-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(5): 351-353
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201005.15

Peripheral Blood System Status of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Depending on Haptoglobin Polymorphism
Shodikulova Gulandom Zikriyaevna, Pulatov Ulugbek Sunatovich
Samarkand State Medical Institute, Samarkand, Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Shodikulova Gulandom Zikriyaevna, Samarkand State Medical Institute, Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of the study is to study the peripheral state of blood (PBS) in RA patients with different haptoglobin phenotypes. The study showed a connection between the course of the disease, the severity of anemia and the type of haptoglobin, which was revealed mainly in patients with the phenotype Hp 2-2. It is one of the factors of formation, development and chronization of the inflammatory process, where immunogenetic predisposition plays an important role. Clarification of these predisposing factors allows to reveal heavy forms of the flow of RA and to carry out timely preventive measures.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, Haptoglobin phenotypes, Peripheral blood state, Anemia
Cite this paper: Shodikulova Gulandom Zikriyaevna, Pulatov Ulugbek Sunatovich, Peripheral Blood System Status of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Depending on Haptoglobin Polymorphism, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 5, 2020, pp. 351-353. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201005.15.
1. Introduction
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease of unknown etiology, characterized by chronic erosive arthritis and systemic damage to internal organs [1,6]. RA is one of the most common joint diseases, occupying about 10% in the structure of rheumatological pathology, it is not only a medical, but also an economic problem, since the debut of the disease in most cases is observed in people of working age [2,5,7]. One of the extra-articular manifestations of the disease is anemia, the prevalence of which ranges from 30 to 70% of cases. Anemia in RA is based on a deficiency of hematopoiesis factors (iron, vitamin B12, folic acid), a chronic inflammatory process (the so-called anemia of a chronic disease - ACH), autoimmune reactions (autoimmune hemolytic anemia) or the toxic effect of drugs (aplastic anemia) [3,4]. Anemia is accompanied by tissue hypoxia and can, on the one hand, lead to damage to various organs and systems, and on the other hand, to a deterioration in the course of the underlying disease and patient prognosis.In recent years, the role of the genetic predisposition of RA development has been widely discussed. Most likely, the disease develops as a result of a complex and largely probable interaction of genetic factors and environmental factors [3]. Of great interest in studying the hereditary predisposition to the disease is also the determination of the HP glycoprotein α 2 -globulin fraction of whey proteins with genetic polymorphism [4,7]. The literature cites evidence that the exchange of NR is closely related to the processes occurring in the connective tissue.The aim of our study was to study the state of UCS in patients with RA with various haptoglobin phenotypes.
2. Methods and Materials
- 185 patients with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for the period 2016–2019 were examined. The diagnosis of the disease was established on the basis of diagnostic criteria proposed by the American College of Rheumatologists. The average age of patients with RA was 54.8 ± 1.4 years, the duration of the disease was 8.6 ± 0.7 years (the correlation index of these indicators was r = 0.48). The determination of the haptoglobin (Hp) phenotype in the blood serum was carried out by Davis electrophoresis in the modification of N.A. Aspen. The blood serum levels of patients were also determined: iron, hepcidin, ferritin, and ADC. The data obtained were subjected to statistical processing using a software package of statistical analysis on a Pentium -4 computer. For statistically significant changes, a confidence level of P < 0.05 was taken.
3. Results and Discussion
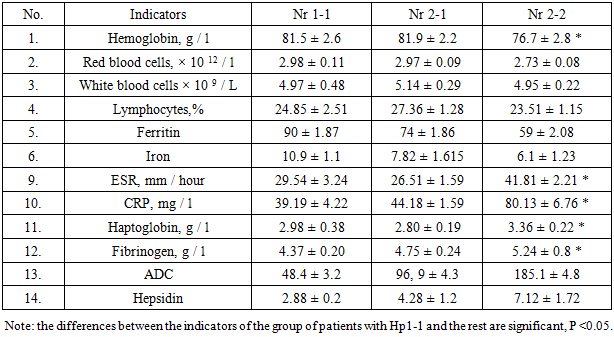
- As you know, in recent years, the degree of anemia is considered a prognostic indicator of RA and is included in the criteria that determine the activity of the disease. According to the literature, the greater the degree of anemia, the worse the prognosis of the disease. In our studies, anemia was observed in 102 patients (55.1%) with rheumatoid arthritis: in 57.3% of cases, chronic disease anemia, in 42.7% of patients, iron deficiency anemia. Hemoglobin in the peripheral blood of RA patients appeared on average 79.1 ± 1.7 g / l, the content of erythrocytes - 2,8 ± 0,06h10 12 / l, iron - 7,1 ± 1,41mkmol / l, ferritin - 74.5 ± 4.11 μg / L, which reflects the average degree of anemia. Change in hemoglobin content, the number of red blood cells, iron and ferritin with various phenotypes of haptoglobin are shown in table 1.
|
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML