Ikhtiyor Abdulkhakov1, Nizom Ermatov2
1Assistant of Department, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
2Head of Department, Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
In our study, 1375 patients (497 men and 726 women) aged 18 to 69 years were taken, who were registered at the regional endocrinological dispensary for diabetes mellitus, living in cities and villages of the Bukhara region. The study analyzed the composition and structure of 216 food rations for the summer, autumn, winter and spring seasons. The daily diet of patients and its physiological composition were compared and analyzed for compliance with Sanitary rules and regulations No. 0007-2020 Average daily standards of rational nutrition for groups by age, sex and profession, aimed at ensuring healthy nutrition of the population of the Republic of Uzbekistan. The quantitative chemical composition of the daily diet was carried out according to the Chemical composition of food. The analysis showed that the patients' daily diet does not meet the approved hygienic requirements. The diet includes an excess of bread and baked goods, various cereals, rice, meat, fish and dairy products, fruits and vegetables, as well as proteins from the main nutrients of the body. The daily diet of proteins in men from 21.5 to 29.5%, in women from 31.0 to 36.8%, fats from 80.2 to 87.3%, especially in winter, it was 23.3% in relation to to the norm. The amount of carbohydrates taken by the patients ranged from 135.8 to 140.4% in men and from 130.2 to 133.6% in women, respectively. The insufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the daily diet was also studied. It was found that non-compliance with the hygienic requirements of the composition of the daily diet of controlled patients is a risk factor for the development of diabetes mellitus and an increase in its complications.
Keywords:
Diabetes, Daily diet, Diet, Patients, Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Vitamins and minerals
Cite this paper: Ikhtiyor Abdulkhakov, Nizom Ermatov, Hygienic Analysis of the Nutrient Composition of the Daily Diet of Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 9, 2021, pp. 649-657. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211109.10.
1. Introduction
Violation of a healthy lifestyle among the population, proper nutrition during the day and a decrease in protein, animal protein, periodic deficiency of animal fats in the diet, a sharp increase in vegetable fats, periodic consumption of trans fats, an increase in carbohydrates, lack of essential minerals and vitamins, among them the fact that the development diseases associated with nutrients, together with the development of various metabolic diseases, has been repeated in a number of scientific sources [2,3,4,11].To date, a number of legal documents have been developed for the prevention of foodborne diseases among various segments of the population. In particular, on June 7, 2010, the Law of the Republic of Uzbekistan No. 251 "On the prevention of micronutrient deficiency among the population" was adopted [1]. Preventive measures to prevent micronutrient deficiencies while fulfilling the objectives set out in this law will reduce the incidence of diseases caused by nutritional deficiencies and increase life expectancy.Today, a decrease in vitamin D and zinc in the daily diet of the world's population leads to a sharp increase in the number of chronic diseases caused by malnutrition, as well as diseases of the immune system [3,8,9,14,15].The development of various somatic diseases, violation of the healthy lifestyle of the population, violation of the nutritional value of the daily diet, unhealthy diet, fast food, the use of palm oil, national traditions, overeating during the day, fried foods after dinner, food consumption leads to a deterioration in the quality and quantity of food [9,10,14,15].Despite the implementation of a number of scientific studies, the number of diseases associated with nutritional status in the developed countries of the world is increasing day by day. These include metabolic disorders, iron deficiency anemia, overweight, obesity and diabetes, and nutritional deficiencies in less developed countries [2,3,7,8,9,10].It has been proven that a sharp decrease in the content of vitamins A, C and D in the diet, as well as trace elements of zinc and precious iron, a trace element of iodine, is also associated with the development of COVID-19, which is the most common. actual problem today.In connection with the above, one of the main risk factors for the development of the disease in patients with diabetes mellitus is the assessment of a healthy lifestyle, and proper nutrition is one of the most pressing problems today.Purpose of the study. In today's era of development, it is worthwhile to analyze the content of nutrients in the daily diet of patients with diabetes mellitus living in the hot climate of our country.
2. Materials and Methods
To conduct a controlled study, patients with diabetes mellitus living in the Bukhara region, under the control of "D" in the regional endocrinological dispensary, and living in urban and rural areas were covered. The study included 1375 patients (497 men and 726 women) from the Bukhara regional endocrinological dispensary aged 18 to 69 years. Basically, we analyzed the daily feeding regimen at home for the period before the treatment of this contingent.The studies analyzed the content and structure of the daily diet at the beginning, middle and end of each month in a separate sample of the season during the summer, autumn, winter and spring seasons of the year. The patient's daily diet and its physiological composition Sanitary rules No. 0007-2020 "Average daily norms of rational nutrition aimed at ensuring healthy nutrition of the population of the Republic of Uzbekistan by age, sex and occupation" [5] Sanitary requirements, Norms and rules, Food hygiene [3] were compared and analyzed for compliance with the requirements specified in. The analysis of the quantitative chemical composition of the daily ration "Chemical composition of food" was carried out according to the program [6].For statistical processing of the results of the study, we used the software package for a personal computer "Statistica for Windows 7.0".
3. Results and Discussion
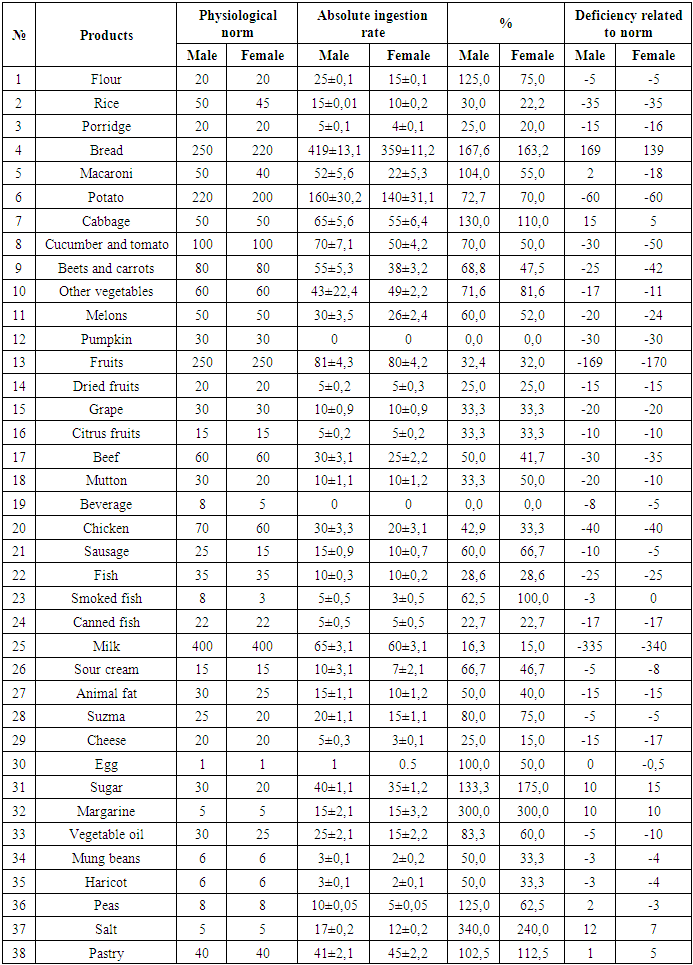
We considered it expedient to analyze the daily diet of patients with type I and II diabetes mellitus with diseases of the endocrine system separately for four seasons of the year and to carry out a comparative analysis of the results with physiological normative indicators.Seasonal analysis of the diet of our patients is the basis for identifying the main risk factors for the development of the disease and hygienic and social analysis of their relationship with each other, as well as the development of diets in combination with targeted measures. ...We considered it expedient to analyze the hygienic analysis of food at home in patients with endocrine system diseases in winter in the ratio of consumption of 38 prescribed foods.However, the physiological normative index does not indicate confectionery products, their composition or other products are not indicated.Therefore, we included confectionery in 38th place, as confectionery is the most common cause of illness.Analysis of the population's diet based on the survey shows that the share of daily food consumption by men differs sharply from the share of women. The daily diet of men consisted of a sufficient amount of excess sweets along with the use of fried, salty, spicy and fried foods. Otherwise, it is one of the main risk factors for the development of the disease.Diseases of the endocrine system in our country are increasing day by day. One of the main reasons for this is a violation of a healthy diet, that is, excessive consumption of high-quality bread and confectionery products from it. In this case, it is important to determine which product is the main factor in the development of the disease.In our study, we decided to elucidate the role and importance of these foods in the development of disease by examining a separate set of these foods in a separate order during the seasons, evaluating their effects.When assessing food consumption, the daily ration and its compliance with hygiene requirements were assessed.The diet of patients with diseases of the endocrine system in the summer at home is shown in Table 1.Table 1. Quantitative norm of daily food intake by patients in summer season
 |
| |
|
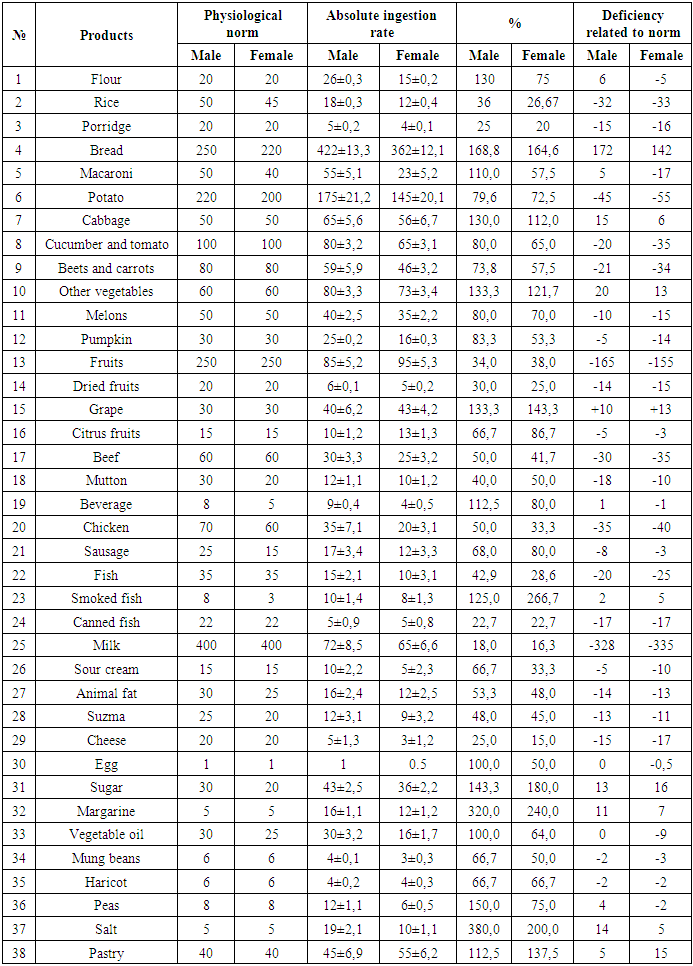
The data in Table 1 show that the analysis of the diet of homegrown patients in the summer of the year shows that the amount of flour in cereals increased by 125% in men, up to 75% in women, 1.25 times in men and 0.75 times in women.The daily consumption of bread by 167.6% in men and 163.1% in women indicates metabolic disorders in both sexes.Unfortunately, despite the fact that in our country there are sufficient conditions for growing vegetables and fruits, our patients consume very little. Hygienic analysis of the level of consumption of these products shows that fruits and vegetables were consumed in various irregular ways, which indicates a lack of vitamins and their conditions for the formation of complications.Pure cabbage was consumed in summer by 130% of men and 110.0% of women, and not enough greens, garlic and onions were consumed.If the level of consumption of fresh cucumbers and tomatoes is similarly lower by 0.7-0.5 times, then the content of other vegetables, onions, eggplants is less by 28.4-18.4%.Another interesting aspect of our study is that, based on the geographical characteristics of the Bukhara region and the traditions of the local population, more beef and chicken are consumed in their daily diet.Due to the specific properties of food additives, the population partially consumes sausages. Their total consumption was 15 grams for men and 10 grams for women, but together with sausage and chicken their total amount was 53.7% and 48.0% for women.The total number of meat products includes sausages with beef and lamb, chicken intestines. Separate analysis and joint food analysis show that this food group is also under-consumed. The consumption of these products in summer was significantly lower than in other seasons.Consumption of fish products at the consumption level this season was 28.5% for men and women, if only clean fish are analyzed.There are also sharp differences in the consumption of salted fish and canned fish. However, salted fish in summer makes up 62.5% in males and up to 100% in females. Therefore, the prevalence of the disease in women is higher than in men.Dairy products are distinguished by their medicinal properties for various diseases. However, in the daily diet of our patients, the level of milk consumption was 6.15 times lower than the physiological norm in men and 6.67 times lower in women.Our scientists carry out a number of studies on the normalization of sugar and confectionery products in the daily diet, as well as table salt and salty foods. The daily salt intake was reduced to 5 grams.In the daily diet of our patients, table salt was 340% higher than the norm in men and 240% in women.The composition of the daily diet of patients in the fall is presented in Table 2.Table 2. Quantitative norm of daily food intake by patients in fall season
 |
| |
|
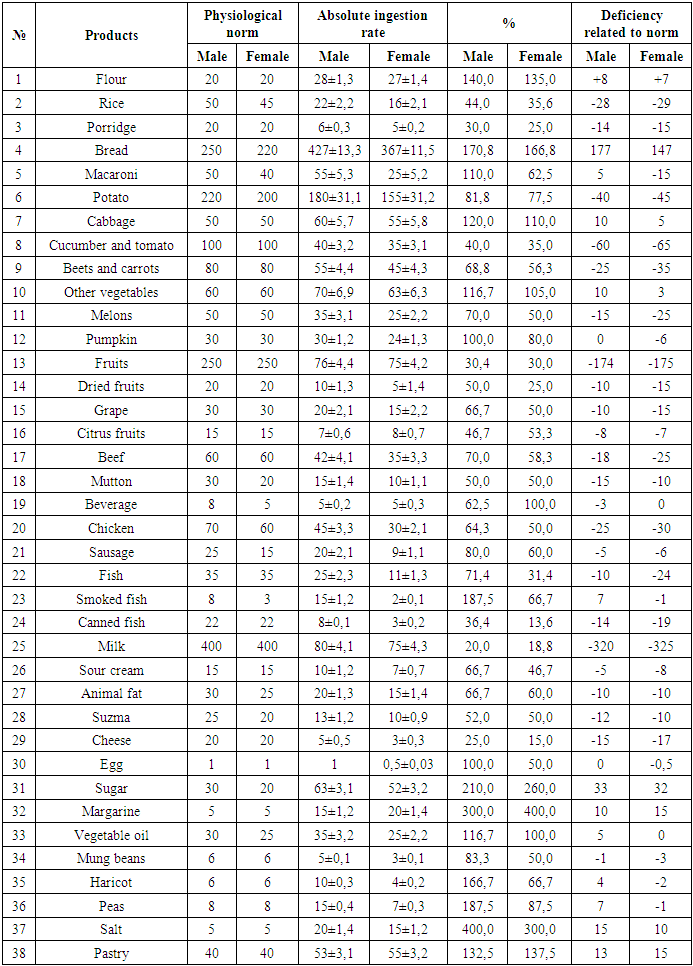
The data in Table 2 show that the hygienic analysis of the autumn diet of patients with diabetes mellitus showed that the amount of food consumed was less than the physiological norm, although the consumption of some foods was relatively high compared to other seasons.We draw your attention to the consumption of pumpkin and a number of melons, as well as grapes in the fall.The consumption of squash is 83.33% for men and 53.3% for women, and the amount of grapes is 133.3% for men and 143.3% for women. Although both foods are seasonal, the role of squash in the body is unique.Pumpkin is a medicine for diabetes mellitus. The amount of sugar in grapes is the main risk factor for the disease, which is a source of exacerbation of the disease in patients.The amount of vegetable oil is lower in men by 6.7% and in women by 20.0%, with the exception of animal fats, that is, animal and meat oils, butter this season in men by 46.7% less, in women by 52.0%.Peas, mung bean and legumes were mainly consumed in the fall and winter months, with a partial overexpenditure compared to other seasons.Peas are the main source of vegetable protein, the excessive use of which, along with flatulence, leads to increased digestive activity. The consumption of peas is 3 times higher than the physiological norm in men and 2 times higher in women.The amount of mosh in the daily diet is 1.5 times more than that of men, 0.7 times less for women, the amount of beans in both sexes is 0.6 times less, which leads to an incorrect distribution of plant proteins in the body.A normal level of dukakali in the daily diet of diabetic patients is important for effective treatment of the disease.The share of confectionery products in the daily diet of the population was 112.5%, women - 137.5%.The amount of margarine is 3.2 times higher in men and 2.4 times higher in women. This leads to the development of metabolic disorders and the formation of diseases.The winter nutrition norms for patients with diabetes mellitus are shown in Table 3.Table 3. Quantitative norm of daily food intake by patients in winter season
 |
| |
|
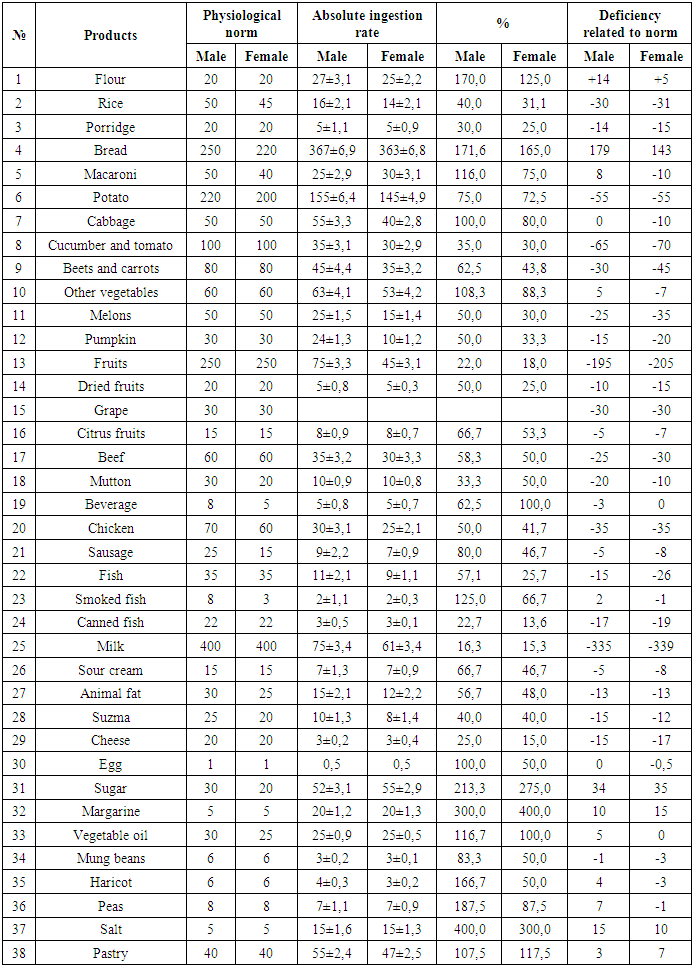
The analysis of the obtained results shows that the ratio of consumption of products of daily consumption in men differs sharply from that in women.The men’s daily diet consisted of ample amounts of excess sweets, along with the consumption of fried, salty, spicy, and fried foods. Otherwise, it is one of the main risk factors for the development of the disease.The share of flour products in the main product composition was 140.0%, for women - 115.0%.Bread and baked goods were analyzed together in a number of hygiene analyzes, and we focused each of our analyzes on a separate study and clarifying the role and importance of foods in disease risk analysis.For men, consumption of basic bakery products such as flour, rice, cereals, bread and pasta ranged from 30% to 170.80%, while for women this indicator ranged from 25.0 to 166.82%.It should be noted that the level of consumption of porridge was adopted sharply, i.e. in small quantities 70-75%. The amount of grain products remaining is a sharp surplus.Instead of pure cabbage, cucumbers and tomatoes, there has been a sharp increase in the number of sauerkraut, pickled tomatoes and cucumbers among the population. The diet includes salted fish.Clean fish is eaten fried and salted.In winter, sugar consumption increased by 210% among men and 260% among women.At the same time, the amount of margarine, vegetable oil, confectionery products also indicates a sharp increase in consumption compared to other seasons.A set of dietary products for patients with diabetes mellitus at home in the spring of the year and its composition are presented in Table 4.Table 4. Quantitative norm of daily food intake by patients in spring season
 |
| |
|
Comparative analysis of food products presented in Table 4 shows that there are sharp differences in the distribution of seasonal products among patients.It can be seen that the amount of milk, meat, fruits, vegetables and other products from the main products in the diet of patients in spring did not meet hygienic requirements.The amount of scarce products in the daily diet increases due to bread and bake-ry products, sugar, and confectionery.In bread and bakery products, the amount of rice and porridge has sharply decreased, among men - by 40%, among women - by 31.1%, porridge - by 30-25%.The amount of meat and meat products, which are considered the most basic and important in the daily diet of patients, is very small at any time of the year, especially in spring, which leads to the development of various diseases and a decrease in immunity.The content of potatoes in the daily diet of patients was 75% in men and 72.5% in women, while consumption of beets and carrots was 62.5% in men and 43.7% in women.The amount of animal fats in the daily diet was 56.6% less for men and 48.0% for women, that is, 43.4% for men and 52.0% for women.It should be noted that the absence of basic products in all four seasons of the year indicates that the population is enriched only with flour, bread and pasta.It has been proven that foods made from high-quality flour, along with metabolic processes, contribute to the development of diabetes mellitus, as well as iron deficiency and iodine deficiency disorders.It was found that the patients over-consumed foods made from it at home, such as bread, pasta, margarine preservatives, biscuits, waffles.The intake levels of essential nutrients, proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the daily diet of patients at different times of the year are shown in Tables 5-6.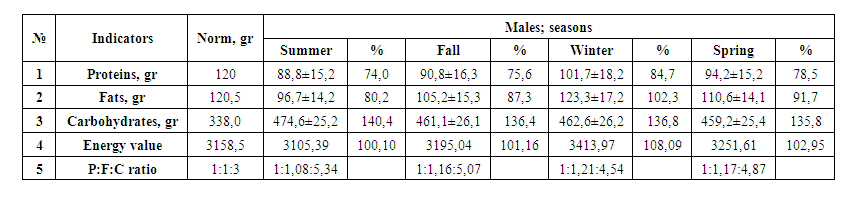 | Table 5. Daily Values of Essential Nutrients in Male Diabetic Patients |
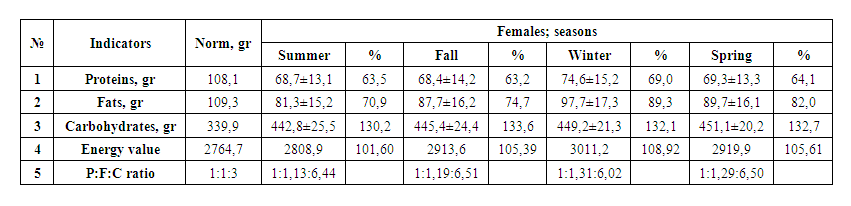 | Table 6. Daily Values of Essential Nutrients in Female Diabetic Patients |
Analysis of the main nutrients of controlled patients shows that in all seasons of the year, the amount of protein in men is provided from 74.0 to 78.5%. The amount of protein consumed during the day is less than the established physiological norm by 21.5-29.5%, and its content is characterized by a lack of animal protein.Hygienic analysis of the composition of the daily diet of women shows that they constitute from 36.8% to 31.0%.Lack of protein in the daily diet of patients leads to the formation of changes throughout the body.The specific properties of fats and oils for the body are given in a number of scientific sources. Among the population, animal fats, butter, lard and sheep oil are used, and vegetable oils are used in sunflower, olive, flaxseed, cottonseed and palm oils.Fats are the source of energy in the body. He also actively participates in the assimilation of a number of vitamins. The absorption of vitamin D also depends on adequate amounts and metabolism of fat in the body.The fat content in the daily diet of controlled patients ranged from 80.2% to 123.3% in men, mainly in winter - with an excess of 23.3%, and in women - from 70.9% to 89.3%.It was found that the amount of carbohydrates in the daily diet of our patients in all seasons increased from 135.8% to 140.4% in men and from 130.2% to 133.6% in women.Excessive level of carbohydrates in the diet, flour, bread, pasta, sugar, salt, confectionery, grapes in the fall, metabolic disorders in the population in hot climates, metabolic disorders, increased blood pressure, the development of the immune system of diabetes mellitus, accompanied by a decrease in the incidence of various viral diseases and their complications with the transition from the first type to the second.
4. Conclusions
1. In the daily diet of the population, the amount of flour in the summer-autumn-winter-spring season was 120-170.0% for men in the acute season, 75% for women in summer and autumn, and 125%. -135% in winter and spring, however, the amount of bread made from high-quality flour was similarly consumed from 167.6 to 171.6% in men and from 163.1 to 166.8% in women.2. The amount of bread and baked goods (bread and pasta) was sharply higher in all seasons, but the total amount of rice and porridge was 27.5–37% in men and 21.1–30% in women compared to the physiological norm. on 2%.3. The level of consumption of meat and meat products (various types of meat, dairy products and sausages) during the year amounted to 37.24; 64.0%; 65.3; 56.8% for men and 38.3; 57.0 for women; 63.6; 57.67%.4. The amount of vegetables in the daily diet during the year ranged from 57.3 to 96.74% for men and 50.9-72.7% for women, and the fact that zucchini was not consumed in summer had a decisive influence.5. The number of fruits during the year is: 32.4% in men in summer, 32.0% in women, 34.0% and 38.0% in autumn, 30.4, 30.0% in winter and 22.7% in spring and 18.0%.6. The amount of sugar per year increased from 133.3% to 213.3% for men and 175.0-275% for women.7. The amount of vegetable oil ranges from 83.3 to 116.67% in men and from 60% to 100% in women.8. The amount of protein was reduced from 21.5 to 29.5% of the established physiological norm in male patients, from 36.8% to 31.0% in women, and the amount of fat - from 80.2% to 123.3% in men. mainly in winter with an excess of 23.3%, and in women from 70.9% to 89.3%, the amount of carbohydrates in all seasons of the year is the same 135.8% -140.4% and 130.2% -133.6% an excess was detected - consumed.
References
| [1] | Law "On prevention of micronutrient deficiency in population." Tashkent, issued on June 7, 2010 #251. |
| [2] | Gerasimov G.A. On the WHO recommendations "Fortification of edible salt with iodine for the prevention of diseases caused by iodine deficiency" // Clinical and expert. thyrodology. 2014. T. 10. No. 4.P. 5-8. |
| [3] | Food hygiene. Edited by Professor G.I. Shaikhova. Tashkent, 2010. -553 p. |
| [4] | A guide to the consumption of sugars for adults and children. Summary. WHO, 2015.11 p. |
| [5] | Sanitary rules and norms №0007-2020 "Average daily norms of rational nutrition aimed at ensuring healthy nutrition of the population of the Republic of Uzbekistan by age, sex and occupation" Tashkent, 2001. |
| [6] | The chemical composition of Russian products: a reference book / edited by I.М. Skurikhina, V.A. Tutelyana), Moscow: DeLiprint, 2002. |
| [7] | Alvaravra Y., Kiernan K., McIver NJ. Changes in nutritional status affect the metabolism and function of immune cells // Frontiers of Immunology. - 2018. -- T. 9. - P. 1055. |
| [8] | Becker S.M., Job K.M., Lima K., Forbes T.J., Wagstaff J., Tran N.K. other. Prospective study of the pharmacokinetics of serum and ionized magnesium in the treatment of children with severe acute asthma // Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019. Vol. 75, N 1.S. 59-66. |
| [9] | Irmatov Nizom, Inoyatov Amrillo, Mavlonov Anvar, Saidov Saidamir, Bobokhanov Otabek. Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy with calcium-containing compounds in experimental osteoporosis. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research October-December 2019 Volume 11 Issue 4. |
| [10] | Irmatov Nizom, Shaikhova Guli, Salomova Feruza, Rustamov Bakhtiyor. Efficacy of red palm oil in patients with gastrointestinal diseases. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research October-December 2019 Volume 11, Issue. |
| [11] | Fernández-Cao J. C. et al. Zinc intake, status and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis // Nutrients. - 2019. - T. 11. - No. 5. - P. 1027. |
| [12] | Kubyak RV et al. Interaction of nutritional status and diabetes on active and latent tuberculosis: a cross-sectional analysis // BMC Infectious Diseases. - 2019. - T. 19. - No. 1. - S. 1-9. |
| [13] | Montagut-Martinez P., Perez-Crusado D., Garcia-Arenas JJ Instruments for measuring nutritional status in diabetes: a systematic psychometric review // International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. - 2020. - T. 17. - No. 16. - S. 5719. |
| [14] | Moore ZE Kh., Corcoran MA, Patton D. Nutritional interventions for the treatment of foot ulcers in people with diabetes // Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. - 2020. - No. 7. |
| [15] | Tan C. W. et al. Cohort study to evaluate the effect of a combination of vitamin D, magnesium and vitamin B12 on the progression of severe outcome in elderly patients with coronavirus (COVID-19) // Nutrition. - 2020. -- T. 79. -- S. 111017. |




 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


