-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(3): 137-140
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.02

The Characteristic of the Immune Status at HIV-Infected Children with Acute Rhinosinusitis
N. U. Narzullayev1, F. S. Ikramova2
1Department of Otolaryngology, Ophthalmology of Bukhara State Medical Institute, Doctor of Medical Sciences
2Assistant of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Ophthalmology of Bukhara State Medical Institute
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The immune status has been studied at 25 HIV-infected children with acute rhinosinusitis. The control group of comparison consisted of 14 practically healthy faces. At a HIV-infected patients with ARS has revealed deep infringements of the immune status, especially from the T-link of immunity and its subpopulations, and also frustration humoral an immunity link, suppression of proinflammatory cytokine IL-10 and increase proinflammatory IFN-γ. Under the influence of the spent treatment have not revealed certain changes from the immune status at patients. It is possible to ascertain only positive changes of maintenance IL-10 and parallel decrease IFN-γ in dynamics of treatment.
Keywords: The immune status, a HIV-infection, Acute rhinosinusitis, Cellular immunity, Humoral immunity, an immunodeficiency, Cytokines
Cite this paper: N. U. Narzullayev, F. S. Ikramova, The Characteristic of the Immune Status at HIV-Infected Children with Acute Rhinosinusitis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 137-140. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201003.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- AIDS is the retrovirus infection characterized by epidemic distribution of global scale, amazingly exclusive T-helpers [1,3]. Last two decades the defining reason of a secondary immunodeficiency (SID) at children became a HIV-infection which pandemic continues to accrue. Defeat of immune system at a HIV-infection has systemic character, being shown deep suppression T- and B-links of cellular immunity [1,2,5].One of the first symptoms of AIDS are quite often diseases of ENT-organs. Acute rhinosinusitis (ARS) often comes to light at children with a HIV-infection, disease of it at children's age fluctuates within 60-75%, and lethality rate makes up 0,01-0,2% of the total diseased [6,9]. According to a number of authors, at HIV-infected children ARSis observed more often, than at children of normal immune system [1,7,8].Aim of the study–To study parameters of the immune system at HIV-infected of children with ARS.
2. Materials and Methods
- We investigated 25 children at the age from 3 till 14 years with HIV-infection with ARS, that were on hospitalization in LOR-branch of the Bukhara regional children's versatile medical centre. Boys have made up 56.6%, girls – 43.4%. Unilateral defeat of sine was observed at 57.8%, bilateral - at 42.2%. Except for the inflammation signs, the general anxiety, a bad dream, refusal of a chest food, headaches were marked. Besides traditional inspection (the general analysis of blood, urine, bacteriological and bio-chemical researches) all patients have passed ENT-survey, under indications - sine sounding (26.5%), X-ray additional bosoms of a nose (9.6%). In the basic group there were 25 HIV-infected with ARS patients, and in a control - almost healthy 14 children of similar age who did not have in anamnesis ARS and a HIV. All 25 HIV-infected children were registered in the Bukhara regional AIDS-center. Patients received antiretroviral therapy, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and local therapy in the conditions of a hospital. The HIV diagnosis was based on revealing of specific antibodies in standard serological tests (ELISA, immune bloating in updating Western-bloat) and comparisons epidemiological and serological data.Immunologic studies were carried out in conjunction with the Institute of Immunology (Tashkent). Researches included patients with a HIV-infection and ARS whose parents have given an informed consent to participation in the given researches (work has been executed according to the Helsinki declaration and it is approved by ethical committee of Bukhara State Medical Institute).Phenotyping lymphocyte carried out indirect by immune fluorescent method with the help monoclonal antibodies to CDs-receptors «Sorbent Ltd» (Russia). Defined T-lymphocytes (totalset - CD3); T-helpers (subset of Th - CD4); T-suppressors (subset of Ts - CD8); B-lymphocytes (subset СD19). Calculated an immunoregulatory index (IRI) – the ratio of CD4/CD8. Concentration serum antibodies (Ig) A, M and G defined a method of radial immune diffusion [7]. Level cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-10) in whey of peripheral blood was studied a method of the immune enzyme analysis with use of test systems by firms "Vectors-best" (Russia). Parameters of the immune status were studied twice: before and 1 month after treatment. The obtained data was exposed to statistical processing with use of computer program Micro-soft Excel 2003 on LG-Pentium IV. Significance of differences when comparing the mean values was determined by Student´s t test. Data are presented as of S.E. Differences were considered significant at P<0.05.
3. Results of Research and Their Discussion
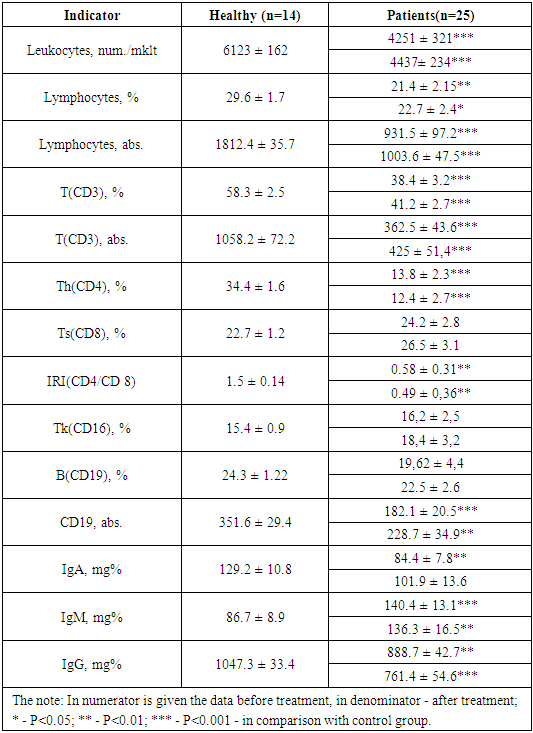
- The retrospective analysis of studying of the immune status at HIV-infected children with ARS has shown that in terms before carrying out before treatment at them essential infringements have been revealed from their immune system (tab. 1). At HIV-infected with ARS patients observed 0.7-fold fall of absolute value of leukocytes and the relative contence lymphocyte, double decrease in the absolute values of lymphocyte. Such decrease was reflected in a statistically significant decrease from 2 to 3 times of absolute values of the total pool Т (CD3) - and В (CD19)- lymphocyte (tab. 1).HIV-infected with ARS patients showed profound suppression T-cell immunity in their relative expression, namely, 0.6-fold reduction in T-cells with the phenotype (CD3), even more significant suppression T-sharehelpers cells - Th (CD4) –up to 13.8 ± 2.3% (in the control group 34.2 ± 1.6%; Р<0.001), while the content of subset of T-cells - Т (CD8)-cytotoxic exceeded the background values in the control group moderate (P>0.05). In this connection in the given group there is an inversion of an immune regulatory index (IRI) –the ratio of CD4/CD8, - which leads to serious changes in immune system of patients with HIV-infection, combined with the ARS. Thus, we find out a disbalance of T-cell subset with a decrease in the proportion of helpers Th(CD4) and increase suppression parts - Ts(CD8) (tab. 1). Reduction of IRI registered by us at HIV-infected with ARS children testifies to functional insufficiency of cages with a phenotype of Ts(CD8), and it is a sign of the profound immunodeficiency which has developed at patients. HIV-infected patients with ARS have revealed small activation of subset of T-killers - Tk (CD16) that, possibly, is also pathognomonic at this pathology. In respect of B-cell component of the immune system can be said that moderate decrease occurred, which was statistically possible to tell that there was a moderate decrease that statistically confirmed (P>0.05). Decrease of B(CD19) lymphocytes was reflected in the spectrum of serum immunoglobulin (SI) content of two classes - IgA and IgG, and quantity IgM, on the contrary, increased (tab. 1).The data obtained by us testifies to profound infringements in the functioning of the immune system in children of patients with HIV-infection and ARS, which were reflected a spectrum cellular and humoral immunity factors. These disorders appear to be quite possible as a fact that plays an important in the pathogenesis of this mixed-pathology in children. The decrease of the relative quantitative properties of Th(CD4) - this aggravating factor, and an unfavorable forecast criterion.The spent treatment did not lead to appreciable changes of parameters of immune system at HIV-infected children with ARS. We observed a tendency of a moderate increase of separate links of cellular immunity and humoral immunity as well as restoration of key parameters of the immune status (tab. 1). Besides, at patients with chronic processes, saved pressure of the humoral component of system of immunity remained at P>0.05. HIV-infected patients with ARS have shown weak increase in Т(CD3) and B(CD19) in their relative and absolute values, and also moderate increase of production of Tk(CD16), Ts(CD8), the concentration of IgA (tab. 1).
|
|
4. Conclusions
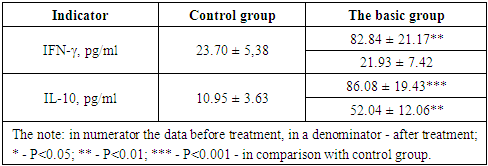
- Thus, the HIV-infected children with ARS have expressed a stimulation of production of both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Such processes can as a necessary condition for protection against the infectious agent and system damaging action of high concentration proinflammatory cytokines.After treatment, carried out in the group of HIV-infected children with ARS, level of IFN-γ has come nearer to control values, and level of IL-10 in dynamics of treatment is decreased, nevertheless remained at high level, in 5.5 exceeding those parameters at children of control group.The parity IFN-γ/IL-10 in the basic group tended to even bigger to decrease, making 0.42.Thus, at HIV-infected children with ARS deep deficiency of most of the parameters of the immune status is observed. One of the major disorders of the immune status is a significant suppression of Th (CD4)-lymphocytes and inversion of the IRI with an increase in functional activity of Ts (CD8) -lymphocytes, which are unfavorable clinical criteria. The given patients did not have positive dynamics of changes of the immune status after treatment was carried out. Under the influence of treatment there was a suppression of proinflammatory of cytokine IFN-γ. However, it should be highlighted that the detected change in the level of IL-10 and a violation of the proportion of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines indicates the presence of preexisting immune de ficiency, which, apparently, was manifested in the form of complications associated with HIV infection.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML