-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(3): 175-178
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.09

Problems of Sepsis Diagnostic and Treatment in Diabetes Mellitus
Abdullaev Sayfulla Abdullaevich 1, Babajanov Axmadjan Sultanbayevich 2, Kurbanov Erkin Yusufovich 1, Toirov Abduxomid Suvonkulovich 3, Abdullaeva Lola Sayfullaevna 3, Djalolov Davlatshokh Abduvokhidovich 3
1Department of Purulent Surgery, Samarkand City Medical Association, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan
2Department of Surgery, Samarkand City Medical Association, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan
3Samarkand State Medical Institute, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan
Correspondence to: Djalolov Davlatshokh Abduvokhidovich , Samarkand State Medical Institute, Samarkand, Republic of Uzbekistan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In most cases, sepsis is caused by gram-positive flora. However, in patients without hematogenous dissemination, gram-negative microorganisms were microbiologically confirmed. Diagnosis of sepsis is a very difficult question. About of 30% of sepsis cases remain without bacteriological confirmation. About of 40-45% of sepsis cases are caused by staphylococci. However, 80% of cases of surgical infection is combined with an anaerobic infection. Surgical treatment of sepsis is considered to be the most relevant. Especially sepsis due to inflammatory diseases of soft tissues, treatment should begin with an urgent surgical intervention. In sepsis, close attention is also paid to glucose levels. In patients with diabetes mellitus, sepsis proceeds against the background of damage to the vascular bed in the form of micro and macroangiopathies. This aggravates the infectious process, causes the occurrence of various complications, lengthening the hospital stay, which leads to high mortality.
Keywords: Sepsis, Phlegmon, Abscess, Infection, Diabetes mellitus
Cite this paper: Abdullaev Sayfulla Abdullaevich , Babajanov Axmadjan Sultanbayevich , Kurbanov Erkin Yusufovich , Toirov Abduxomid Suvonkulovich , Abdullaeva Lola Sayfullaevna , Djalolov Davlatshokh Abduvokhidovich , Problems of Sepsis Diagnostic and Treatment in Diabetes Mellitus, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 175-178. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.09.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Despite development of medical science, the problem of a surgical infection remains a current problem. Sepsis is response to various infections of bacterial, virus, fungal character. For the first time the term sepsis was used by Hippocrates 2000 years ago. This term is meant as pathological disintegration of fabrics with rotting. In recent years sepsis on a global scale began to accrue, (more than the 50th million people a year), and mortality is 5.3 million cases. Sepsis frequency in the developed countries of 200-275 people on 100000 population a year. Annually in the USA 500 thousand cases of sepsis, mortality from 20 to 50% meet. Many authors, having studied sepsis epidemiology, consider 4 main localizations of primary center: pulmonary, wound, abdominal, urological. According to us, at a diabetes mellitus, often pyoinflammatory diseases of soft tissues, extremities and a crotch were the centers of sepsis. Now it is proved that in most cases sepsis develops owing to bacteria of gram-positive flora. However at some infectious patients sepsis develops at the expense of a gram-negative bacterium.At present in daily practice the criteria of diagnostics and classification of sepsis offered by association of the American pulmonologists are applied.1. Sepsis - reciprocal inflammatory reaction of an organism to infections, availability of the center of an infection and two or more signs of a syndrome of system inflammation.2. The heavy sepsis which is combined with organ dysfunction, hypotension, disturbance of fabric perfusion.3. Septic shock - sepsis with fabric and organ hypofunction and hypotonia with dysfunction of systems and bodies.Taking into account introduction of a syndrome of system inflammatory reaction of an organism the concept of PIRO is developed for specification of the authentic diagnosis of sepsis: predisposition (P-predisposition) - age, genetic factors, associated diseases; an infection (I-infection) - localization of the center of an infection, a contagium; reaction (R-response) - clinical manifestations of infectious process; (O-organ dysfunction) - assessment of degree of organ dysfunction on SOFA scale.
2. Work Purpose
- Improvement of results of surgical treatment of pyoinflammatory process at a diabetes mellitus complicated by sepsis.
3. Materials and Methods
- In it is purulent - septic office of the Samarkand city medical association were on hospital treatment of 29 patients with a diabetes mellitus with various pyoinflammatory diseases, complicated by sepsis. Age of sick from 30 to 72 years, from them 16 patients were at efficient age. There were 17 men, women - 12 people. On localization of the pyoinflammatory center were: in the lower extremities and a crotch at 18, the upper extremities - at 5, post-injection abscesses in buttocks - at 4 and suppuration of postoperative wounds of an anterior abdominal wall at 2 patients. Thus, acute paraproctites (ischiorectal and pelviorectal - at 6 patients, phlegmon is crotches and Fournier's disease with distribution on an anterior abdominal wall - at 5, it is purulent - necrotic phlegmon of foot - at 7, commissural phlegmon with distribution to a forearm - at 2, phlegmon in a shoulder complicated by a mephitic gangrene - at 3, deep postinjection abscesses of a buttock with a complication anaerobic phlegmon - at 4 and suppuration of a postoperative wound with phlegmon of an anterior abdominal wall (after appendectomy, the restrained ventral hernia) - at 2 patients. For comparative study we divided patients into two groups. 14 patients with average weight of a diabetes mellitus 2 types at which sepsis is revealed entered into the first group. In the second group - 15 patients with a severe form of a diabetes mellitus with purulent necrotic processes with the complicated fascites at which the diagnosis heavy sepsis and septic shock was exposed. The syndrome of diabetic foot, phlegmon of the lower extremities, acute paraproctites, postoperative suppuration of a wound, post-injection abscesses were the reasons of development of an infection of soft tissues. At development of a fascitis as nosological process the first are surprised superficial a fascia, the hypodermic fatty tissue and skin is involved in process again. In our observation it became clear that patients an acute paraproctitis out of time handled in a hospital, a complication crotch phlegmon, Fournier's disease, big phlegmons of an anterior abdominal wall. In this stage of a disease, primary signs do not appear. Emergence of a dermahemia, ischemic vials of leather and formation of necrotic skin is sign that patients late came to a hospital. In necrotic fascites massive hypostases develop, in certain cases is surprised several segments of extremities, local pain and symptoms of intoxication. It should be noted that the condition of intoxication of patients does not coincide with local survey change. In our observation generally revealed distribution of purulent process to a crotch and an anterior abdominal wall. At localization it is purulent - necrotic process of area of feet and fingers, purulent process extends up fastion and to a synovial membrane of muscles that in diagnostics is extremely relevant as for the first time there is no exact feature set of sepsis. Especially it concerns inflammatory diseases of soft tissues. Therefore even in clinical cases the diagnosis of sepsis is made or is extremely rare, or too late. Observation showed that the clinical current of clostridial and non-clostridial forms of a mephitic gangrene has distinguishing characters. At clostridial infections the disorientation, euphoria, a liver failure and disseminate intravascular coagulation, functions of a respiratory organs for the first time quickly develops day is not broken. At non-clostridial infections of the expressed intoxication it is much less, and in early terms respiratory frustration are noted. Therefore 2, 3 and 4 signs of a syndrome of system inflammatory reaction sometimes appear. Limited inflammation, sepsis, heavy sepsis and multiorgan insufficiency are reaction of an organism to inflammation. Now the 5th ball system of assessment of weight of disturbance of bodies and systems at sepsis is accepted. In diagnostics careful survey with identification of clinical signs is very important. Especially when still definitely the infection center is not established, we were guided by clinical laboratory criteria of sepsis. Treat temperature increase up to 38.5°C the general criteria, or a hypothermia, temperature is below 36°C, pulse rate - (it is more than 90 blows in min.), a tachypnea, consciousness disturbance, a hyperglycemia. In addition it is necessary to be based on criterion of inflammation: a leukocytosis (12*109/l) or a leukopenia (4*109/l), shift towards unripe forms, hemodynamically - arterial hypotension (<90 - 70 mm Hg.), saturation (SvO2<70%). At sepsis often there comes organ dysfunction in the form of an arterial anoxemia, an acute oligouriya, increase in creatinine, thrombocytopenia, a hyperbilirubinemia and paresis of intestines. At survey it is possible to reveal symptoms of fabric hypoperfusion in the form of marbling skin of limbs.Ultrasonography is a high-informative diagnostic method on localizations of purulent process of a soft tissue, its sizes, defeat depth.In principle the general treatment of sepsis it is very important to pay attention to infectious process in a zone of primary damage of fabric - it is the reason of inflammatory process. The center size, a species of microflora, its pathogenicity and virulence, availability of a premorbidal background at the patient, t e is of great importance. factors, directly influence distribution of reactions of an organism. The surgical method of treatment is necessary if there is no multiorgan insufficiency. When at patients the clinical picture of multiorgan insufficiency, expansion of volume of expeditious treatment developed not only leads to an additional trauma, but also aggravates weight of a condition of the patient. Therefore there are old postulates at primary surgical treatment of a wound, the greatest possible removal of necrotic fabrics and decrease in microbic pollution of a wound. It is necessary to tell that full removal necrotic of the changed fabrics sometimes becomes an impracticable task. To expand operation volume - performance of a necrectomy in full that can become additional risk for the patient. Just the same task faces the surgeon at extensive, deep purulent processes of a soft tissue. In such cases wide cuts with reliable drainage of a wound can be a way out. The full-fledged surgical section, adequate drainage and antiinflammatory treatment allows to perform prevention of distribution of inflammatory reactions rather fully. All our patients in due time were exposed to expeditious treatment, that is wide cuts opened paraproctites, with long wide cuts of phlegmon of a hip, crotches, shins with removal of necrotic fabrics. In the postoperative period the landmark necrectomy was carried out. 8 patients have 6 times, 5 patients have 4 times, and at other 16 patients on 3 times the landmark necrectomy with adequate drainage of a wound was made.
4. Results and Discussion
- At a severe form of a diabetes mellitus with pyonecrotic phlegmons often there is sepsis. Not only disturbance of exchange of carbohydrates is a basic reason of this process at a diabetes mellitus, but also exchange of proteins and fats. In addition, rough changes occur in warmly - the vascular system, hepatonephric and nervous systems. Purulent infections adversely affect the metabolism and lead to a weakened defensive reaction of the body, which contributes to the spread of infection. In these states, absolutely in most cases, at patients develop it is purulent - necrotic phlegmons and fascites. In treatment necrotic fastsi-that use of an early radical operative measure yields good result. If in the postoperative period temperature increase, tachycardia, pains in the field of a postoperative wound develops, deterioration in the general condition of the patient - it is indications to repeated audit of a wound for search of a source. If control ultrasonography for a number of reasons did not give effect, then it is necessary to use CT, MRI. In some cases, when above the given researches are not successful, we applied puncture methods of inspection of a zone of postoperative wounds.In recent years in use of antibiotics in treatment of sepsis there are various approaches. If infectious process is localized on the lower extremities, a crotch, rumps, then generally activators are gram-negative sticks. This circumstance has to be considered when performing antibiotic treatment. Success of an antibioticotherapia depends on carrying out radical secondary surgical treatment of a wound.If the diagnosis sepsis, heavy sepsis, septic shock is established to the patient it is necessary to follow the antibioticotherapia differentiated scheme. We widely use cefipim (cephalosporins 4-generations) in a combination metronidazole, a carbopenims ultrabroad spectrum of activity (meropeny). According to literature in the conditions of sepsis the need of an organism for energy increases up to 50-60 kcal/kg, in proteins - up to 2-3 g/kg a day, average daily loss of nitrogen reaches up to 30-35 g/days. Proceeding from it, sick sepsis full nugritsionny support, enteral and parenteral food is necessary.Intestines of the person body the performing a number of functions (endocrine, immune, mechanical, metabolic, barrier homeostasis) of activity of all organism. The large role is played by intestines in a pathogeny of development of multiorgan insufficiency and in hit of patients in a critical state.Now really proved immunocorrection method at heavy sepsis and septic shock is intravenous use of immunoglobulins in a dose of 3 ml/kg/days within 3-5 days. If at patients heavy sepsis and septic shock is revealed, then it is necessary to begin an intensive care urgently. The main objective of an intensive care is timely improvement of transport of oxygen to cells. All above-stated categories of patients received intensive cares in resuscitation office. From 29 patients with a diabetes mellitus of the second type with heavy sepsis and septic shock which was complicated by multiorgan insufficiency at 9 there came death.
5. Conclusions
- Timely establishment of the diagnosis and complex active, adequate surgical treatment, wide cuts and a landmark necrectomy yields good results in treatment of sepsis at a diabetes mellitus. Authors declare no conflict of interest.
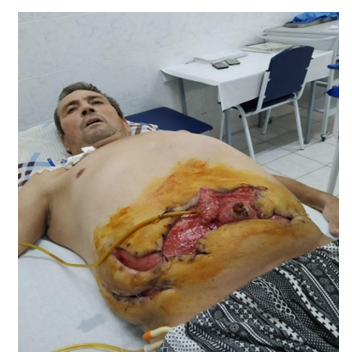 | Figure 1a. Patient M., 51 years old. At admission: Phlegmon hernia sac. Diabetes mellitus type II. At the time of the autopsy phlegmon |
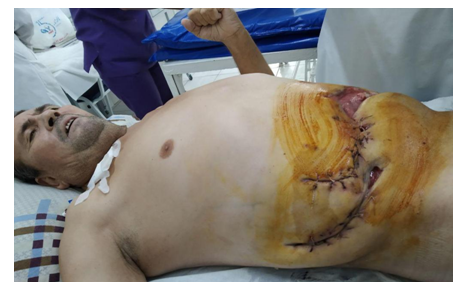 | Figure 1b. After suturing the wound |
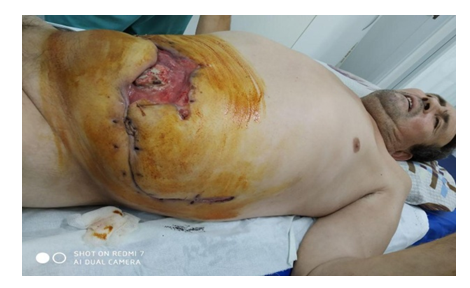 | Figure 1c. After suturing the wound |
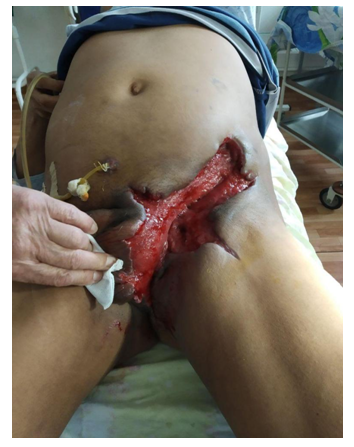 | Figure 2a. Patient R., 46 years old. At admission: Fournier's Disease, Diabetes mellitus type II. At the time of the autopsy perineal phlegmon |
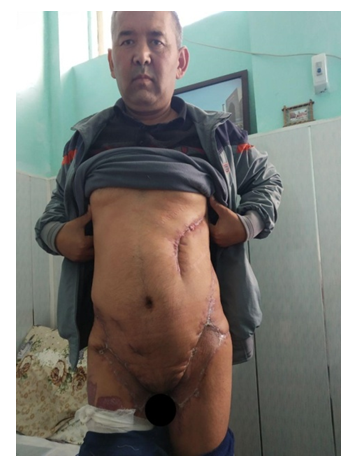 | Figure 2b. After suturing the wound |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML