chronic toxicity
Cite this paper: Ziyavidenova S. S., Vypova N. L., Enikeeva Z. M., Agzamova N. A., Nishanov D. A., Madaliev A. A., Alimkhodjaeva L. T., Study of the Toxic Features of the Antitumor Drug Decoglitz, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 10, 2021, pp. 705-710. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.08.
1. Introduction
Currently, antitumor drugs are largely created from natural compounds and there are dozens of such effective drugs known in oncology.We created new less toxic and more active than the original alkaloids, as well as other mitosis-inhibiting agents, antitumor drugs on the basis of colchicine and colhamine [1]. The new drug Decoglitz is a supramolecular complex derived from decocin which was synthesized from colchicine and glycyrrhizic acid.Decoglitz is 2.6 times less toxic than decocin, from which it was created and when administered orally to rats, the drug Decoglitz belongs to the VI class of relatively harmless compounds, and with intraperitoneal administration - to the V class of practically non-toxic substances. Decoglitz, by its antitumor activity, exceeds the effect of decocin by 15-30% on a number of animal tumors, as well as 5-fluorouracil and etoposide (ascitic and solid Ehrlich tumor, Sarcoma 180, C-45 and ovarian tumors (OT)) [2-4]. It should be also noted that the new drug Decoglitz shows fewer side effects than comparison drugs [3-4], in addition, Decoglitz is intended for the treatment of tumors in oral form. The data obtained indicate the prospects of this substance for successful use in the clinic. To further promotion of the drug, it was necessary to find out its side effects which were solved by studying its chronic toxicity.Aim of the drug "Decoglitz" chronic toxicity studies was to establish the nature and severity of its damaging effect on the body of experimental animals and to assess its safety.
2. Material and Methods
The general toxic effect of the drug Decoglitz with repeated oral administration was studied on 40 non-linear white rats (males and females) with an initial weight of 160±15g. The experimental animals were divided into 3 groups, 10 rats (5 males and 5 females) in each.The drug has been administered orally daily (7 days a week) to rats at doses of 13.0, 26.0 and 68 mg/kg for 30 days. The control animals received distilled water in a bioequivalent volume.All pharmacological studies were carried out on healthy mature animals that had been quarantined for at least 10-14 days. The animals were kept on a standard diet under natural lighting conditions and had free access to water and food in the vivarium at the Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center of Oncology and Radiology.At the end of the experiment, all rats and mice were euthanized under ether anesthesia, in accordance with the International Rules for the Protection of Vertebrates. All experiments were performed in accordance with the recommendations and requirements of the “World Society for the Protection of Animals (WSPA)” and “European Convention for the Protection of Experimental” (Strasbourg, 1986).The condition of animals with intraperitoneal chronic administration was assessed by the following parameters of peripheral blood: hemoglobin (Hb)content, g/dl; the number of red blood cells, 1012/l; reticulocytes, %0; platelets, 109/l; leukocytes, 109/l; the average volume of erythrocytes MCV, n, the average concentration of hemoglobin in the erythrocyte MCHC, g / dl, color indicator MCH, n / g and leukogram; evaluation of liver function by glucose content, mmol/l; total protein, g/dl; alanine - and aspartate - aminotransferase (ALT, AST) U/E hour in blood serum, on a semi-automatic biochemical analyzer «Rayto Life and Analytical Seiences Co., Ltd» using the test kits by Cypress Diagnostica, Belgium. The effect of the drug on coagulogram parameters was determined on a single-channel coagulometer of HUMACLOT Junior (Germany) with the use of reagents by Cypress Diagnostics, Germany (prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thrombin time (APTT) and fibrinogen (F).Kidney function was judged by diuresis with a water load (5% of body weight) for 4 hours, blood urea, urine acidity (pH), the presence of nitrites, glucose, leukocytes in urine, etc. (qualitative reactions) with the help of a set of Combina, Germany and urinary precipitation.Hematological and biochemical investigations were performed 10 and 30 days after the start of the experiment and in some animals - after 1 month of the recovery period. At the same time the body weight of the animals was determined. At the end of the experiment, some of the animals were slaughtered by decapitation and material was taken for pathomorphological studies according to the list approved by the Pharmacological Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan 5-7. Some of the animals were left to study the recovery process. Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out with the determination of the Student's criterion using statistical programs WindowsExcel 2010.
3. Results
The results obtained with chronic oral administration of drug Decoglitz to rats are presented in Tables 1 and 2. The data obtained show that after 10 and 30 days of administration, there were no significant deviations in the composition of the peripheral blood of rats: in the content of hemoglobin, erythrocytes, in the number of blood cells themselves, its precursors (reticulocytes), as well as leukocytes. The indicators of the leukocyte formula in rats are within the physiological norm. On the basis of obtained data it can be concluded that the drug Decoglitz, when administered orally chronically, does not have a toxic effect on the quantitative composition and morphology of the peripheral blood of experimental animals.Table 1. Morphological structure of peripheral blood of rats after 10 days with oral administration of the drug Decoglitz (М±m; n=5)
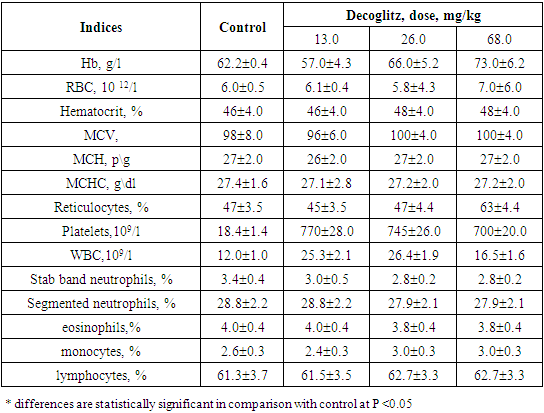 |
| |
|
Table 2. Morphological structure of peripheral blood of rats after 30 days with oral administration of the drug Decoglitz (М±m; n=5)
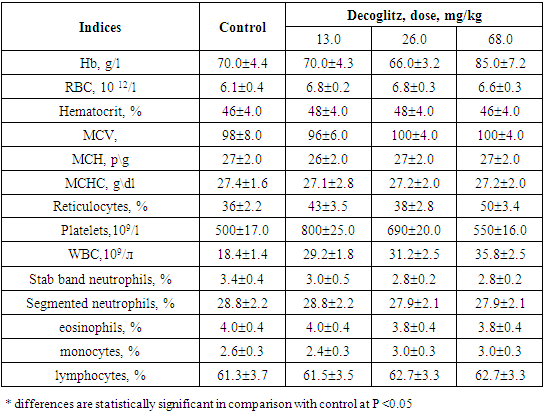 |
| |
|
When studying the effect of the drug Decoglitz on some rat urine parameters, on the 10th and 30th days of the experiment in chronic experience, it was shown that after 10 administrations at doses of 13 and 68 mg / kg, the drug did not change diuresis, and at a dose of 26 mg / kg, it reduced it by 3.5 times. After 30 days of the experiment at a dose of 13 mg / kg diuresis did not differ from the control, at a dose of 26 mg/ kg it was 2.2 times less, and at a dose of 68 mg/kg it was 21% higher than in the control group of animals. The urea quantity in the blood of rats at a dose of 13 mg /kg varied within the normal range, and at doses of 26 and 68 mg/kg it was increased by 25-33%. Semi-quantitative indices of urine (bilirubin, glucose, blood, leukocytes, nitrites, etc.) did not differ in experimental and control rats. The acidity of urine in all studied groups did not change during the entire experiment, and its pH was 6.5-7.0. Pathological changes in the content of urine sediments were not detected. The results obtained allow us to conclude that the drug does not have a toxic effect on kidney function.Liver function in trials on rats was studied by the most sensitive tests after 10 and 30 days of the experiment. The level of glucose, protein, and AST enzyme activity in all experimental rats after 10 and 30 days of the experiment did not differ from the control in blood serum. At a dose of 13 mg/kg, ALT increased 3 times after 10 days and 5 times after 30 days. An increase in ALT was also observed at a dose of 26 mg/kg after 30 days of the experiment (2.5 times) (Tab. 3).Table 3. Some indicators of liver function of rats treated with the drug Decoglitz in a chronic trial (М±m; n=5)
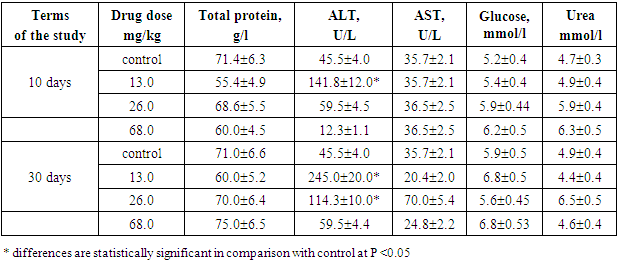 |
| |
|
Thus, the drug Decoglitz, when administered orally daily to rats at doses of 13.0, 26.0 mg / kg, significantly increased ALT and it indicated that the drug had a toxic effect on the liver function of rats. Since the drug Decoglitz will be used parenterally, it was necessary to find out how the blood clotting process would change with its repeated use. As it can be seen from the coagulogram indicators shown in Table 4, under the action of the drug Decoglitz, after 30 days of oral administration, the prothrombin time decreased by 5 - 33%. The deficiency of the prothrombin complex and the activity of the external coagulation pathway are judged according to this test. The normal content and quality of fibrinogen depends on the content of factors II, V, VII, X (activity of the prothrombin complex). The synthesis of these coagulation factors in the liver depends on the presence of vitamin K in the body, the antagonists of which are indirect anticoagulants or anticoagulants of indirect action (AIA). Therefore, a prothrombin test is used to monitor therapy with indirect anticoagulants.Table 4. Indices of the coagulogram of rats on day 30 with chronic oral administration of the drug Decoglitz (M±m; n=10)
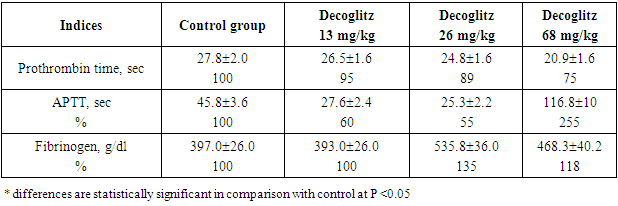 |
| |
|
The APTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time) test is used to evaluate the effectiveness of the internal coagulation pathway and to monitor patients receiving heparin. Prolonged APTT indicates hypocoagulation and can be observed with: deficiency of factors XII, XI, X, IX, VIII, V, II or fibrinogen, the presence of both pathological and other blood clotting inhibitors. In our experiment, this indicator decreased by 72% and 81% at doses 13 and 26, and increased by 155% at a dose of 68 mg/kg, while the amount of fibrinogen increased by 18-35% (Tab. 4).Thus, even with repeated subchronic administration, Decoglitz had a multidirectional effect on the blood clotting process, mainly on APTT.The dynamics of the body weight of experimental animals with oral chronic administration of Decoglitz differed from the control. The weight of animals in the control and experimental groups after 10 days increased by 11-14%, and after 30 days of the experiment - by 28-32% in relation to the initial indicators. The animals throughout the experiment were active, neat, ate food normally, drank water, their fur was smooth, shiny. The behavior of the experimental rats did not differ from the behavior of the animals from control groups. Macroscopic examination of slaughtered animals revealed the correct location of internal organs. There was no free fluid in the pleural and abdominal cavities. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity was clean, moist, characteristic color, edema, hemorrhages were not detected. The tissues of the lungs, stomach and intestines are also of a characteristic color, without signs of edema, hemorrhages and ulceration. Pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands unchanged (Tab. 5). Table 5. Dynamics of rats body weight with subchronic oral administration of the drug Decoglitz (М±m; n=10)
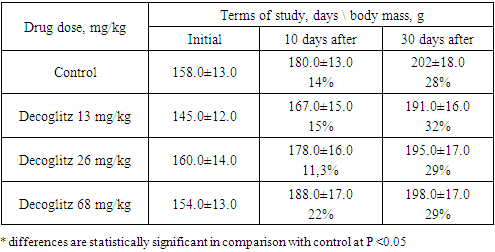 |
| |
|
4. Discussion
As it can be seen from the data given in Tables 6 and 7, the mass of animal organs of the experimental and control groups did not significantly differ from each other.Table 6. Averaged indicators of internal organs weight measurements, the mass coefficient of rats with oral chronic administration of the drug Decoglitz (М±m; n=5)
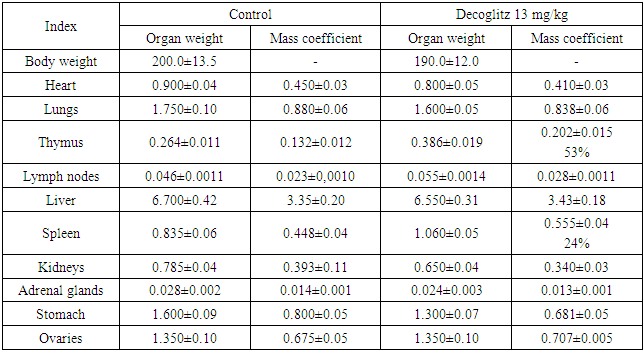 |
| |
|
Table 7. Averaged indicators of internal organs weight measurements, the mass coefficient of rats with oral chronic administration of the drug Decoglitz (М±m; n=5)
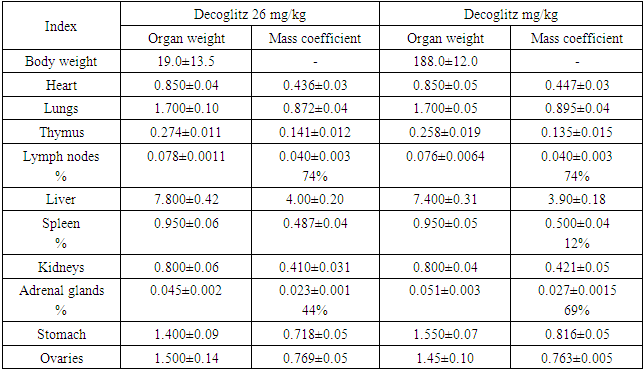 |
| |
|
As it can be seen from the results shown in Table 7, after 30 days of administration of the drug Decoglitz, an increase in the adrenal glands and lymph nodes was noted at doses of 26 and 68 mg / kg, which was most likely due to the presence of glycyrrhizic acid in the drug, and an increase in lymph nodes was connected with the effect of the drug on humoral immunity. So, the mass ratio of the adrenal glands increased by 44 and 69%, and the lymph nodes by 74 and 74%, respectively. All these indicators changed within the physiological norm after 1 month of the recovery period.As a result of a pathomorphological study of the internal organs of 3 groups of rats (lungs, liver, gastrointestinal tract, intestines, heart and spleen) after using Decoglitz for 30 days in a chronic experiment, it was shown:- in the first and second groups, when applying a dose of 13-26 mg / kg, single dystrophic changes were noted. In these doses, the drug does not show toxicity when affecting internal parenchymal organs; - in the third group, the use of the drug at a dose of 68 mg / kg was manifested by the presence of dystrophic changes and lymphocytic infiltration in individual loci of parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, lungs and gastrointestinal tract). At this dose, the drug showed little toxicity to internal parenchymal organs. Here is an example of the drug effect on the lungs. So, in the lungs of all rats of the first and, more often, the second group, the blood vessels around the bronchi and bronchioles were full-blooded. Areas of inflammation and isolated areas of anthrocosis were detected. In some places underdeveloped fibrosis was noted.Bronchial epithelial hyperplasia and lymphocytic infiltration were detected (Fig. 1).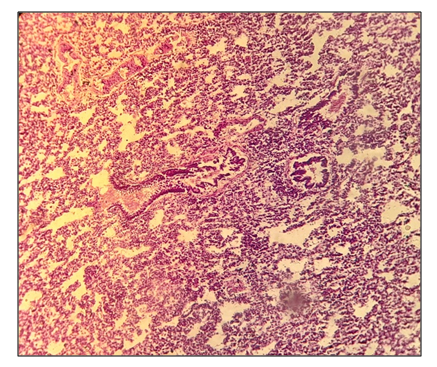 | Figure 1. Group 2. There are areas of bronchial epithelial hyperplasia and lymphocytic infiltration in some places |
In the third group, the blood vessels were full-blooded with signs of inflammation with lymphocytic infiltration. There was a single developed fibrosis in some places, the bronchial epithelium was hyperplasized. The vessels around the bronchi and bronchioles were full-blooded with areas of inflammation, with areas of anthrocosis (Fig. 2).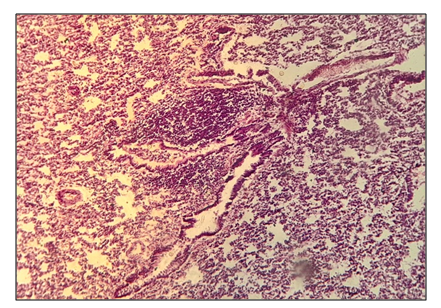 | Figure 2. Group 3. The vessels around the bronchi and bronchioles were full-blooded with areas of inflammation and lymphocytic infiltration |
Thus, a therapeutic dose of 13 mg/ kg, as well as a doubled dose of 26 mg/ kg is well tolerated by animals and does not have a toxic effect on the functions of vital organs and systems. The maximum dose of the drug 68 mg / kg in experimental animals shows low toxicity to internal parenchymal organs.
5. Conclusions
The conducted studies allow us to propose a new drug Decoglitz in a therapeutic dose in the form of tablets or capsules for use as a cytostatic agent.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been executed at financial support of fund of applied researches of Republic Uzbekistan (the project № FV 2020196206).
References
| [1] | Enikeeva Z.M., Ibragimov A.A. A new class of cytostatics with stimulation of colony-forming units on the spleen (CFUs) in Russian. Tashkent, 2016. "Fanvatexnologiya", p.173. |
| [2] | Enikeeva Z. M. Ibragimov A. A., Agzamova N.A., Vypova N.L., Saidhodjaeva S.S., Kholturaeva N. R., Abdirova A.Ch., Tuychiev O.D., Polatova J. Sh., Kadirova D. A., Salihov F. S. Study of the Antitumor Activity of the Drug Dekoglitz on Two Tumors and Some Aspects of Its Mechanism of Action. Journal of Oncology Research, Volume 3, 2021, р.11-16. |
| [3] | Agzamova N.A., Enikeeva Z.M., Ibragimov A.A., Saidhodzhaeva S.S., Kholturaeva N.R., Khasanova D., Tuichiev O.D., Umarov M.H. The activity of the drug decoglitz in rats with ovarian tumor and its effect on immunity in Russian. \\ Materіali V Mіzhnarodna naukovo-praktichna konferencіya «Lіki – lyudinі. Suchasnі problemi farmakoterapії і priznachennya lіkars'kih zasobіv» Kharkiv, March 11-12, 2021, p.181-184. |
| [4] | Enikeeva Z.M., Agzamova N.A., Ibragimov A.A., Saidkhodzhaeva S.S., Kholturaeva N.R., Abdirova A.CH., Tuichiev O. Preclinical studies of the new drug decoglitz in Russian // INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC JOURNAL «GLOBALSCIENCEANDINNOVATIONS 2020: CENTRALASIA» NUR-SULTAN, KAZAKHSTAN, DECEMBER 2020, No. 6(11). p.84-88. |
| [5] | Lifshits V.M., Sidelnikova V.I. Medical laboratory tests inn Russian. Directory, M.: Triad-X, 2011. |
| [6] | Gatsura V.V. in the book: Methods of primary pharmacological research of biologically active substances in Russian, М., 2000. |
| [7] | Reference book. Physiological, biochemical and biometric indicators of the norm of experimental animals in Russian /ed. Makarova V.G. // St. Petersburg: Publishing house "LEMA". -2013. – p. 19-35. |




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML





