-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2021; 11(10): 669-672
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.02
Received: Sep. 8, 2021; Accepted: Sep. 27, 2021; Published: Oct. 15, 2021

Prospects of Using the Program to Determine Anthropometric Phenotypes and Psychophysiological Characteristics, Taking into Account the Polymorphism of Genes Responsible to Metabolism for the Selection of Young Athletes
Jalolova Vazira Zamirovna
Bukhara State Medical Institute named after "Abu Ali Ibn Sino", Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacolog, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Jalolova Vazira Zamirovna, Bukhara State Medical Institute named after "Abu Ali Ibn Sino", Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacolog, Uzbekistan.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

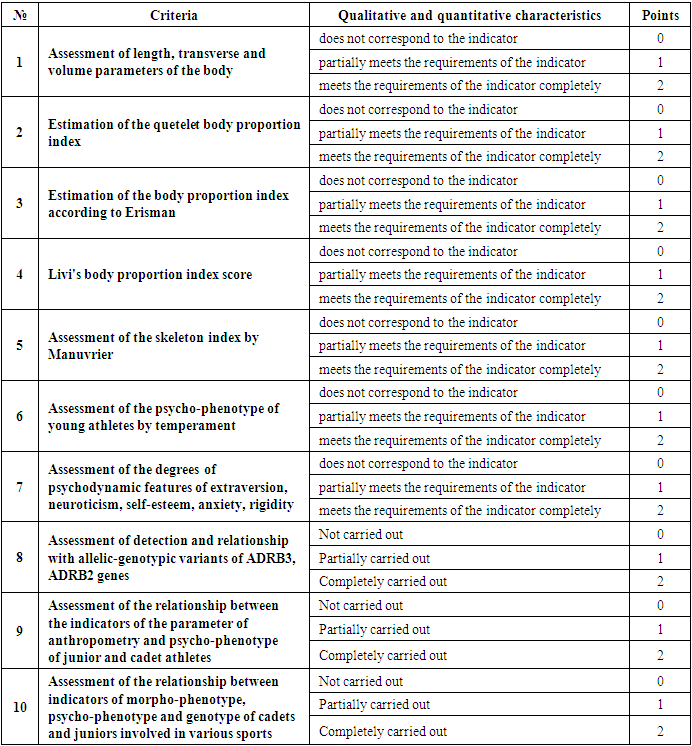
The level of results in modern sports is so high that in order to achieve them, an athlete must have rare morphological data, a unique combination of a complex of physical and mental abilities that are at an extremely high level of development (Platonov V.N., 2004). Therefore, one of the central problems in the system of training highly qualified athletes is the problem of sports selection. The last decades of world professional sports are characterized by the development of molecular genetic diagnostics, which develops the issues of choosing a sports specialization that are adequate to the genetic characteristics of athletes and allows for a scientifically based selection of children for practicing a particular type of physical activity. The aim of the study is to study the practical significance of the program we created for determining the anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics of young athletes, taking into account the polymorphism of genes responsible for the metabolism of junior and cadet athletes. 60 junior and cadet athletes were analyzed. All of them were divided into 3 main groups: All these athletes passed the test program, a questionnaire to determine the anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics of young athletes, taking into account the polymorphism of genes responsible for metabolism. As follows from the data obtained, athletes cadets and juniors who passed the test questionnaire according to the program prepared by us to determine the composition of the body and neurophysiological characteristics, the following result was obtained: 1 group of athletes who received from 0 to 7 points there were 18, 2 group of athletes who received from 8 to 14 made up 47 athletes, the 3rd group of athletes who received from 15 to 21 made up 10 junior and cadet athletes. The program can be used in sports schools for sports selection and identification of technical solutions, which in turn will help improve the level of sports achievements.
Keywords: Programs for determining anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics, Taking into account the polymorphism of genes responsible for metabolism, Selection of young athletes, Molecular genetic diagnostics
Cite this paper: Jalolova Vazira Zamirovna, Prospects of Using the Program to Determine Anthropometric Phenotypes and Psychophysiological Characteristics, Taking into Account the Polymorphism of Genes Responsible to Metabolism for the Selection of Young Athletes, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 10, 2021, pp. 669-672. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211110.02.
1. Introduction
- Often, the innate features of a person determine his capabilities in labor and sports activities. The combination of congenital morphological and functional characteristics characterizes a person's giftedness in a particular type of activity [1,8,9,18]. V.M. Volkov (1983) notes that the constant growth of sports results is possible only with the systematic and complex implementation of the selection and control of promising young athletes, taking into account their individual characteristics, which allow realizing the athlete's potential [2,3,5,7,11]. L.P. Matveev (2004) gives the concept of selection the following definition - it is a set of measures that allow to determine a high degree of predisposition (giftedness) of a child to one or another kind of sports activity (kind of sport) [4,6,10,12]. Obraztsova N.N. (2012) supplements this definition, speaking of sports selection as a set of activities that allow to determine a high degree of a child's predisposition to a particular sport based on abilities - a set of personality traits that correspond to 12 objective conditions and requirements for a particular activity and ensure successful its implementation [13,14,15,19]. At the same time, Devyatkina G. The. (2010) believes that sports selection is a long, multi-stage process that can be effective only if at all stages of the athlete's long-term training, a comprehensive methodology for assessing his personality is provided, involving the use of various research methods [16,17,20,30,31]. Balsevich V.K. (1994) in his works notes that sports selection is a process of making and implementing a decision to include or not include a possible participant in sports activity based on a scientific forecast [21,23,24,27].Sports genetics is one of the leading directions in the development of modern medicine, which will allow athletes to achieve high results. According to modern concepts of functional genomics, it is believed that individual differences in the degree of development of certain physical and mental qualities, as well as susceptibility to certain diseases of athletes, are largely due to DNA polymorphisms (variable regions in the DNA sequence). [22,25,28]. The study of such gene dependence is a new scientific direction in our republic - pharmacogenetics, one of the works in this direction is this work. DNA is a hereditary material that is identical in all cells of our body. A gene is a segment of the DNA chain responsible for the production of a specific protein. Genes contain information about where and when to produce the required protein, and also determine its composition, which is the basis of structural and functional features [26,28,29].Purpose. The аim of this work is to introduce modern computer programs that are designed to study and evaluate indicators of the composition of the body, types of the nervous system of junior and cadet athletes, as well as the relationship between the component composition of the body and allele-genotypic variants of the ADRB3, FABP2 gene in cadets and juniors engaged in various types of sports.
2. Materials and Methods
- On the basis of the obtained data of the point assessment, we analyzed 60 athletes, juniors and cadets. All of them were divided into 3 main groups: All these athletes passed the test program, a questionnaire to determine the anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics of young athletes, taking into account the polymorphism of genes responsible for metabolism.
3. Results and Discussion
- As follows from the data obtained, athletes cadets and juniors who passed the test questionnaire according to the program prepared by us to determine the anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics of young athletes, taking into account the polymorphism of genes responsible for metabolism, were divided into 3 main groups: 1 group, athletes who received from 0 to 6 their points were 14, the 2nd group of athletes who received from 7 to 14 was 36 athletes, the 3rd group of athletes who received from 15 to 21 was 10 athletes of juniors and cadets.
4. Conclusions
- Based on the above, the program for determining the anthropometric phenotypes and psychophysiological characteristics of young athletes, taking into account the polymorphism of the genes responsible for metabolism, can be used in sports schools for sports selection, which in turn will help to improve the level of sports achievements.
References
| [1] | Bal'sevich V.K. Vyyavleniye i razvitiye sportivnogo talanta/ V.K. Bal'sevich // Tezisy mezhd. Konf «Sovremennyye dostizheniya sportivnoy nauki» − SPb., 1994. − S. 3. |
| [2] | Bêseda V. V. Osoblivostí rukhovogo statusu dítey doshkíl'nogo víku kategoríí̈ «praktichno zdoroví» / V. V. Bêseda // Nauka í osvíta. – 2014. – № 4/SKHKHÍ. – S. 22–27. |
| [3] | Volkov V.M. Sportivnyy otbor/ V.M. Volkov, V.P. Filin - M.: Fizkul'tura i sport, 1983. - 176 s. |
| [4] | Gavrilova Ye. A. Sovremennyye predstavleniya o sindrome peretrenirovannosti / Ye. A. Gavrilova // Sportivnaya meditsina: nauka i praktika. – 2013. – № 1 (10). – S. 77–78. |
| [5] | Gladkov V. N. Nekotoryye osobennosti zabolevaniy, travm, perenapryazheniy i ikh profilaktika v sporte vysshikh dostizheniy / V. N. Gladkov. – M. : Sov. sport, 2007. – 386 s. |
| [6] | Grayevskaya N. D. Sportivnaya meditsina: kurs lektsiy i prakticheskiye zanyatiya / N. D. Grayevskaya, T. I. Dovlatova. – M.: Sov. sport, 2005. – 299 s. |
| [7] | Gur'yanov M. S. Sostoyaniye zdorov'ya i puti sovershenstvovaniya meditsinskogo obespecheniya detsko-yunosheskikh sportivnykh shkol: avtoref. dis. kand. med. nauk / M. S. Gur'yanov. – Kazan', 2002. – 22 s. |
| [8] | Guba V.P. Novoye v issledovanii problemy sportivnogo otbora i ranney oriyentatsii / V.P. Guba// Chelovek v mire sporta: Novyye idei, tekhnologii, perspektivy: Tez. dokl. Mezhdunar. kongr. - M., 1998. - T. 1. - S. 286. |
| [9] | Derevoyedov V. V. Professional'nyye zabolevaniya v sporte vysshikh dostizheniy / V. V. Derevoyedov. – M.: LFK i massazh, sportivnaya meditsina. – 2008. – №8 (56). – S. 3–6. |
| [10] | Kleyn K. V. Problemy vozrastnykh norm dopuska k zanyatiyam sportom detey i podrostkov / K. V. Kleyn, I. V. Nikolayeva, A. V. Lyulyushin // Materialy Í Vserossiyskogo kongressa «Meditsina dlya sporta». – M., 2011. – p. 196–198. |
| [11] | Efficency of PDT in severe cervical dysplsia.Akhmatova G. Vol.11. Issue 3. P.418-419. |
| [12] | Matveyev L.P. Teoriya i metodika fizicheskoy kul'tury/ L.P. Matveyev – SPb.: Izd-vo «Lan'», 2004. – 160 p. |
| [13] | Mavlyanov Z.I., Jalolova V.Z., Rakhmatova M.R., Yuldasheva N.M. Kharakteristika komponentnogo sostava gena FABP2 u yunykh sportsmenov zanimayushchikhsya razlichnymi vidami sporta // Tibbiyotda yangi kun. – 2019. - № 4. – P. 35-42 |
| [14] | Mavlyanov Z.I. Osobennosti somatotipa sportsmena i yego vzaimosvyaz' so sportivnymi genami. Diss. Rab. na soisk. Uchen. Step. PhD. – 2018. – P. 18. |
| [15] | Mavlyanov Z.I., Zhalolova V.Z., Rakhmatova M.R., Analiz antropometricheskikh pokazateli fizicheskogo razvitiya u yuniorov i kadetov v sportivnoy meditsine // Tibbiyotda yangi kun – 2020. - № 2(30/2). – P. 38-42 |
| [16] | Miroshnikova YU. V. Mediko-biologicheskoye v obespecheniye detsko-yunosheskom sporte v Rossiyskoy Federatsii (kontseptsiya) / YU. V. Miroshnichenko, A. S. Samoylov, S. O. Klyuchnikova, I. T. Vykhodets // Pediatriya. – 2013. – T. 92, № 1. – P. 143–149. |
| [17] | Xodjieva D.T, Akhmatova N.R. Clinical and neurological predictors of cerebrovascular disease in gepothyroiz.Vol.2. Issue 3. P.37-39. |
| [18] | Níkolaêv S. YU. Ozdorovcha spryamovaníst' zasobív atletichnoí̈ gímnastiki dlya yunakív starshogo shkíl'nogo víku / S. YU. Níkolaêv // Molodízhniy naukoviy vísnik. – 2013. – № 9. – P. 85–88. |
| [19] | Obraztsova N.N. Sovremennyye problemy sportivnogo otbora / N.N. Obraztsova, N.N. Shcherbakova // Razvitiye odarennosti v sovremennoy obrazovatel'noy srede: sb. mat. Vserossiyskoy zaochnoy nauch. -prakt. konf. s mezhdunarodnym uchastiyem 2 oktyabrya 2012 goda. Chast' II. – Belgorod, 2012. – P. 130-134. |
| [20] | Morphofunctional characteristics of thymus under exposure to various environmental factors. Vol. 11. Issue 3. Azimova S.B. P.420. |
| [21] | Platonov V. N. Sistema podgotovki sportsmenov v olimpiyskom sporte. Obshchaya teoriya i prakticheskiye prilozheniya // V. N. Platonov. – Kiyev: Olimp. lit., 2004. – 808 s. |
| [22] | Polyakov S. D. Problemy sovremennogo detskogo sporta i puti ikh resheniya / S. D. Polyakov, I. Ye. Smirnov, I. T. Korneyeva, Ye. S. Tertyshnaya // Ros. pediatricheskiy zhurn. – 2008. – № 1. – P. 53–56. |
| [23] | Rakhmatova M.R., Zhalolova V.Z. Yunior va kadet sportsmenlarda tananing kompazitsion tarkibini ŭrganish.// Tibbiyotda yangi kun. - № 2 (30/2). - P. 67-70. |
| [24] | Tkhazeplov A.M. Prognozirovaniye i otbor v sporte/ A.M. Tkhazeplov// Uchebno-metodicheskiye materialy - Nal'chik: Kab. -Balk. un-t, 2002. – 50 s. |
| [25] | Vimaleswaran, Karani S., et al. "Candidate genes for obesity-susceptibility show enriched association within a large genome-wide association study for BMI." Human molecular genetics (2012): P.283. |
| [26] | Vanden, Heuvel JP. "Nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics of ω3 polyunsaturated fatty acids." Progress in molecular biology and translational science 108 (2011): 75-112. |
| [27] | Fenech, Michael, et al. "Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics: viewpoints on the current status and applications in nutrition research and practice." Journal of nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics 4.2 (2011): 69-89. |
| [28] | Weggemans, R. M., et al. "Genetic polymorphisms and lipid response to dietary changes in humans." European journal of clinical investigation 31.11 (2001): 950-957. |
| [29] | Djordjevic, Natasa, et al. "Induction of CYP1A2 by heavy coffee consumption is associated with the CYP1A2−163C> A polymorphism." European journal of clinical pharmacology 66.7 (2010): 697-703. |
| [30] | Jalolova V.Z., Rakhmatova M.R., Anthropometric indicators of juniors and cadets in sport medicine // Электронный научный журнал «Биология и интегративная медицина» №4 – июль-август (44) 2020– P.5-16. |
| [31] | Mavlyanov Z.I, Jalolova V.Z, Rakhmatova M.R Research of health conditions and genetic variants of young athletes involved in mixed sports // ACADEMICIA: An International Multidisciplinary Research Journal https://saarj.com 10.5958/2249-7137.2021.00421.3. |
| [32] | Mavlyanov Z.I, Jalolova V.Z, Rakhmatova M.R. The study of genetics in modern sports medicine is the key to high achievements of young athletes // ACADEMICIA: An International Multidisciplinary Research Journal https://saarj.com 10.5958/2249-7137.2021.00417.1. |
| [33] | Mustafaeva S.A., Rakhmatova M.R., Jalolova V.Z., Mavlyanov Z.I. Peculiarities of the morphophenotype and characteristics of the physical performance of young football players and their relationship with the gaming amplitude // ACADEMICIA: An International Multidisciplinary Research Journal https://saarj.com 10.5958/2249-7137.2021.00537.1. |
| [34] | Rakhmatova M.R., Jalolova V.Z., Methods of research of body composition in athletes // Elektronnyy nauchnyy zhurnal «Biologiya i integrativnaya meditsina» №4 – iyul'-avgust (44) 2020– S.16-29. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML