-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(8): 584-586
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201008.10

Modern Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis Depending on the Stage
Irismetov M. E., Safarov N. B., Razhabov К. N., Tadzhinazarov M. B.
Republican Specialized Scientific and Practical Medical Center for Traumatology and Orthopedics Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The purpose of this scientific work was to determine the tactics of treatment depending on the degree of osteoarthritis and the characteristics of the disease. 196 patients with different severity of osteoarthritis and osteoarthrosis of the knee, treated in the department of Sports Traumatology of RSSPMC TO in the period from 2014 to 2019 were included to the study material. All patients underwent standard examination methods. Patients were treated with surgical methods according to our proposed 5 types, depending on the severity and characteristics of the disease, in addition they received physiotherapy and exercise therapy. The results of treatment were evaluated by Lysholm score taking into account certain indicators with the summation of the ball scales. In the majority of patients (188 patients), an improvement in the condition of the knee joint was noted. Only in 4 patients after the arthroscopic intervention a short-term remission was occurred for only a few months, which was associated with the severity of the pathological process - osteoarthritis IV stage. Conclusion. The use of an individual approach depending on the severity and characteristics of disease and the complex treatment of gonarthrosis is reasonable with many benefits and positive consequences in the postoperative period.
Keywords: Osteoarthritis, Knee joint, Arthroscopy, Treatment
Cite this paper: Irismetov M. E., Safarov N. B., Razhabov К. N., Tadzhinazarov M. B., Modern Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis Depending on the Stage, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 8, 2020, pp. 584-586. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201008.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Osteoarthritis of the knee is a polyetiological degenerative – dystrophic disease characterized by damage to the articular cartilage, the subchondral and metaphysical bone layer, as well as the synovial membrane, ligaments, capsule, and muscles. It is accompanied by the pathological formation of bone and cartilage growths named as osteophytes, and manifested by pain and restriction of movement in the joint [2]. According to epidemiological studies, this pathology affects from 8% to 20% of the adult population, and the knee is the most frequent localization of this type pathological process accompanied by the degenerative – dystrophic changes of the joint, which result in temporary disability [2,8]. In aging groups, the incidence of osteoarthritis increases. The causes of osteoarthritis are not fully studied. In development of osteoarthritis trauma of the joints, physical activity have their role. Overweight people have a large load to the joints and this also contributes to the development of osteoarthritis. Not only the articular cartilage in the pathological process, but all elements of the joint, including the subchondral bone, ligaments, capsule, synovial membrane and periarticular muscles involve to the process.Osteoarthritis of the knee causes disability in adults. In general practice, physical disability of patients is directly related to comorbidity. OA refers to diseases with a high level of comorbidity [1,3,4,5,6,7]. Majority of patients with osteoarthritis usually have 5-6 diseases. Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is combined with other musculoskeletal diseases, especially osteoporosis. In osteoarthritis of the knee joint arterial hypertension (more than 50% of patients), coronary heart disease, heart failure, obesity, diabetes, lung diseases (chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases) and the gastrointestinal tract are more frequently observed pathologies. [1,3,4,5,7].At present time radiological studies, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, X-ray densitometry and arthrosocopic method are used to determine the pathological process in the diagnostic of knee osteoarthritis.
2. Materials and Methods
- In 2014-2018 in the department of Sports Traumatology 196 patients treated with osteoarthritis of the knee. The age of patients ranged from 35 to 80 years. From this group 134 (68.4%) patients were women, 62 (31.6%) patients were men. Some patients had comorbidities such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, vascular atherosclerosis of the neck and brain vessels, and osteoporosis, and besides a number of concomitant diseases increased with increasing of age. During examination inflammatory processes in the form of synovitis, bursitis, ligamentitis, and periarthritis were revealed in varying degrees in all patients.All patients underwent arthroscopic surgery suggested by one of 5 types of surgical procedures. After surgery, all patients were prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy exercises, osteotropic drugs, physiotherapy, general strengthening medications, chondroprotectors, vasodilators.Majority of patients with arthritis, especially women, had varicose veins, which were recommended venotonics to maintain the veins tone of lower extremities. Because of this, in postoperative period ointments and gels containing heparin were prescribed. The bandaging of the lower extremities with an elastic bandage from the tips of the fingers of the foot to the groin area or the wearing of elastic stockings prevents venous stasis of blood.
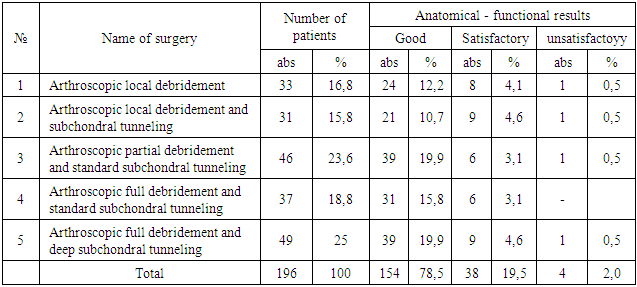
3. Results of the Study
- The study included patients with osteoarthritis of the knee at various degrees. This disease is most common in older patients, and the presence of concominant diseases affects the outcome of the surgery. We performed 5 types of arthroscopic surgery in 196 patients with knee OA. Results of treatment with one of 5 types of surgeries assessed as good, satisfactory and unsatisfactory results (1-table). Pain at rest disappeared in patients from the next day after surgery. From the next day, patients were allowed weight-bearing to the operated extremity, with following a gradually increasing load.
|
4. Discussion
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used to relieve the inflammatory process. Important meaning to the success of treatment is physiotherapy. In the absence of contraindications, as precancerous conditions, damage to the skin following procedures as well as electro-and phonophoresis of various drugs, a magnet-laser, diathermy are appointed. Paraffin-ozokerite applications, massage for arthritis are prescribed in cases of osteoarthritis without signs of joint synovitis, otherwise these latter procedures may lead to an increase of the amount of effusion in the joint.Medications for improving blood circulation were prescribed with the aim of improving the microcirculation of the joint, normalizing the redox processes in the joint. A special place in the treatment of osteoarthritis is physiotherapy. In most patients with osteoarthritis, the muscles become flabby, part of them is hypotrophied. As is well known, along with the capsule-ligament apparatus, the muscles are also stabilizers of the joints. In cases of decreasing of muscles’ tone or muscle hypotrophy, the load to the joint increases. With regular performance of physical therapy, the muscles are strengthened, thereby reducing the load on the joints and as a result, the pain reduces.The important point is the appointment of chondroprotectors containing chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine. Since arthritis has a degradation of the articular cartilage, for their restoration it is necessary to take preparations containing chondroitin sulfate and glucosamines. These medications are used for a long time, both in oral and in the injection form. With the use of chondroprotectors, the endogenous deficiency of glucosamine is replenished, the synthesis of proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid is stimulated. Also with the use of chondroprotectors, enzymatic processes in the cells of the synovial membrane and articular cartilage are restored, they promote sulfur fixation during the synthesis of chondroitin-sulfuric acid, the development of degenerative processes in the joints in their diseases is inhibited, thus the severity of arthralgia is reduced.Due to regional osteopenia or osteoporosis, it is necessary to replenish the body with medications containing calcium. In severe cases with last ones, bisphosphonates are recommended - medications containing alendronate and zoledronic acid, also medications containing calcitonin. As fortifying drugs vitamins, especially group B, nicotinic acid, etc. are prescribed.
5. Conclusions
- 1. Standart studies in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis is an MRI, radiography of the knee joint. It is necessary to take into account X-ray picture of osteoarthritis of the knee does not always coincide with the clinical findings or complaints of the patient.2. In osteoarthritis with injuries of elements of the knee joint, in the presence of indications, arthroscopic debridement with subchondral tunneling is performed.3. Physiotherapy is prescribed after the surgery to strengthen the periarticular muscles of the knee and to reduce venous stasis of blood in the veins of the lower extremities.4. In case of persistent pain syndrome, when there is severe deformity, instability of the knee joint, athroplasty of the knee joint is recommended.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML