-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(4): 262-265
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201004.19

The Role of Indicators of Ferrokinetics and Endogenous Erythropoietin in Anemia of Pregnant Women
Sarkisova L. V., Yuldasheva R. U., Kurbanova Z. Sh., Aslonova M. J.
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Bukhara State Medical Institute, Abu Ali IbnSina of the Ministry of Health of Uzbekistan
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

To study the parameters of ferrokinetics in the dynamics of pregnancy, taking into account the severity of anemia For the period from 2017-2019. We examined 90 pregnant women with anemia, 50 of them were untreated, received in the maternity ward with a kind of activity, and 40 were treated in the department of pathology of ward with a kind of activity, and 40 were treated in the department of pathology of pregnant women. The control group consisted of 40 conditionally healthy pregnant women. Under our supervision and examination, there were 40 pregnant women with anemia, aged 17–35 (28 ± 0.1) years, who were registered in female consultations and were treated in the department of pathology of pregnant urban maternity complex No. 1. Bukhara.
Keywords: Iron deficiency anemia, Ferrokinetics, Erythropoietin
Cite this paper: Sarkisova L. V., Yuldasheva R. U., Kurbanova Z. Sh., Aslonova M. J., The Role of Indicators of Ferrokinetics and Endogenous Erythropoietin in Anemia of Pregnant Women, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 4, 2020, pp. 262-265. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201004.19.
1. Introduction
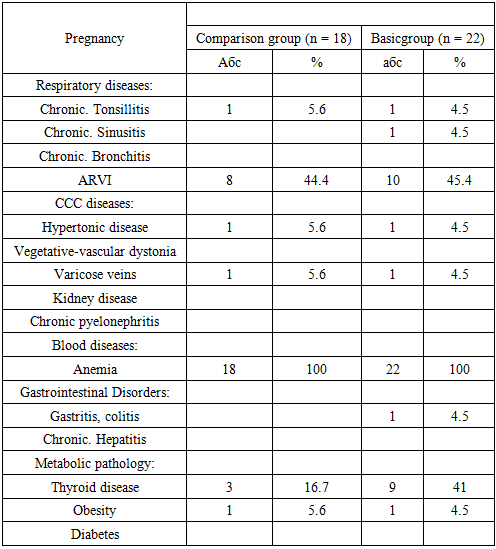
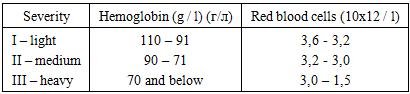
- The main criteria for IDA are a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and a color index reflecting the hemoglobin content in the erythrocyte. Morphologically determined hypochromia, erythrocytes, microcytosis, anisocytosis and poikilocytosis. The content of reticulocytes in the blood, as a rule, remains within the normal range. An important diagnostic value is a decrease in the level of serum gland and ferritin and an increase above the standard values of transferrin and the total iron binding capacity of the serum. Recently, the importance of determining the level of transferrin receptors inblood plasma, which is a sensitive indicator of the degree of tissue iron deficiency. According to the WHO recommendation, the lower limit of normal hemoglobin concentration for a pregnant woman is reduced to 110 g / l (outside pregnancy - 120 g / l), hematocrit – to 33% (non-pregnant - 36%). Laboratory criteria: In addition to hemoglobin (Hb), as a parameter of the functional fund, other hematological parameters are determined: red blood cell count (RBC) and hematocrit (Ht). The reserve fund is estimated by the level of serum ferritin (SF), and iron – regulatory - by erythrokinetic indicators: erythropoietin (EPO) and the coefficient of adequacy of EPO products.Severe anemia is the main cause and starting mechanism for the development of complications leading to maternal mortality and perinatal pathology. Among the deceased mothers, IDA is observed, mostly moderate (20%), severe (60%) and extremely severe (20%). A large proportion of deceased males with moderate and severe anemia (55.7%) was noted, in which pregnancy and childbirth in 7% of cases were complicated by pathological blood loss.Pregnant women suffering from severe anemia, the risk of childbirth increases with decreasing hemoglobin and increased hypoxia of organs and tissues due to the development of profuse, hypo- and atonic bleeding, severe coagulopathy and postpartum septic diseases. The frequency of detection of IDA during pregnancy depends on the three-mestria. So, in the first trimester, it is rare, in 25% of cases. In the second trimester, IDA is detected in 60% of cases, more often after the 25th week of pregnancy. In trimester III, IDA occurs in 80% of pregnant women.Normal hemoglobin levels do not always indicate a sufficient supply of iron in the body. Even in the absence of a decrease in hemoglobin, erythrocyte and hematocrit, there may be signs of adrenal or latent iron deficiency. 40-60% of women of childbearing age, even before pregnancy, there is a deficiency of this trace element. The presence of IDA, especially before the onset of gestation, significantly increases perinatal morbidity and mortality, fetal growth retardation syndrome is observed in 32% of cases, hypoxic brain injury is bad - 40%. The combination of IDA and placental insufficiency complicates the gestational process in 20-40% of cases. The aim of the study was to improve the quality of medical care for pregnant women by improving the methods of treating anemia and preventing complications of childbirth.
2. Research Objectives
- To study the parameters of ferrokinetics in the dynamics of pregnancy, taking into account the severity of anemia.
3. Materials and Methods
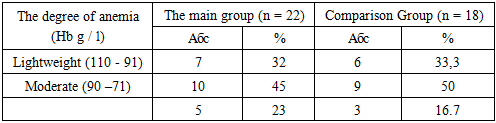
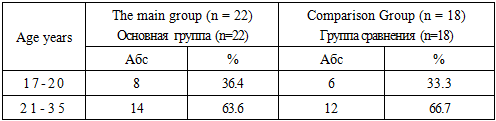
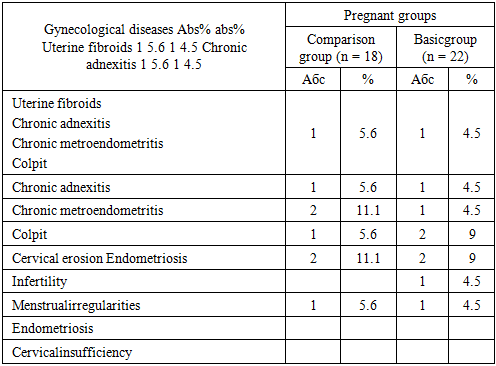
- For the period from 2017-2019. We examined 90 pregnant women with anemia, 50 of them were untreated, received in the maternity ward with a kind of activity, and 40 were treated in the department of pathology of pregnant women. The control group consisted of 40 conditionally healthy pregnant women. Under our supervision and examination, there were 40 pregnant women with anemia, aged 17–35 (28 ± 0.1) years, who were registered in female consultations and were treated in the department of pathology of pregnant urban maternity complex No. 1. Bukhara.Hemoglobin content 95 g / l and below, serum iron 15 μmol / l and below, gestational age of 20 weeks or more, and absence of other blood diseases were the criteria for selection of pregnant women into groups.The main complaints of pregnant women with anemia were general weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath with mild physical exertion, flickering of "flies" before the eyes, dizziness, nasal hemorrhages, sleep disorders and mood for no apparent reason, decreased appetite, memory loss.Depending on the type of antianemic therapy, the patients were divided into 2 groups: the comparison group — 18 pregnant women — received ferron 100 mg, 1-2 capsules daily for 2-3 months, until normal hemoglobin level in the blood was reached; the main group - 22 pregnant women, received ferron100 mg 1-2 capsules daily for 2-3 months, until normal hemoglobin level in blood and REPO 2000 MED are achieved subcutaneously after 3 days 2-3 injections depending on the severity anemia. The distribution of pregnant women, depending on the severity of anemia, is presented in table 1.
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
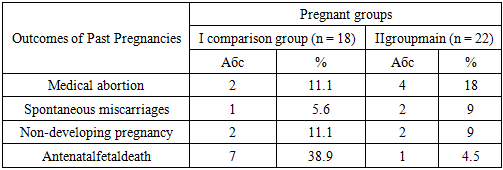
- It was established that the progression of mild anemia in every second, the development of PE and prenatal discharge of water in every third was a distinctive feature of the course of pregnancy. Births were often complicated by bleeding during pregnancy (PONRP - 6.3%) and after delivery (13.5%) and injuries of the soft birth canal (70%). Syndrome of delayed fetal development and the birth of low-weight babies was observed in 30% of patients. The findings showed that anemia is a high risk factor for the development of pregnancy complications and rhodes, which dictated the need to optimize complex therapies for pathology throughout the entire gestation period, which will prevent complicated pregnancy and childbirth and will be one of the antenatal measures fetal protection.A study of ferrokinetics in the dynamics of pregnancy has shown that anemia is iron deficient, with the degree of reduction of iron content, KNTZh and ferritin and increase of transferrin level depends on the severity of the disease. Treatment of IDA with iron-containing drugs only is not effective enough. Hb level <90g / l and resistance of anemia to treatment with Fe preparations is an indication for REPO therapy, especially when preparing for delivery.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML