-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(10): 780-783
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201010.12
Received: Sep. 8, 2020; Accepted: Oct. 2, 2020; Published: Oct. 15, 2020

The Characteristic of Energy Metabolism Disorders and Its Correction in Children with Celiac Disease
Dustmukhamedova D. Kh., Kamilova A. T.
The Republican Specialized Scientific, Practical Medical Centre of Pediatrics of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

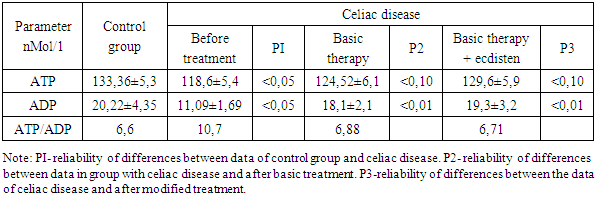
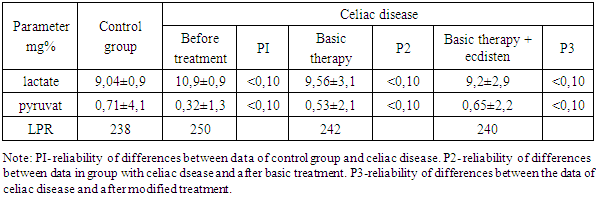
This article presents results of investigations of the disorders of energy metabolism and possibility of its correction with phytoecdisteroid ecdisten in children with celiac disease. Investigation was performed during the period from January 2009 to December 2012 in the Department of Gastroenterology of the RSRPMC of Pediatrics. There were studied 45 children with celiac disease at the age of 3 to 14 years. The investigations performed showed that in patients with celiac there were damaged processes of energy production: the synthesis of ATP and ADP was reduced, increased their ratio, 4-time reduction of LTT and GTT, there has been registered gain of the parameter of the state lactat/pyruvat, that indicated about prevalence of tissue hypoxia in children. In contrast of basic therapy the treatment of patients with celiac disease with use of phytoecdisteroid (ecdisten) decreases in duration of clinical-laboratory symptoms among the patients with celiac disease.
Keywords: LTT, GTT, ATP, ADP, Children, Metabolism, Celiac
Cite this paper: Dustmukhamedova D. Kh., Kamilova A. T., The Characteristic of Energy Metabolism Disorders and Its Correction in Children with Celiac Disease, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 10, 2020, pp. 780-783. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201010.12.
- The significance of the problems connected to chronic bowel diseases is explained by their wide distribution among the children's population, and also by frequency of development of the heavy forms with unfavoured outcomes and unpredictability of the prognosis. The special place among them is occupied by celiac disease, which is most unfavourable in relation to prognosis of disease, characterized by diffusive atrophy of the intestinal mucosa developing due to gluten (protein of cereals) intolerability [1,2,3,4,5,7,18]. The previous researches showed that celiac disease © in children in our region progresses with marked metabolic disorders, that requires correction of these conditions [5].Now the constant diet free of gluten appeared to be single method of C treatment. The adherence to this very restrictive diet is rather inconvenient because of presence of gluten in the contents of many products. Even at strict keeping to diet involuntary gluten usage fluctuates from several milligrams up to two gr a day [17,20]. The receiving even of such insignificant quantity of gluten induces clinical signs and histological changes, such as atrophy of the intestinal mucosa and increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes [14,22].Therefore many patients, even if they follow strictly to gluten-free diet they do not reach clinical remission, and thus there is no complete restoration of the intestinal mucosa even on a background of gluten-free diet [15,19].Thus, only keeping to gluten-free diet is not sufficient for the complete control of a health state of many patients with celiac disease.Attempts of revealing of new parts of pathogenesis of the enteric insufficiency and development on their basis of the pathogenic approaches to treatment of this heavy pathology now proceed. Over the last decade in medicine the metabolic direction has been developed intensively with purpose of performance of theoretical and applied analysis of metabolic processes of different levels as a basis or a background for many illnesses. The knowledge about a role of disturbances of the cellular energy metabolism in development of various pathological processes has been actively formed. The key part in this complex are mitochondria which are structures presenting in the cytoplasma of all the cells and performing functions vital for every cell. With the account of abovementioned it is clear, that the disorders of cellular energy metabolism on the basis of which, first of all, the mitochondrial insufficiency is found leading to the wide spectrum of clinical expressions.The level of adenyl nucleotides, and first of all, ATP, reflecting final stage of energy accumulation in the tissue, may be considered as indicator of energy state of cells. The energy level of tissue is also characterized by the sum of all adenyl nucleotides and their ratio [9].The fact of confirmation of efficiency of phytoecdisteroids in stimulation of protein-synthesizing processes in the body seems to be important [11]. As the modulators of energy metabolism there are of great interest investigators of the native researchers on use of phytoecdisteroids isolated from Leuzea carthamoides and Turkestan lively creature for bioenergy of the liver cell under the conditions of hepatitis characterized first of all by sharp changes in the mitochondria functioning. [12].Our researches in vitro [6] present data about obvious dissociation of a respiratory circuit in the suspension of mitochondria in the model of enteral failure in the growing rats. While using Ecdisten as correcting agent it was revealed that practically all parameters of oxidative phosphorylation were nearer to control meanings.The purpose of our research was to prove application of phytoecdisteroid ecdisten for correction of disorders of energy metabolism in celiac disease in children.
1. Materials and Methods
- The clinical examinations were carried out in 45 children with celiac disease at the age of 3 till 14 years, the average age was 7,1±2,3 years.The diagnosis of celiac disease was verified on the basis of the positive tests to tissue transglutaminase IgA (increase more 10 times from norms), and results of mucosa biopsy with evaluation of histological changes by March. Diagnosis of celiac disease was made in 26% of patients at the age before 12 months, in 43,5% - before 5 years of life, in 26,0% - to 8 years and in 4,5% of children at the age of above 8 years. In order to study the state of digestion and absorption of the disaccharides there were used tests with glucose - glucose tolerant test (GTT), which were given per orally in dose 1.75 g/kg with the following measurement of glucose content by glucose oxidant method 30 and 60 minutes later. The norm was considered as increase in glycemia for an hour more than 1,1 mmol/1. Measurement of ATP and ADP in the blood serum as performed with use of chromatography on the gas-liquid chromatograph “LKB” (Sweden), with following spectrometry on the SF “BEKMAN”. The pyruvic and lactic acids were determined on the biochemical analyzer “Basis Secomam” (France). The contents of pyruvic acid was measured by method of Friedman F. et al [8].For correction as a preparation improving processes of oxidative phosphorylation, membrane digestion and absorption in the intestine there was used phytoecdisten as the natural substance of steroid structure isolated from roots of Leuzea carthamoides, made by Institute of Chemistry of Plant Substances of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Uzbekistan. There were developed the following doses of preparation: 2,5 mg/ kg body weight a day for 14 days taking into account its cumulative effect during a month [6].For evaluation of the efficacy of preparation in the complex treatment of children with celiac disease in 2 groups of patients: group 1 included 20 children.Received basic therapy (elimination diet, pancreatic enzymes, probiotics, partial parenteral feeding according to indications), 25 children were selected to the group of patients receiving modified treatment (basic therapy + ecdisten 2,5 mg/kg/day for 14 days). Efficacy of preparation was assessed by clinical manifestations as well as by laboratory investigations reflecting the state of membranous and cavitary hydrolysis and absorption, evaluation of the state of cellular energy by contents of lactic and pyruvic acid, their ratio, quantity of adenyl nucleotides in the blood in 3 months later.The statistical processing of the received results was performed by a method of Student - Fisher criteria. There was calculated average arithmetic size (M), average mistake (standard mistake - m), and parameter of reliability (P). Size P less than 0,05 is considered as a parameter of reliable distinctions.
2. Results and Their Discussion
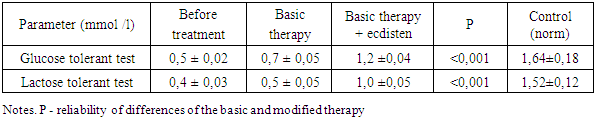
- The research was carried out during the period since January 2009 till December 2012 in the department of gastroenterology of the Republic Specialized Research Practical Medical Center of Pediatrics. Among the patients with celiac disease the boys were prevailed (54%).The comparative analysis of the parameters of membranous digestion revealed almost 4 -time reduction of LTT and GTT (Table 1). After basic therapy in children there was noted tendency to increase in level of glycemia gained. The modified therapy positively influenced on the parameters of membranous digestion that was confirmed by reliable increase in glycemia gained in children (P < 0,001).
|
|
|
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML