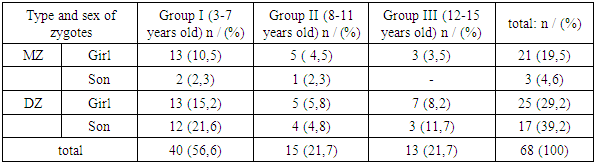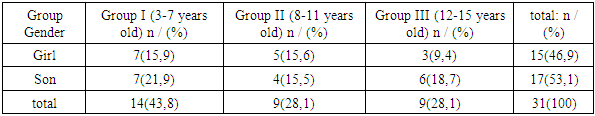-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(7): 484-486
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201007.10

Prevalece of ENT Diseases in Twin Children and the Effect of CAF Factores at the Stage of Exacerbation
Nurov Ubaydullo Ibodullayevich
Associate Professor of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Ophthalmology of Bukhara State Medical Institute
Correspondence to: Nurov Ubaydullo Ibodullayevich, Associate Professor of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Ophthalmology of Bukhara State Medical Institute.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

To date, due to the hereditary and exogenous influence on the fetus and their specific role in the period of female twin pregnancy, pathological diseases of the ENT organs are observed with an increase in the number of congenital and acquired diseases associated with them. That is, Diseases of ENT organs are common among children with Monozygotic and dizygotic disorders in the same twin pregnancy compared to the same single fetus due to the birth factor, the risc factors of postpartum, low weight, which are common in twin children during pregnancy, and for some other reason. To assess the role of hereditary and environmental factors and to know the process of disease development, to date, pathological changes in the functions and anatjmical aspects of ENT organs in the Twins are studied.
Keywords: ENT (Otorhinolaryngology) organs, Twin, Monozygote, Dizygote, Intrapioral analogy, Chronic tonsillitis
Cite this paper: Nurov Ubaydullo Ibodullayevich, Prevalece of ENT Diseases in Twin Children and the Effect of CAF Factores at the Stage of Exacerbation, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 7, 2020, pp. 484-486. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201007.10.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The health problem of children born of twin pregnancies was first studied in 1876 in London by Francis Galton. Although this is the first research in this field, it has retained its importance to this day. Twins make up 2.0% of the world's population [1,2]. There are a number of factors and characteristics related to pregnancy and childbirth (premature birth, underweight, birth trauma, etc.) that affect the overall development of the child and the functioning of its organs and systems, in particular the anatomy, histology and functional functioning of the ENT organs.Assessment of the role of hereditary and environmental factors and the development of disease suggest that to date, functional and anatomical pathological changes have been observed in the ENT organs of twins. In addition, the pathology of anatomical and physiological defects in the ENT organs is more common in twin children during the perinatal period compared to twins born alone. Respiratory organs and changes related to the functioning of this system are more noticeable, including ENT organs and especially in the formation of the sound analyzer, nasal barrier curvature, nasal obstruction defects will affect other body parts in the future.Pathological conditions related to the auditory organs in twins are 3% more common than in other ENT organs [2]. Hearing status is of direct importance for human social development and intellectual potential, especially for young children, because at this time the auditory analyzer serves to develop "cognitive" processes that take place under the control of brain functions, especially attention and auditory memory., [3,4]. Higher brain functions such as attention, memory, and the condition of the auditory analyzer affect the results of audiometry in auditory examination, but to date, congenital pathology of the auditory organs in twins is more common [7]. The reason for this has been found in many experiments to be related to the development of brain organs and the incomplete satisfaction of the oxygen demand of brain cells [3]. The presence of tissue in relative hypoxia is associated with placental enlargement and the prevalence of inflammatory diseases common in twin pregnancies [8]. In the process of fleeting and ontogeny, it is very important to determine the origin of the pathology of the ENT organs and the causes of the disease [5,6,7]. This identifies risk factors for ENT disease and promotes the development of an ENT disease prevention system.
2. The Aim of Our Research
- To determine the prevalence of diseases of the ENT organs in monozygotic and dizygotic twins, to analyze the causes of pathology of the ENT organs in them.
3. Materials and Methods
- The choice of research methods was determined by the tasks to be performed and included: The anatomical, physiological, and functional conditions of the ENT organs in the twins were fully studied. The studies used data collected on the basis of functional examinations of ENT organs in monozygotic and dizygotic twin children who visited clinics and hospitals in Bukhara, Navoi, Kashkadarya regions, cities and districts. Determining the type of zygote, collection and analysis of anamnestic data on the patient's relatives, screening, ante-intranatal, postnatal life; zygote type anamnesis was determined according to phenotypic data, i.e. similarity and immunological methods using blood group and serum protein detection, leukocyte formula, histomoscopic HLA polysymptomatic diagnosis method.The functional condition of the body was assessed according to the results of clinical and neurophysiological examination. Clinical otorhinolaryngological examination includes endoscopic, auditory tuning fork, and speech detection of ENT organs.From 2014 to 2019, 71 twins born were examined, which formed the main group: 13 pairs of them were monozygotic twins, 21 pairs were dizygotic twins and one triplet; the age distribution of the children surveyed is given in Table 1.
|
|
4. Results of Research and Discussion
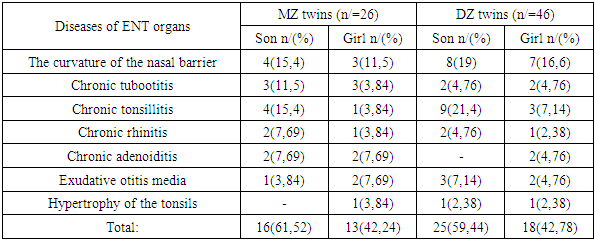
- The study concluded that diseases of the ENT organs in monozygotic and dizygotic twins were as follows. Table 3. Intrapareal similarity analysis showed that in monozygotic couples, nasal barrier curvature was 26.9% in both twins, 15.4 in boys, 11.5 in girls, and 35.6% in dizygotic couples (19 boys, 16.6 girls, ie at the same time). curvature of the nasal barrier in both twins was found to be 7 times more common in monozygotic twins than in dizygotic twins.
|
5. Conclusions
- Several twins have a combination of ENT diseases that occur simultaneously.The origin of these cases was determined as a result of the perinatal process of the ENT organs and its severity, as well as the influence of risk factors during childbirth, that is, the perinatal period, a number of factors affect the formation and development of ENT diseases. As a result, in twins with severe perinatal period, there is a sufficient tendency for the development of pathology of the ENT organs. This results in a risk group. Otorhinolaryngologists should monitor twin children from an early age for prevention, early diagnosis, and timely treatment of ENT diseases.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML