Gulnoza Akhmadjonova1, Shukhrat Teshaev2, Dilbar Nazhmutdinova3, Khabiba Negmatshaeva1
1Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan
2Bukhara State Medical Institute, Bukhara, Uzbekistan
3Tashkent Medical Academy, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Gulnoza Akhmadjonova, Andijan State Medical Institute, Andijan, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The authors present the results of studying the peculiarities of the clinical characteristics of women in the city of Andijan, with the identified antiphospholipid syndrome and reproductive losses in the anamnesis and the effectiveness of detecting laboratory markers of antiphospholipid syndrome as predictors of the threat of fetal antigen loss. It was shown that out of 1200 (100%) examined patients with reproductive losses, 169 (14.08%) patients had antiphospholipid syndrome: studies for the presence of antiphospholipid syndrome were carried out in the central research laboratory of the Andijan State Institute on the basis of the compiled scientific and technical agreements between the institute and the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, as well as on the basis of the maternity complex No. 2 in the city of Andijan. Written consent was obtained from all patients, they were informed about the objectives of the study. This study was approved by the Andijan State Medical Institute's Maternal and Child Welfare Committee. The work is based on the analysis of data obtained during the examination, observation, treatment, and pregnancy management of 169 women with a history of reproductive losses, in whom primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) was revealed during the examination.
Keywords:
Pregnancy, Fetal loss, Antiphospholipid syndrome, Morphometry, Ultrasound
Cite this paper: Gulnoza Akhmadjonova, Shukhrat Teshaev, Dilbar Nazhmutdinova, Khabiba Negmatshaeva, Clinical Characteristics of Women with Early Gestational Fetal Loss with Antiphospholipid Syndrome, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 11 No. 8, 2021, pp. 563-568. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20211108.03.
1. Introduction
Spontaneous abortion is an urgent problem of modern obstetrics and gynecology and entails not only demographic losses, but also disrupts the reproductive, social and psychological well-being of women. The frequency of miscarriage is 10 to 35% of desired pregnancies [1,10]. Scientific interest in the problem of miscarriage is increasing due to the emergence of new diagnostic capabilities that allow clarifying etiological factors and a new approach to elucidating the pathogenetic mechanisms of miscarriage, the unknown genesis of which in its structure is 25-57% [7,10].Recently, numerous theories of maternal-fetal tolerance have been discussed in the literature. The embryo constantly rearranges the subsequent stages of immunological "events" occurring by the secretion of molecules with immunological activity. However, these molecules are often secreted not by immune cells, but by trophoblast and uterine epithelium [2,3,4,6,7,10,11,12]. Moreover, the violation of the gene makes itself felt, only in certain circumstances - during pregnancy, surgery, with injuries, taking hormones [2,5]. These are the conditions under which perinatal losses in 55-62% are due to defects in coagulation proteins or platelets [1,7,9]. The results of scientific works in recent years have significantly expanded the understanding of this problem, but it has not been finally solved [2,3].Among immunological aspects, an example of such an autoimmune interaction is a condition in which antibodies to phospholipids (APL) are detected in the blood - a heterogeneous population of autoantibodies that react with negatively charged, less often - neutral phospholipids and / or phospholipid-binding serum proteins, which is called antiphospholipid syndrome (AFL) [2,3,4,5,7,8].The main purpose of this study was to determine the frequency of antiphosphodlipid syndrome in women with a history of recurrent miscarriage in the city of Andijan and to identify predictors of preceding fetal loss and perinatal complications in this category of patients.
2. Materials and Methods
A prospective study of 1200 patients with reproductive losses was conducted for the periods from January 2018 to December 2020 on the basis of the city maternity complex No. 2 together with the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Andijan State Medical Institute.With the aim of in-depth study of the effect of APS on the course of pregnancy and the fetus, we examined and observed 169 (14.08%) pregnant women with a history of reproductive losses, in whom the APS was detected during the examination, which constituted the main group. When choosing patients to be examined and observed, we took into account the presence of hormonal, endocrine, infectious disorders, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, women with the above-mentioned disorders were not included in the survey group. We were also examined for the presence of TORCH, an infection affecting the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus, if any one of them was identified, we preliminarily performed treatment with an examination for avidity (women with high avidity were included). In order to elucidate the role of APS in obstetric and perinatal pathology in the examined group, we studied the state of hemostasis, in which APS was detected during the study. Lupus anticoagulant (VA) was tested at least twice at 6-8 weeks interval, according to the International Society for Thrombosis and Hemostasis Subcommittee on Science and Standardization.As a control group, 45 apparently healthy pregnant women were selected, not identified antiphospholipid syndrome and other autoimmune, hormonal, endocrine, infectious disorders, as well as isthmic-cervical insufficiency.The clinical examination included the collection of anamnesis of the present disease, the number of episodes of reproductive loss over the past 3 years, and the treatment measures taken for previous episodes of the disease. We also analyzed the severity of clinical symptoms of this pregnancy.The studies were carried out during their inpatient treatment for various complications of pregnancy.The age of the surveyed ranged from 18 to 35 years (average age - 23.18 ± 0.22 years), in the control group - the average age was 23.07 ± 0.49 years. The gestational age in the main group is from 8 to 32 weeks. Of these, 18 were in the first trimester, 11 in the second, and 9 in the third. The main contingent of the surveyed pregnant women - 50.0% of the main group and 60% of the control group - were homemakers.Because of the data of the study of the anamnesis, it was revealed that 23.68% of the examined in the main group and in 17.78% of the control group had frequent acute respiratory viral infections in childhood. 47.37% of pregnant women in the main group and 15.56% of women in the control group suffered from viral hepatitis. Otitis media, chronic tonsillitis and sinusitis in childhood were ill in 55.26% of women in the study group and 24% of women in the control group.In addition, measles (36.84%) and rubella (26.32%) were more often observed in pregnant women of the main group than in the control group (6.67%, 8.89%, respectively). It was found that pregnant women in the main group had a history of renal pathology in (36.84%) in the control group (13.34%), in (23.68%) varicose veins of the lower extremities, which indicates the role of APS in the genesis perinatal losses in this group (Fig. 1).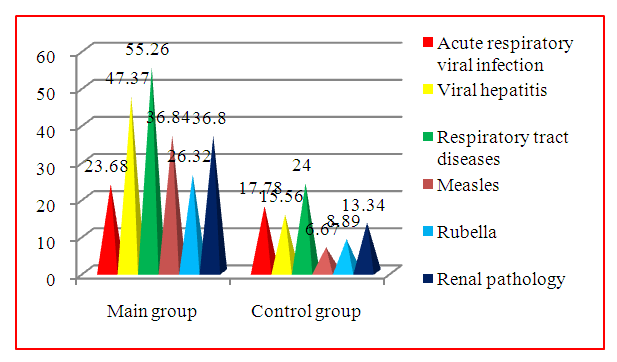 | Figure 1. Medical history |
Thus, a viral infection in childhood was more often observed in the study group. After analyzing the structure of childhood infections, in the group of women with APS, it was found that acute respiratory viral infections and Botkin's disease were more often observed.Analysis of menstrual function in pregnant women of the main group showed that 84.21% of menstruation came on time, at the age of 12-14 years. Early onset of menarche was not observed in the surveyed women of this group. At the age of 16-17, menarche was noted in 15.79%. In the control group, menstrual function was also analyzed: menstruation came on time in 82.5% of women, and in 8% there was a delayed onset of menstrual function. Thus, later menarche is observed 2 times more often in the main group than in the control group. In the control group, there were no further menstrual dysfunctions.The analysis of gynecological diseases examined showed that 71.05% of women in the main and 66.7% of the control group had a history of cervical erosion, colpitis, endocervicitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genitals.In the main group, colpitis was observed in 23 (60.53%) women. Erosion of the cervix occurred in 17 (44.74%), endocervicitis - in 5 (13.16%) women with APS. A history of endometritis was observed in 8 (21.05%), in combination with adnexitis - in 13.16% of the studied women (Fig. 2).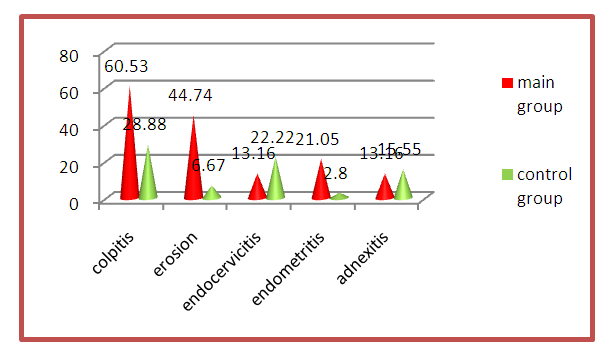 | Figure 2. Gynecological history of the study groups |
In the control group, colpitis was noted in 28.88%, cervical erosion in 6.67%, and endocervicitis in 22.22%. Adnexitis in the anamnesis was 15.55% of the examined women, endometritis was not registered.Thus, a history of colpitis was more often recorded in women diagnosed with APS. When comparing the incidence of the cervix between the main and control groups, it turned out that endocervicitis and adnexitis were more common in women in the control group. Erosion of the cervix in percentage terms prevailed in the main group.Analysis of the reproductive function of women in the main group showed that two pregnancies were detected in 18 (47.36%) pregnant women, three pregnancies - 11 (28.94%), four pregnancies - 5 (13.15%) women. The fifth pregnancy was registered in 2 (5.2%), the sixth - in 2 (5.2%). In the control group, the examined women had from 1 to 3 pregnancies (Fig. 3.).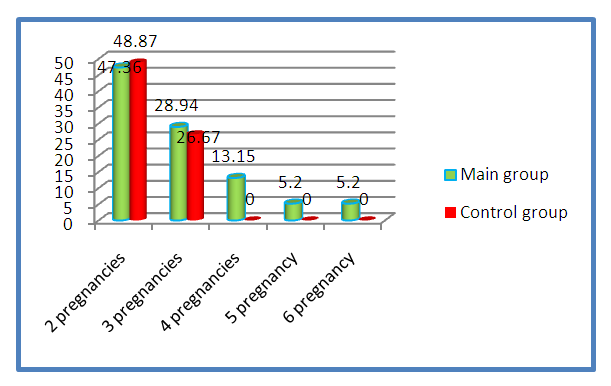 | Figure 3. Obstetric history of the study groups |
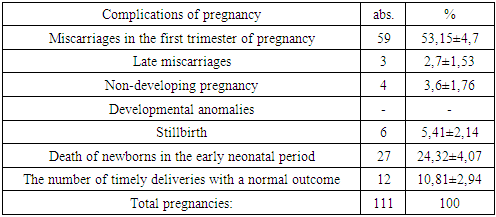
Anamnestic data analysis showed that 111 pregnancies were observed in 38 pregnant women and only 12 (10.81%) of them ended in timely delivery 9 (75%). The rest of the women in the main group do not have children from previous pregnancies.The obstetric history of the examined women of the main group is complicated by spontaneous abortions, late miscarriages, premature births, missed pregnancies, which is presented in Table 1.Table 1. Obstetric history of examined pregnant women (n = 169) with antiphospholipid syndrome
 |
| |
|
As can be seen from the table, spontaneous abortions in the first trimester took place in the anamnesis in 53.15% of all pregnancies. In 2.7% of cases, miscarriages were late. Habitual miscarriage in the main group was 64.86%.A history of non-developing pregnancy in women with APS was noted in 3.6% of pregnancies (Fig. 4).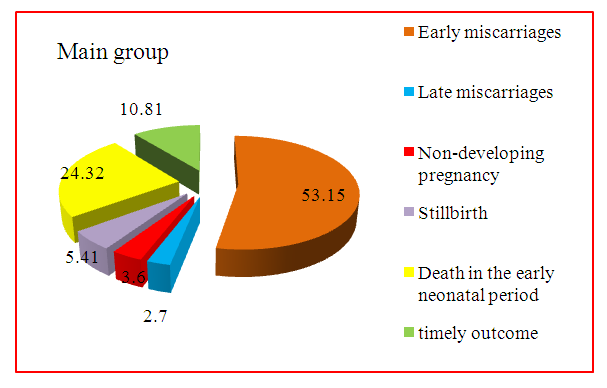 | Figure 4. Outcomes of previous pregnancies in women with APS |
Stillbirth was noted in 5.41% of all pregnancies. Early neonatal mortality in intrauterine fetal hypoxia has a particularly high rate.The death of children in the early neonatal period was noted in 24.32% of cases, all newborns were born on time.The pregnant women in the control group had 91 pregnancies in total, 91 of them ended in the birth of healthy, full-term babies. There was no lethality of children or undermaturity in women in the control group.Thus, in women with a burdened obstetric history and APS, 53.15% of pregnancies ended in spontaneous abortions, 2.7% of pregnancies - late miscarriages, 5.41% - stillbirths and early neonatal deaths, 3.6% - non-developing pregnancies. Moreover, 24.32% had early neonatal mortality.This suggests that women with APS and RP are at high risk of miscarriage and obstetric pathology.The structure of obstetric complications with which pregnant women were admitted to the hospital is presented in Table 2.Table 2. Obstetric complications with which pregnant women were admitted
 |
| |
|
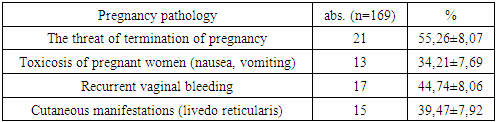
As follows from the table, the most frequent and main complication of pregnancy with which patients were admitted to the hospital is the threat of termination, which was noted in 55.26% of women. Almost every pregnant woman from among the surveyed women, pregnancy was complicated by the threat of its termination, despite the therapy, aimed at preserving the pregnancy.Despite repeated therapy aimed at preserving pregnancy, every second woman had a threat of termination during the entire study period. It was also noted that in these patients, in previous pregnancies that ended unsuccessfully, the phenomena of the threat of termination were also observed.In terms of frequency, spotting from the vagina was recorded in second place (Fig. 5). Recurrent bleeding from the vagina in pregnant women with the threat of termination was observed in 17 (44.74%). At the same time, they excluded placenta previa using ultrasound.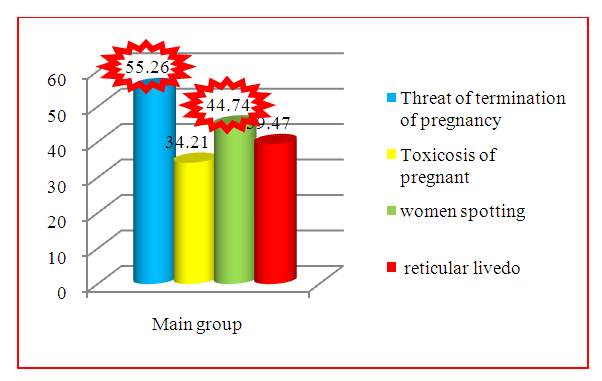 | Figure 5. Complications of a real pregnancy |
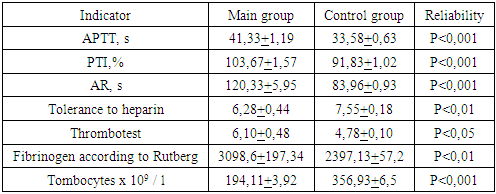
Periodic bloody discharge, apparently, was often preceded by antiphospholipid antibodies circulating during pregnancy, which were later diagnosed in all pregnant women.In this contingent, in 39.47%, skin manifestations in the form of thin blood nets (reticular livedo), aggravated in the cold, vasculitis and microangiopathies in the form of spider veins were also noted. Subsequently, the subjects were consulted with a dermatologist in order to exclude their connection with dermatological diseases.Features of the hemostasis system in the dynamics of pregnancy in women with antiphospholipid syndrome.We studied the data of pregnant women with a history of reproductive loss with APS (main group).The main links of hemostasis were examined - activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), prothrombin index (PI), plasma recalcification (AR), thrombotest, fibrinogen according to Rutbergun, determination of the number of platelets in peripheral blood on the basis of the Central Scientific Research Laboratory and the biochemical laboratory of the clinic Andijan State Medical Institute.The study of the hemostatic system shows a general tendency towards hypercoagulation of the procoagulant link (Table 3.). When assessing the procoagulant activity of plasma, there is a tendency to an increase in APTT in 11 (28.94%) patients of the main group in the first trimester, in 4 (22.22%) pregnant women in the second trimester and in 5 (13.15%) pregnant women in the third trimester. The AVR parameters were also higher in the main group of patients compared to the control group (P <0.001).An increase in AR of the main group was observed in 16 (42.10%) pregnant women in the first trimester, in 11 (28.94%) pregnant women in the second trimester. However, and in the third trimester, there is a tendency for a slight increase in this indicator compared to the previous trimesters (Tables 3 and 4), and yet, in 4 (10.52%) women of the study group, high AVR rates remained (Fig. 6).Table 3. Features of the hemostasis system in pregnant women (I trimester)
 |
| |
|
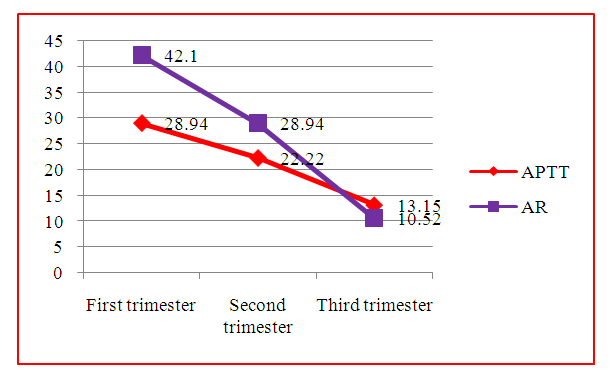 | Figure 6. Indicators of hemostasis parameters of the main group |
When studying the indicators of PTI, its significant increase was noted in the main group (P <0.001). The highest rates were noted in the first trimester compared to both the control group and the second and third trimesters.Table 4. Features of the hemostasis system in pregnant women (II trimester)
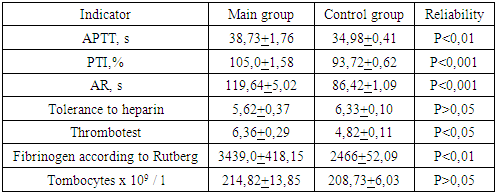 |
| |
|
The study of tolerance to heparin does not determine significant changes. A significant tendency to increase this indicator is not revealed, although it was found to decrease, starting from the moment of examination, to the third trimester of pregnancy in the main group.Our studies show that the data between the thrombotest indicators were insignificant, while there is a significant increase in Rutberg fibrinogen indicators already from the early stages of pregnancy, which is expressed by the end of the second trimester of pregnancy in the main group (P <0.001), apparently characterized by due to participation and adaptive hypercoagulation, increasing by the end of the second trimester.By the third trimester of pregnancy, the Rutberg fibrinogen indices in the main group were higher in 11 (28.94%), in 7 (18.42%) in the second trimester, in the third trimester in 4 (10.52%) pregnant women (Table 5) and almost 1.5 times higher than the control group (P <0.001).Table 5. Features of the hemostasis system in pregnant women (III trimester)
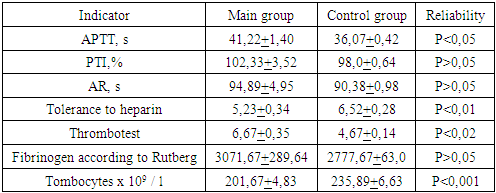 |
| |
|
At the same time, persistent hypercoagulation of both the procoagulant and vascular-troPhmbocyte link was found. There is a persistent increase in the indicators of the hemostasis system, which is not typical for the gestational age. An increased increase in the procoagulant activity of the parameters of the blood coagulation system with the progression of pregnancy was noted.
3. Conclusions
Thus, analyzing the structure of the threat of termination of pregnancy in the studied pregnant women, it should be noted that1) most often pregnancy was complicated by the threat of termination of pregnancy (55.26%);2) in every second pregnant woman during the period of APS diagnosis, the threat of termination was noted in all trimesters, despite the repeated traditional treatment aimed at maintaining pregnancy;3) predominantly the threat of interruption was combined with bleeding from the vagina (44.74%), skin manifestations (39.47%) and toxicosis (34.21%).Thus, the study of the clinical picture of the course of pregnancy in women with AAA confirms that APS affects the development of pregnancy complications.According to our data, the patients of the main group showed an increase in the procoagulatory potential, which develops earlier than hypercoagulation associated with the adaptive mechanism of hemostasis during physiological pregnancy and normal reproductive function.In the patients of the main group, an increase in the procoagulation potential was noted, which develops earlier than hypercoagulation, associated with the adaptive mechanism of hemostasis during physiological pregnancy and normal reproductive function. There are significant changes in the hemostatic system throughout pregnancy, starting from the early stages of gestation. Already from the first trimester of pregnancy, hypercoagulation in the plasma link of hemostasis is detected, which is not characteristic of early pregnancy.And so, the study of the clinical data of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome allows us to identify predictors of reproductive losses, thereby ensuring a differentiated approach to therapy and reducing the development of complications and unreasonable measures for the management of patients with this pathology.
References
| [1] | Abaeva I. Sh. Clinical significance of control over markers of inflammation in pregnant women with fetal loss syndrome and thrombophilia / Abstract of the thesis. dis ... cand. honey. sciences. - Moscow. -2011. -from. -3-4. |
| [2] | Baratova M.T., Sultanov S.N., Khairutdinova N.Kh., Babakhanova A.M. et al. The role of low molecular weight heparins in the treatment of placental insufficiency // News of dermatovenerology and reproductive health. -2012. -Number 3. from. -17-19. |
| [3] | Volik N.K. Methodological aspects of Doppler assessment of uterine-placental // Radiation diagnostics, radiation therapy. -2012. -№4. -from. -77-83. |
| [4] | Gadzhieva F.R. Cytokines as pathogenetic markers of the inflammatory process in miscarriage of infectious genesis // Problems of reproduction. - 2011. - No. 1. from. - 110-113. |
| [5] | Gazieva IA Immunopathogenetic mechanisms of the formation of placental insufficiency and early reproductive losses / Dissertation. doct. biol. sciences. Yekaterinburg. -2014. S. -6.19.38. |
| [6] | Dykan IN, Volik NK Intraplacental hemodynamics in complicated pregnancy // Journal of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine. -2013, -t. 19, No. 4. -C. 502-507. |
| [7] | Zhabchenko I.A., Tsypkun A.G., Zhitskiy A.M., Skripchenko N.Ya. Modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of placental dysfunction // Tavrichesky medico-biological bulletin. -2011. -T.14. -Number 3. –Part 1 (55). –S. 81-88. |
| [8] | I. V. Ignatko, M. A. Kardanova. Pregravid training and obstetric tactics in women with antenatal death // International research journal. No. 8 (27) 2014. Part 3. S. -29-33. |
| [9] | Karimov A. Kh., Nazhmutdinova DK, Fazylova SA Modern ultrasound technologies used in the examination of pregnant women. - T., 2012. S. 11. |
| [10] | Sidelnikova V.M. Preparation and management of pregnancy in women with recurrent miscarriage // Methodical manuals and clinical protocols. Moscow "MEDpress-inform". 2013. -p. -145-154. |
| [11] | Maniyozova G., Negmatshaeva H., Yuldasheva O., Turaeva G., Parpieva D. Use of enzymes in complex treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome in women with reproductive losses of andijan state // European medical Heals and Pharmaceutical Journal. –Chechiya, 2014 V7, I2. -pp.1-2. |
| [12] | Maniyozova GM, Turaeva G. Yu., Babich SM, Negmatshaeva HN, Mamajanova SA, Abdukaharova S., Hakimova K. Use of Essentiale Forte N in Complex Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Women of Ferghana Valley // Journal of Medical Research and Development. - Germany, Jan. 2015, Vol. 4 Iss. 1, pp. 8-10. |









 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML



