-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(3): 147-153
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.04

Participants’ Gender and Theoretical Knowledge of Bystander Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation after Two Methods of CPR Training
Adedamola Olutoyin Onyeaso 1, Chukwudi Ochi Onyeaso 2
1Department of Human Kinetics and Health Education, Faculty of Education, University of Port Harcourt, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
2Department of Child Dental Health, Faculty of Dentistry College of Health Sciences, University of Port Harcourt / University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital, Port Harcourt, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Adedamola Olutoyin Onyeaso , Department of Human Kinetics and Health Education, Faculty of Education, University of Port Harcourt, Port Harcourt, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Introduction: Adequate information on influence of gender on CPR could help to adjust or improve future education in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. This study aimed at assessing the possible impact of gender on the post-training theoretical knowledge of bystander CPR involving both the conventional CPR group and the hands-only CPR group. Materials and Method: Using a quasi-experimental cohorts design, two cohorts of some University students were exposed to the conventional CPR and hands-only CPR techniques. Before CPR trainings, 140 copies of a self-administered questionnaire on the knowledge of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) were distributed to assess the pre-training CPR theoretical knowledge of the participants - 70 of them in each of the two cohorts. The participants were again served the same questionnaire in the post-training stage to respond to the same questions on CPR theoretical knowledge. The data was analysed with descriptive statistics and the ANOVA with the level of significance set at P < 0.05. Results: The male gender was found to have statistically significant association with post-training CPR knowledge in one of the questions in the hands-only CPR group and another one in the conventional CPR group (P < 0.05), while the female gender had statistically significant association with post-training CPR knowledge in one question in the conventional group (P < 0.05). Conclusion: Although statistically significant gender associations were found in three of the CPR knowledge questions, this study has revealed no consistent gender association with either of the genders with neither of the CPR training techniques.
Keywords: Gender, CPR Knowledge, Hands-only and Conventional Techniques, Nigerian students
Cite this paper: Adedamola Olutoyin Onyeaso , Chukwudi Ochi Onyeaso , Participants’ Gender and Theoretical Knowledge of Bystander Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation after Two Methods of CPR Training, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 147-153. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Evaluation of factors that could influence the effective provision of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is crucial in realising the best possible outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) victims. The global public health challenge of OHCA has been on the increase [1-5]. Previous studies have provided conflicting reports on gender associations with cardiopulmonary resuscitation knowledge [6-9]. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure performed as an attempt to restore spontaneous circulation by performing chest compressions with or without ventilations [10]. Studies have also shown that poor CPR knowledge has contributed to the fear and reluctance to attempt bystander CPR for victims of OHCA [11-14]. Adequate information on influence of gender on CPR could help to adjust or improve future education in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Amacher et al [15] reported that female gender was associated with a lower number of secure leadership statements. They concluded that future education of rescuers should take gender differences into account [15]. Wigginton et al [16] stated that they believed gender-and sex-related differences in resuscitation are important, and that research designed to both better understand and better treat these differences may significantly improve outcomes in the nearfuture.Although there are few reports from Nigeria on theoretical knowledge of cardiopulmonary resuscitation [17-21], there is need to explore further any significant association of gender of the potential bystander CPR providers with the theoretical CPR knowledge. In addition, the previous related studies were based only on conventional CPR training of participants.Therefore, this study aimed at assessing the possible impact of participants’ gender on the post-training theoretical knowledge of bystander CPR involving both the conventional CPR group and the hands-only CPR group. We hypothesized that: (1) the gender of the participants would not have any significant association with the post-training theoretical CPR knowledge in the conventional CPR group; (2) the gender of the participants would not have any significant association with the post-training theoretical CPR knowledge in the hands-only CPR group; and (3) there would be no statistically significant gender differences in the post-training CPR knowledge acquired by the participants when the separate groups are compared.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
- This study was carried out using a quasi-experimental cohorts design – one cohort was exposed to the conventional CPR training while the other cohort was taught hands-only CPR technique. However, both cohorts were taught together during the theoretical teaching before the different hands-on sessions.
2.2. Population of the Study
- The two groups (cohorts) were part of the larger 200-Level students of the Department of Human Kinetics and Health Education in the Faculty of Education of the University of Port Harcourt. The students were admitted into the Department in 2016. Although not all the thirty six (36) States in Nigeria are represented in the sample, but due to the Admission Policy in all the Federal Universities in Nigeria which ensures that candidates from all the six (6) Geo-political Regions in the country are fairly admitted into every programme, the participants gave a very fair representation of the different States in Nigeria.
2.3. Stage 1 (Pre-training Phase)
- Before CPR teaching and trainings, one hundred and forty (140) copies of a self-administered questionnaire on their knowledge of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) were distributed to assess the pre-training CPR theoretical knowledge of the participants - seventy (70) in the hands-only cohort and another seventy (70) in the conventional CPR group. Nine questions on bystander CPR were captured in the questionnaire (Appendix).
2.4. Stage 2 (Immediate Post-training Phase)
- Immediately after the teaching and trainings on bystander CPR, another one hundred and forty (140) copies of the same questionnaire were given to the same participants to answer the same questions on CPR which they answered before the teaching and training sessions. All the participants in the two groups responded to the questions again.
2.5. Determination of Good and Poor CPR Theoretical Knowledge
- For each of the nine (9) questions on CPR knowledge, a score of 50% was considered good while any score less than that was considered as poor CPR theoretical knowledge. (See the 9 questions on CPR knowledge in the attached Appendix).The following null hypotheses were generated and tested:Ho1: That the gender of the participants would not have any significant association with the post-training theoretical CPR knowledge in the conventional CPR groupHo2: That the gender of the participants would not have any significant association with the post-training theoretical CPR knowledge in the hands-only CPR groupHo3: That there would be no statistically significant gender differences in the post-training theoretical knowledge of the two cohorts compared.
2.6. Data Analysis
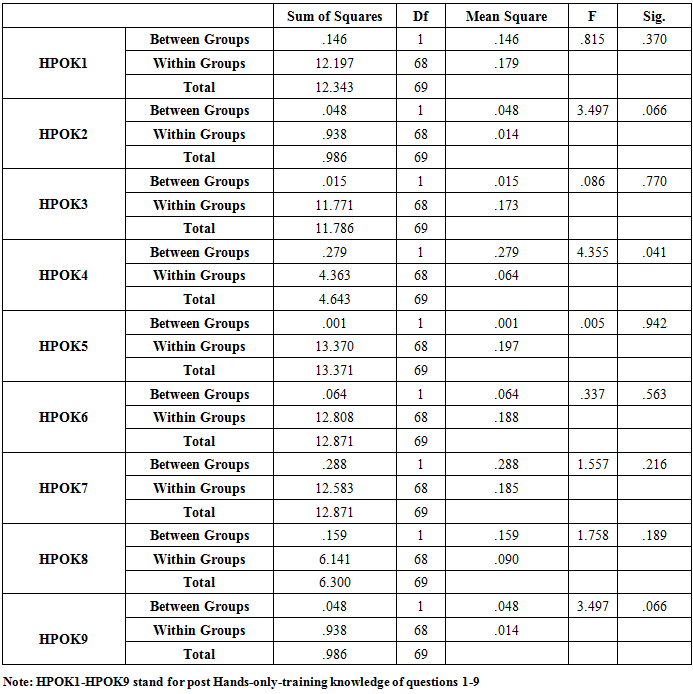
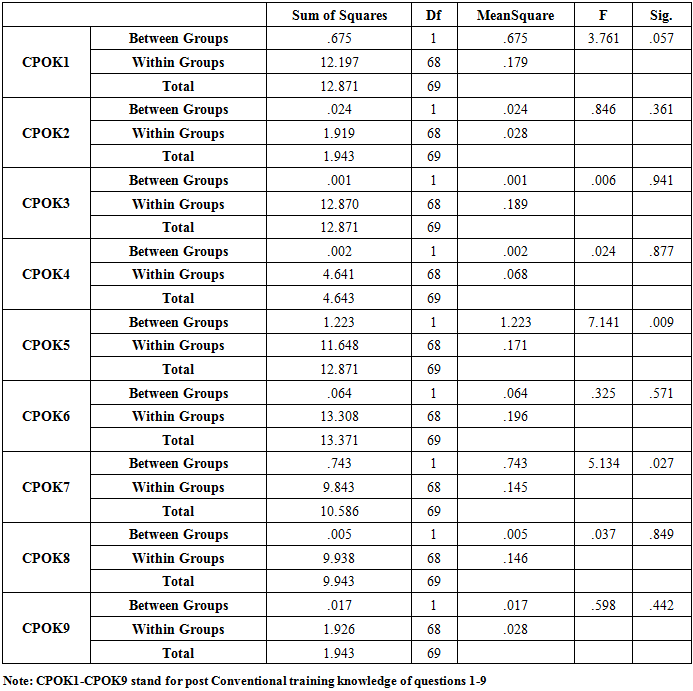
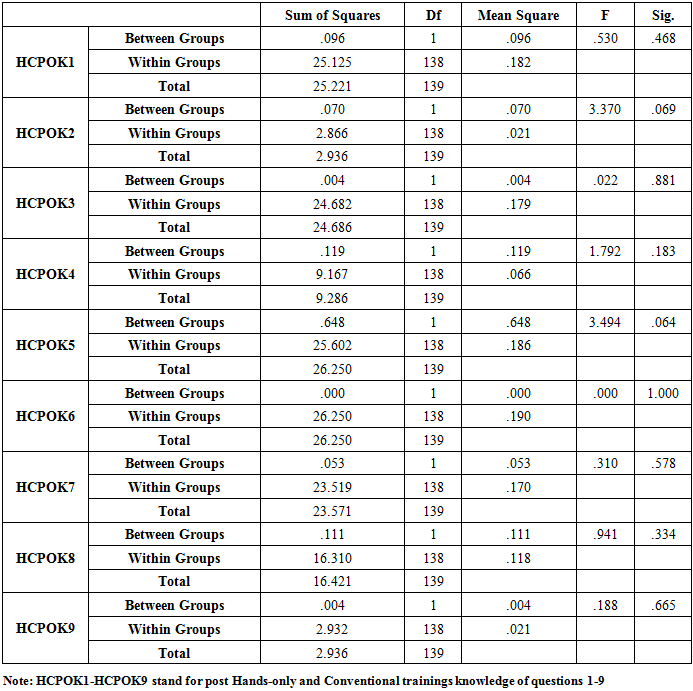
- The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS Version 20) was used to analyse the data. In addition to descriptive statistics, the data was analyzed using the analysing of variance (ANOVA) at P < 0.05 level of significance.
3. Results
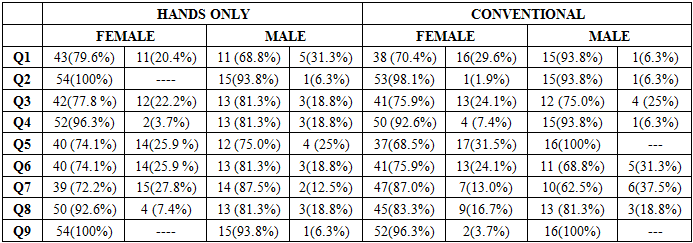
- Both Hands-Only and Conventional CPR groups had 70 participants each with equal number of males and females: 54(77.1%) females and 16(22.9%) males in each group and mean ages of 21.26 + 2.92 (SD) and 21.17 + 2.59 (SD) for hands-only and conventional groups, respectively.Table 1 below provides the post-training CPR knowledge of the two cohorts according to gender showing similar patterns.
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- The present Nigerian study has generally shown that there was no consistent association of any gender with CPR knowledge, as well as no significant differences between the two cohorts. The current finding of this study is consistent with an earlier related Nigerian report [20].This present finding of this Nigerian study is very much in line with the conflicting findings in the literature about gender and CPR knowledge as stated earlier [6-9]. The study by Alkandari et al [7] showed that gender significantly associated with CPR knowledge among dentists in Kuwait. Alsharari et al [8] did not find any statistical gender differences in the variables (questions) that were used to assess the CPR knowledge of their participants. Alotaibi et al [9] reported higher CPR mean score by the female gender than their male counterparts in the study. Parnell et al [22] reported no general poor CPR knowledge among the studied students without any significant differences between the male and female participants. According to Amatya and Gorkhali [23], knowledge score did not correlate significantly with sex among the health personnel who generally had poor CPR knowledge. Although they found comparable male and female CPR knowledge, Krammel et al [24] recommended that specially tailored programmes should be put in place to increase the awareness and willingness among both the female and elderly community for future educational intervention.Their recommendation was occasioned by the general poor CPR knowledge with females and the elderly lacking the willingness to perform CPR among the Viennese population. In the study by Tsegaye et al [25], 83% of the male University undergraduate medical students had good CPR knowledge as against 10% of their female counterparts.However, no significant association was found between sex and the CPR knowledge of the students but there was significant association between academic year, source of information of CPR and knowledge of CPR.The Strengths and Limitations of this studyThe study samples for the two cohorts were drawn from a fairly representative population of students admitted to a Federal Government University where candidates are uniformly selected from different states of the country. However, the male and female proportions were not even in this study which we could not influence as the female/male ratio reflect the actual number of both genders in the entire class. In addition, the sample sizes for the two cohorts were not very large and as such the generalization of the results should be done with caution.
5. Conclusions
- This study has revealed no consistent gender association with either of the genders for any of the CPR training techniques. However, statistically significant gender associations were found in three of the CPR knowledge questions only.
6. Recommendations
- There is need to carry out more gender-specific cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) studies with larger samples in Nigeria involving the body mass index (BMI) of the participants.The Federal Government of Nigeria should without delay promote the introduction of CPR education in Nigerian schools (primary, secondary and higher institutions) so as to increase the number of bystander CPR providers in our communities.
Appendix
- QUESTIONNAIRE ON CPRSection A: Personal DataPlease tick as it applies to you1. Gender :
 2. Age in years: ---------------------------------------------------3. Faculty: --------------------------------------------------------Department: -------------------------------------------Level: --------- Matriculation No: ----------------------------------Section B: Please honestly provide your answers to these questions on CPR4. What is the first thing you should do if you come across a collapsed personCall an ambulanceTry to get the person to respond to youCheck to see if the person is breathing normally5. Why would you shake and shout at a collapsed person?To open the airway To restart the heart To check for response.6. The five steps in the Adult Chain of Survival include all of the following EXCEPTEarly CPRTo check for responseAdvanced airway placement 7. What action would you use to open the person’s airway?Tilt the head back and lift the chinTilt the head and push the chin downTilt the head down and turn the chin to the right8. If a victim has dentures, what should you do?Remove the dentureLeave them in position as long as they are not obstructing the airwayUse the of nose9. What is the first link in the “chain of survival” for cardiac arrest victims?Early recognition of a cardiac arrestCardiopulmonary ResuscitationCitizen Please Respond10. When giving rescue breaths, for how long do you breathe into the person’s mouth1 second5 seconds10 seconds11. Which of the following are signs of airway obstruction?Poor air exchangeHigh-pitched noise while inhalingInability to speakAll of the above12. How many chest compressions and rescue breaths would you give per cycle of CPR?20 presses and one breathe 30 presses and two breaths 30 presses and three breathsTHANK YOU.
2. Age in years: ---------------------------------------------------3. Faculty: --------------------------------------------------------Department: -------------------------------------------Level: --------- Matriculation No: ----------------------------------Section B: Please honestly provide your answers to these questions on CPR4. What is the first thing you should do if you come across a collapsed personCall an ambulanceTry to get the person to respond to youCheck to see if the person is breathing normally5. Why would you shake and shout at a collapsed person?To open the airway To restart the heart To check for response.6. The five steps in the Adult Chain of Survival include all of the following EXCEPTEarly CPRTo check for responseAdvanced airway placement 7. What action would you use to open the person’s airway?Tilt the head back and lift the chinTilt the head and push the chin downTilt the head down and turn the chin to the right8. If a victim has dentures, what should you do?Remove the dentureLeave them in position as long as they are not obstructing the airwayUse the of nose9. What is the first link in the “chain of survival” for cardiac arrest victims?Early recognition of a cardiac arrestCardiopulmonary ResuscitationCitizen Please Respond10. When giving rescue breaths, for how long do you breathe into the person’s mouth1 second5 seconds10 seconds11. Which of the following are signs of airway obstruction?Poor air exchangeHigh-pitched noise while inhalingInability to speakAll of the above12. How many chest compressions and rescue breaths would you give per cycle of CPR?20 presses and one breathe 30 presses and two breaths 30 presses and three breathsTHANK YOU. Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML