-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(2): 102-105
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201002.06

Diagnostic Value of p53 Protein, Epidermal Growth Factor, and Endothelial Vascular Growth Factor (VEGF) in Polypous Rhinosinusitis
Avezov Mukhiddin Ikromovich1, Jabbarov Karim Djabbarovich2, Abdurakhmanov Otabek Bakhtiyorovich3
1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Urgench Branch of the Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench
2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Tashkent Stomatology Institute, Tashkent
3Department of Oncology, Tashkent Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education, Tashkent
Correspondence to: Avezov Mukhiddin Ikromovich, Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Urgench Branch of the Tashkent Medical Academy, Urgench.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The frequency of polyposis rhinosinusitis (PRS) has a clear tendency to increase, the specific gravity in the structure of the incidence of ENT organs is 5-20%. Material and methods: We examined 122 patients with PRS treated in the ENT department of the Khorezm Multidisciplinary Medical Center from 2015 to 2018. All patients were divided into 4 groups depending on the duration of PRS: Group I - 30 patients with a duration of PRS of up to 3 years; Group II - 31 patients with a duration of PRS of 3-6 years; Group III - 29 patients with a duration of PRS of 6-10 years; Group IV - 32 patients with a duration of PRS of 10-15 years. Results. Determination of the level of EGF revealed a significant difference in the median values of this indicator in blood plasma, while the median level of EGF was 1.4 times higher with PRS compared with the control group. We found that the VEGF content in blood plasma is higher than the indices of the control group in 104 (85%) of 122 examined patients, while the average value and median of this indicator also significantly increased in polypous tissue (p <0.05). A significant increase was also revealed in the level of VEGFR-2 (p <0.05) in polypous tissue. Comparing the levels of VEGFR-2 in blood plasma compared with the control group, we found an increase in its polype content by 3-87% in 82% of patients. Conclusion. 1. The study of the concentration of p53 protein, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in plasma in patients with PRS is important in the diagnosis of the disease and the control of the recurrence of the process. 2. After surgical removal of polypous, the levels of p53, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in the blood serum decrease inversely with the duration of the disease, normalizing for 6 months. 3. The level of p53 protein, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in the blood are significant prognostic markers of PRS.
Keywords: p53 protein, Epidermal growth factor, Endothelial vascular growth factor, Polypous rhinosinusitis
Cite this paper: Avezov Mukhiddin Ikromovich, Jabbarov Karim Djabbarovich, Abdurakhmanov Otabek Bakhtiyorovich, Diagnostic Value of p53 Protein, Epidermal Growth Factor, and Endothelial Vascular Growth Factor (VEGF) in Polypous Rhinosinusitis, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 102-105. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201002.06.
1. Introduction
- The frequency of polyposis rhinosinusitis (PRS) has a clear tendency to increase, the specific gravity in the structure of the incidence of ENT organs is 5-20%. The search for new approaches to earlier diagnosis and well-timed medical treatment of polyposis rhinosinusitis is relevant not only due to frequent recurrence of the disease, but also to the high prevalence of this disease. The frequency of PRS has a clear tendency to increase, the specific gravity in the structure of the incidence of ENT organs is 5-20% [1]. According to the observations of A.S. Lopatin polyps in the nasal cavity are found in 1.02% of people, and this only applies to clinical manifested forms of the disease, taking the real prevalence of PRS into account subclinical forms is much higher [2].According to normative document EP3OS, adopted in 2012, PRS is a chronic disease of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, characterized by two or more necessarily present symptoms: blockade (obstruction) of nasal breathing and runny nose (rhinorrhea), and associated symptoms (pain or sensation) tension in the forehead and nose, loss and decrease in smell), last more than 12 weeks. According to EP3OS, about 1% of the world's population suffers from polypous rhinosinusitis [3].The p53 protein is a transcription factor that regulates the cell cycle. p53 acts as a suppressor of the formation of malignant tumors; accordingly, it is a tumor marker and is expressed in all cells of the body.In the absence of damage to the genetic apparatus, the p53 protein is in an inactive state, and when DNA damage occurs, it is activated. One of the stimuli of p53 activation is hypoxia, which is inevitable with a long course of PRS. The result of p53 activation is stopping of cell cycle and DNA replication; with a strong stress signal - the start of apoptosis.One of the markers of disruption of biological processes at the cellular level is VEGF.VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) is one of the members of the family of structurally similar proteins that are ligands for the receptors family of VEGF. VEGF affects the development of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) and the survival of immature blood vessels (vascular support) by binding to activating two closely related membrane tyrosine kinase receptors (VEGF receptor-1 and VEGF receptor-2). These receptors are expressed by endothelial cells of the blood vessel wall [4]. The binding of VEGF to these receptors triggers a signaling cascade that ultimately stimulates the growth of vascular endothelial cells, their survival and proliferation [4,5].Endothelial cells are involved in such diverse processes as vasoconstriction and vasodilation, presentation of antigens, and also serve as very important elements of all blood vessels - both capillaries and veins or arteries. Thus, by stimulating endothelial cells, VEGF plays a central role in the process of angiogenesis. VEGF stimulates the permeability of small blood vessels. Increased permeability leads to “leakage” of plasma proteins through the vessel wall and the formation of extravasal fibrin gel. This gel is a suitable medium for the growth of endothelial cells [4].Epidermal growth factor (EGF) - refers to a group of growth factPRS and is a polypeptide, it is resistant to acids and high temperatures. It belongs to the most stable of all studied proteins. It presents in the cells of all body tissues, regulates cell growth [6]. EGF plays an important role in the regulation of metabolic and recovery processes. It binds to receptors on the surface of cell membranes specifically, stimulates taxis of anti-inflammatory cells.Under normal conditions, the content of growth factors in the human body is relatively small and stable. However, with any damage, the number of receptors sensitive to EGF increases, due to this its concentration increases [6,7].The search for new approaches to early diagnosis and timely medical treatment of PRS is relevant not only to the frequent recurrence of the disease, but also to the high prevalence of this disease.After analyzing the foregoing, we set the goal of the study - to assess the presence or absence of dynamics of the concentration indicators of p53, VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 and EGF in polypous tissue and blood plasma before and after surgical removal of polypous tissue in PRS.Objective of investigation: to determine quantitative indications and their importance in treatment of p53, VEGF-A and VEGFR-2 and EGF in blood serum and polyps in patients with polypous rhinosinusitis.
2. Material and Methods
- We examined 122 patients with PRS treated in the ENT department of the Khorezm Multidisciplinary Medical Center from 2015 to 2018.Patients aged from 27 to 34 years, the average age was 29.1 ± 0.7. Among patients, women were 47 (38.5%), men - 75 (61.5%).The diagnosis of PRS was made according to generally accepted criteria based on complaints, medical history, data of anterior, posterior rhinoscopy, radiography and computed tomography of SNPs. The general condition of patients, the presence of concomitant somatic diseases were determined.All patients were divided into 4 groups depending on the duration of PRS:Group I - 30 patients with a duration of PRS of up to 3 years;Group II - 31 patients with a duration of PRS of 3-6 years;Group III - 29 patients with a duration of PRS of 6-10 years;Group IV - 32 patients with a duration of PRS of 10-15 years.The control group consisted of 26 practical healthy people of a comparable age category who did not have a history of bad habits and polypous diseases.Patients were divided into 3 groups according to their complaints, rhinoscopy and endoscopic examination. Endoscopic examination of the patients’ nasal cavity was done by using Endoscope apparatus Eleps (Kazan, TO-ElePS po TU 9442-034-12966357-2010) with diameter 3 mm, length 175 mm and viewing angle 0°.Also, patients were divided into 3 groups according to the degree of obstruction of the nasal cavity with polypous tissue:A group - 1/3 of the lumen of the nasal cavity;B group - 2/3 of the lumen of the nasal cavity;C group - complete obstruction of the lumen of the nasal cavity.Samples of polypous tissue were taken during surgery and immediately sent for enzyme immunoassay. The concentration of indicators was expressed per 1 mg of total protein determined by the Lowry method. The studied parameters in the lysates were evaluated using standard kits for direct enzyme immunoassay in accordance with manufacturers' instructions. Values were measured on an ELX800 automatic universal micro plate reader.When comparing the indicators were used Student t-test, Mann-Whitney test, median test, Pearson correlation test (r) and Spearman rank correlation test (R). Statistical data processing was carried out using the software packages “Statistica 6.0” (StatSoft Inc.) and “R-2.15.0 for Windows” (R-project).
3. Results
- The concentration of p53 in polypous tissue with PRS increases with increasing duration of PRS. The same trend was observed in the study of the content of p53 in serum, so with a duration of PRS of up to 3 years, the number of p53 exceeded the norm by 1.5 times, and with a pathology of 10-15 years, 2.9 times (table 1).
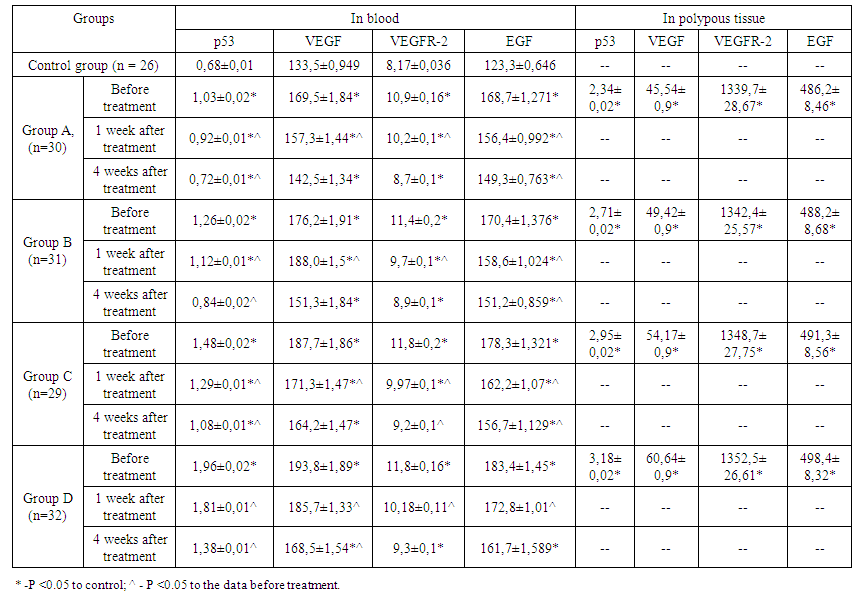 | Table 1. The concentration of p53, VEGF, EGF in plasma and polypous tissue |
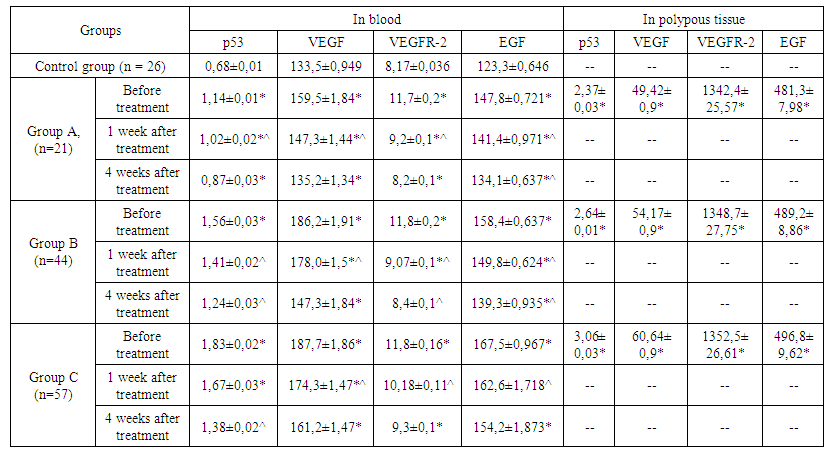 | Table 2. The concentration of p53, VEGF, EGF in plasma and polypous tissue |
4. Summary
- 1. The study of the concentration of p53 protein, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in plasma in patients with PRS is important in the diagnosis of the disease and the control of the recurrence of the process.2. After surgical removal of polypous, the levels of p53, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in the blood serum decrease inversely with the duration of the disease, normalizing for 6 months. 3. The level of p53 protein, VEGF and VEGFR-2 and EGF in the blood are significant prognostic markers of PRS.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML