-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences
p-ISSN: 2165-901X e-ISSN: 2165-9036
2020; 10(2): 86-95
doi:10.5923/j.ajmms.20201002.04

p53 Immunoexpression as a Prognostic Indicator of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Ruchi Dhuria1, Kavita Sahai2, Tribhuvan Pal Yadav3, Gayatri Vishwakarma4
1USMPMHS, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi, India
2Department of Pathology, Army Hospital Research & Referral, New Delhi, India
3Department of Paediatrics, Ram Manohar Lohia Hospital, New Delhi, India
4Department of Biostatistics, Indian Spinal Injuries Centre, New Delhi, India
Correspondence to: Ruchi Dhuria, USMPMHS, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, New Delhi, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Morbidity and mortality of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remain substantial across the globe. Despite all the considerable technical efforts and intensive therapeutics, HNSCC survival rates have not improved significantly over the past two decades. HNSCC are subject to various recommendations for early detection and management in order to control this devastating disease. Therefore, it is essential to ascertain new prognostic molecular markers which may help to recognize the biological behaviour of the tumor and identify patients with high risk of disease recurrence. The aberrations in the p53 pathway in HNSCC imply that molecular and immunohistochemical analysis (IHC) of this critical tumour suppressor marker may be of diagnostic and prognostic utility in the clinical management of the disease and improve the survival of HNSCC patients. Aim & objective: The prospective study was aimed to determine the association of p53 protein expression in HNSCC cases with certain clinicopathological variables, disease recurrence, overall survival and disease free survival and to assess whether tumor suppressor p53 protein has any prognostic significance in primary HNSCC. Materials & Methods: Expressions of p53 protein were assessed in a series ofhundred histopathologically diagnosed, surgically treated, randomly selected and formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) biopsy specimens of HNSCC by IHC procedure. Clinical and histopathological data were gathered and patients were followed up for one year/death from the date of surgery. Pearsonchi-square test/ Fisher exact test were used to explore the statistical associations of p53 protein expression with clinicopathological parameters and disease recurrence of HNSCC. In order to investigate the relevance of p53 staining with overall survival and disease free survival, survival analysis was performed by using Kaplan-Meier log rank test. Results and Conclusion: The positive nuclear immunoexpression of p53 was found in 70% of the investigated malignancies, using a threshold of 10% stained cell nuclei. Out of 100 HNSCC cases, 41 died and 16 had disease recurrence during one year follow up. Statistically significant associations were observed for individual tumor stage (p = 0.010), early and advanced tumor stage (p = 0.004) and lymph node involvement (p = 0.028) with p53 immunoexpression. However, no significant correlation was found between p53 immunostaining and disease recurrence (p = 0.634), overall survival (p = 0.556) and disease free survival (p = 0.608) in HNSCC. Thus, our findings suggest that p53 serves as a poor potential prognostic biomarker in HNSCC. Clinical implications and prognostic relevance of p53 expression in HNSCC needed further studies to evaluate its role as a potential tumor marker.
Keywords: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, p53, Tumor suppressor gene, Disease recurrence, Disease free survival, Overall survival
Cite this paper: Ruchi Dhuria, Kavita Sahai, Tribhuvan Pal Yadav, Gayatri Vishwakarma, p53 Immunoexpression as a Prognostic Indicator of Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma, American Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Vol. 10 No. 2, 2020, pp. 86-95. doi: 10.5923/j.ajmms.20201002.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Head and neck cancers (HNC) are a heterogeneous group of malignancy that arise from transformed epithelium of upper areodigestive tract. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is destructive proliferation of anomalous cells in stratified squamous epithelium, which has potential of distant metastasis [1]. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is common histological subtype of HNC and accountable for approximately 5,50,000 new incidences per annum worldwide [2]. HNSCC represents the sixth most prevalent cancer globally [3] and the second most common cancer in India [4]. The prevalence of HNSCC in India is about 35% of global incidences probably attributed to exceedingly large population [5]. Males are affected significantly more than females with the ratio ranging from 2:1 to 4:1 possibly due to less exposure of carcinogens to females. Though existing literature does not reflect the true burden of HNC in Indian population and what comes into the picture is only the “tip of iceberg” condition [6]. Different demographics, risk factors, poor diet, low socioeconomic conditions, poor hygiene, viral infections and family history are possibly responsible factors for excessively higher prevalence of HNC in India [7,8]. The disease is multifactorial in its pathogenesis [9]. Both extrinsic and intrinsic factors have an imperative role in development of SCC [10]. HNSCC is epidemiologically strongly associated with alcohol abuse, tobacco consumption (smoking and/or smokeless tobacco) [11] and social factors [12]. Cancer cases generally have a poor prognosis in low and middle income countries like India possibly due to low cancer awareness, late diagnosis and poor curative treatments in comparison with high income countries [13,14]. HNSCC survival remains poor despite of all the tremendous technical and therapeutic advancements possibly due to rapid disease recurrence, distant metastasis and its advanced stage of disease [15]. An early diagnosis and comprehensive tumor characterization is essential to improve the probability of survival in HNSCC [16]. Discrimination of HNSCC patients is important to avoid unnecessary treatments, severe short term toxicity and long term functional impairment affecting their quality of life. Histopathological grading and TNM staging have been used for many decades in an attempt to predict the clinical behaviour of HNSCC [17]. Many molecular markers have been introduced to discover more accurate prognostic factors for determining the accurate preventive treatment plan and disease management to improve the survival of cancer patients [18]. Changes in immunoexpression may take place before cancer development, raising the hope of developing tumor markers to detect very early stage lesion in head and neck [19]. The advanced diagnostic method for cancer includes IHC, molecular diagnosis, flow cytometry and tumor markers diagnosis [20]. IHC is an effective armamentarium as it provides insight into tumor histopathogenesis and has contributed to more precise determination of patient’s prognosis. Such histological methods which disclose prognostic parameters of cell proliferation and apoptosis might help in identification of individuals with high risk of developing tumor besides having prognostic influence on therapeutic approach offered to an individual. Proliferative activity in malignancy correlates with progression and prognosis of the disease [21]. Therefore, understanding of molecular pathogenesis in HNSCC patients will better predict the diverse outcomes and potential therapeutics targeted to patients for cancer management.Cancer genes are of two types, oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. The oncogene are involved in initiation and progression of the malignancy, whereas the tumor suppressor genes are the normal genes which gets activated by DNA damage, hypoxia, viral infections and produce tumors either due to their mutational damage or deregulation of pathways controlling growth and differentiation [22,23]. The human p53 (TP53), a tumor suppressor gene, is a phosphoprotein made up of 393 amino acids, is located on the seventeenth chromosome (17p13.1). p53 was identified by Arnold Levine, David Lane and William Old in 1979. It was originally presumed as oncogene but later declared as a tumor suppressor gene in 1989 [24]. The name p53 was given possibly due to its molecular mass; p53 kDa fraction of cell protein. p53 acts as a master transcription factor which is responsible for activation of cell cycle inhibitors and proapoptotic proteins [25,26]. It has a role in cell cycle control as G1checkpoint (cell growth arrest in G1 to S phase), DNA repair and apoptosis [27]. p53 has been described as “the guardian of genome” and “policeman of the oncogenes” referring to its role [28]. p53 protein bound to the large T-antigen of SV40 virus that induce tumor [29]. Aberrations of p53 are the frequently identified during malignant progression of various types of human cancers including HNCs with mutations in exons 5-9 at p53 locus [30]. p53 mutations are usually considered to be an early event in tumorigenesis in HNSCC. The mutation of p53 protein leads to the pathogenesis of HNSCC patients with expression of p53 protein from 50-60% of the malignant cells [31]. Half life for p53 protein is 6-20 minutes [32], whereas its mutant form has upto 6 hours of half life possibly due to stabilisation of the protein [33]. This increase in half life makes detection of mutant p53 protein possible in tumors by using IHC. p53 remains controversial prognostic indicators for HNSCC despite having such significant role in carcinogenesis. The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the immunohistochemical expression of potential tumor marker p53 in HNSCC and its correlation with various clinicopathological parameters, disease recurrence, overall survival and disease free survival. Molecular and IHC analysis of this crucial tumor suppressor gene p53 may be of diagnostic and prognostic significance in clinical management of HNSCC for better outcomes.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection Criteria and Tissue Samples
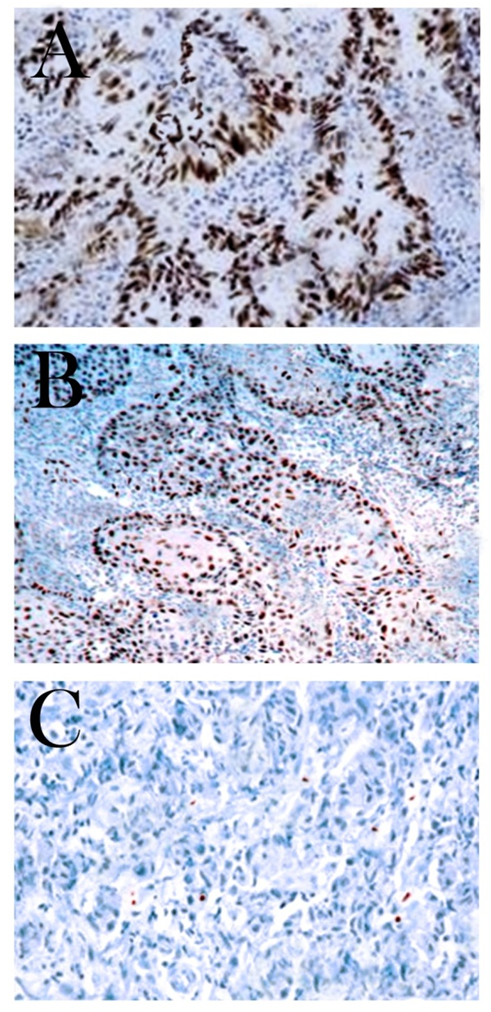
- The study cohort was a series of hundred HNSCC patients referred to surgery in Oncology and Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) department of Base Hospital and Army Hospital Research & Referral, New Delhi, India, from 2013 to 2015. All these randomly selected cases were histopathologically confirmed primary HNSCC cases (92 males & 8 females) with mean age of 57±11.2 (range - 32 to 80) years. Patients who received any kind of anticancer treatment (radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy) before surgical resection, presented with metastatic disease and secondary SCCs of head and neck region were excluded from the study. Ethical approval for the research was obtained from the institutional ethical committee. All subjects were informed about the research work and written consent was taken from all HNSCC patients and controls in accord with set guidelines by ethical review board. The epidemiological and clinicopathological data of these patients were collected from the medical records and reviewed for patient’s clinical outcomes. The clinical staging (stage I to IV) was according to American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM (tumor size, nodes, metastasis) classification system of malignant tumors [34]. Stage I & II were categorized as early stage and stage III & IV were considered as advanced stage of tumor. The morphological gradations of differentiation of the tumors were made according to Broders criteria into well differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated SCC [35]. Procurement of HNSCC biopsy specimen from surgical resection for block formation was done by standard procedure given by AJCC [34]. The tissue sections were fixed in 10% buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin wax for histopathological and IHC analysis. These FFPE blocks were attained from the pathology department of the hospital and cut into 4µm thick sections. One section from each representative block was stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) to confirm the diagnosis. The IHC evaluation was performed on these HNSCC tissue sections to determine p53 protein expression. Epithelial cells with clear brown nuclear staining irrespective of intensity of immunoexpression were considered p53 positive. Colorectal carcinoma served as a positive control for p53 protein in our series.
2.2. Follow up
- All HNSCC patients underwent clinical examinations and received standard adjuvant treatments as required. Tumor response was assessed by follow up of patients for one year / death from the date of surgery at every 2 months interval. The overall survival time was defined as the interval between the dates of surgery and the date of death / last follow up or the last information for censored observations [36]. The disease free survival time was the definite period from surgical resection to the date of the first documented tumor recurrence or a new developed primary tumor observed in head and neck region [37]. Only four patients were lost to follow up (censored) in the current study.
2.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
- IHC for p53 protein expression were performed on 4μm thick tissue sections of primary HNSCC prepared from FFPE tissue blocks. Tissue sections were taken on poly-L-lysine coated slides and fixed in an incubator for approximately half an hour. Sections were deparaffinised in xylene and rehydrated through descendant grades of ethanol. Slides were put in citrate buffer and heated up in pressure cooker for antigen retrieval (pH - 6.0, low pH retrieval). After cooling slides at room temperature for almost 30 minutes and proper washing, sections were subsequently pre-treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in Tris buffered saline (TBS) (pH - 7.4) for 10-15 minutes for blocking endogenous peroxidase activity. After washing with TBS, the slides were incubated in a humidifier chamber with primary monoclonal antibody p53 (DAKO, Denmark). After three thorough washes with TBS, slides were sequentially incubated with streotavidin-horseradish peroxidase complex (secondary antibody, HRP) (Dako, Denmark) for 30 minutes at room temperature according to manufacturer’s guidelines. Immune reactions were revealed by peroxidase activity in 3, 3’- diaminobanzidine (DAB) solution (chromogenic substrate) for approximately 10 minutes. Counterstaining was executed with Mayer’s Hematoxylin, subsequently, dehydrated and cleared with xylene. Mounting of slides was done by Dibutyl phathalate distyrene xylene (DPX) and glass coverslips. Positive and negative controls were also prepared and used to ratify each run of IHC. Colorectal carcinoma served as a positive control for p53 protein with strong nuclear immunoexpression. Negative controls were sections processed in the same manner by using tris buffer and omitting the primary antibody incubation. p53 protein expression was scored as positive if greater than 10% neoplastic cells presented with clear brown color nuclei regardless of staining intensity. Therefore, subsequent analyses were carried out using 10% nuclear reactivity cut-off value based on earlier study for p53 protein [38-40].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Statistical software SPSS (IBM Corp. Released 2017. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp) was used for data compilation and evaluation. Statistical analysis comprehended Pearson chi-square test or Fisher exact test, as appropriate; to assess the association of p53 immunoexpression with clinicopathological parameters (sex, age, TNM stages, tumor grades, alcohol & tobacco consumption habits, family history, tumor sites, lymph node involvement, post-operative adjuvant treatments). Univariate analysis was performed to identify significant involvement of these variables with HNSCC prognosis and survival. Survival analysis (overall survival and disease free survival) was done by using the Kaplan-Meier log rank test [41]. Tests were considered statistically significant when their p-value were < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
- Hundred biopsy proven primary HNSCC cases were inducted for p53 protein expression (92 males & 8 females), which was carried out from 2013 to 2015. The mean age at the time of diagnosis was 57±11.2 (32 to 80) years. 12% patients were under 40 years of age, 47% were between 40-60 years and 41% HNSCC patients were above 60 years. All these primary HNSCC tumors were examined by standard H&E staining and conventional IHC method for p53 expression. All patients were without evidence of distant metastasis (M0) at the time of diagnosis. Tongue (20%) and larynx (20%) were the most common sites involved by HNSCC. According to TNM classification (AJCC) 12% HNSCC diagnosed as stage I, 18% cases as stage II and 18% belonged to stage III. Majority of the cases were diagnosed at the highest clinical stage of cancer (Stage IV- 52%). Thus, locally advanced tumors (stage III & stage IV) accounted for 70% of HNSCC patients and rest 30% had early stage of disease (Table 1). 43% of HNSCC were classified as well differentiated SCC (WDSCC), 47% as moderately differentiated SCC (MDSCC) and 10% as poorly differentiated SCC (PDSCC) as per histological grading system. Of 100 patients, 84% had tobacco either by smoking and/or chewing, 67% were alcohol consumers, 62% had history of consuming both tobacco and alcohol concurrently, whereas 9% had never consumed such stuff. 14% cases had positive family history for malignancy. 74% patients had a positive nodal status at the time of diagnosis. All HNSCC patients had undergone surgery for treatment followed by required adjuvant treatment (radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy) (Table 1).
3.2. One Year Follow up
- Of the 100 individuals included in the current study, four were lost to follow up, hence censored. These censored cases were disease free upto last information. Within one year of follow up period, total 41 patients had died and tumor recurrence was reported in 16 cases. Of these 41 deaths, disease recurrence was cause of death in 13 HNSCC cases and 28 died due to other reasons. Of 55 survived HNSCC patients at the end of analysis, 3 survived with disease and 52 were disease free survivors (Figure 2).
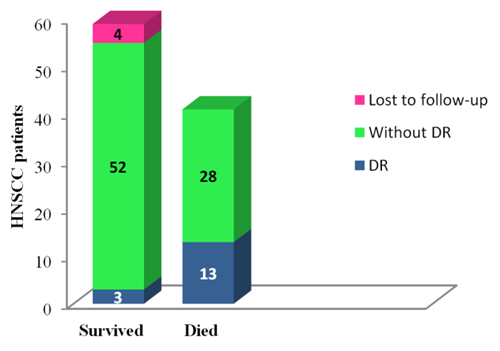 | Figure 2. One year follow-up for HNSCC patients |
3.3. Association between p53 Protein Expression and Clinicopathological Parameters in HNSCC
- The statistical association of p53 immunoexpression and clinicopathological parameters in HNSCC are summarized in Table 1. No significant association was detectable between p53 immunoexpression and sex, age (below 40, 40-60 and above 60 years), tumor grades, tobacco and/or alcohol consumption habits, family history, tumor sites, treatment and disease recurrence. However, this analysis revealed that p53 immunoreactivity was significantly associated with tumor stages (stage I to IV individually, early and advanced tumor stage, p = 0.010 and 0.004 respectively) and lymph node involvement status (p = 0.028) for HNSCC patients (Table 1). Therefore, these were considered as prognostic clinical parameters associated with p53 immunostaining in HNSCC.
|
3.4. Association between p53 Protein Expression, Overall Survival and Disease Free Survival in HNSCC
- Survival analysis was performed by using Kaplan-Meier log rank test to detect the association of p53 immunoexpression with the survival time of HNSCC patients. p53 negative patients had a statistically insignificant tendency for longer overall survival in HNSCC (62.1%) (p = 0.556) (Table 2) (Figure 3). There was no statistically significant difference between duration of disease free survival in p53 positive (77.4%) and p53 negative group (84.6%) (p = 0.608) (Table 2) (Figure 4). Thus, statistical analysis revealed that p53 status had no influence on both overall and disease free survival in HNSCC (Table 2).
|
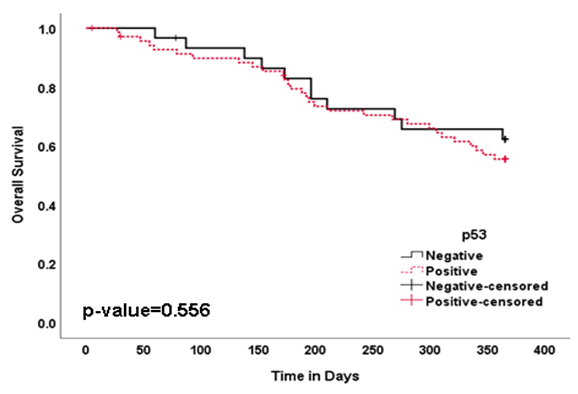 | Figure 3. Survival Curves Showing Overall Survival (OS) in HNSCC Patients with p53 Immunoexpression |
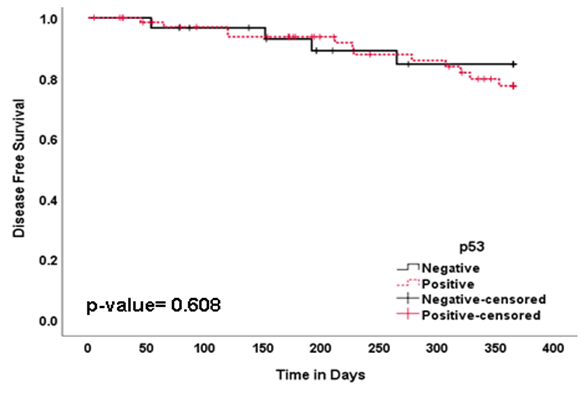 | Figure 4. Survival Curves Showing Disease Free Survival (DFS) in HNSCC Patients with p53 Immunoexpression |
4. Discussion
- HNC is an assorted entity in terms of location, biological or clinicopathologic behaviour determined by several factors. HNSCC patients with same tumor stage have different response to similar therapy, disease progression, disease recurrence and survival [42]. New anticancer therapeutic agents with higher efficacy and lower toxicity are needed for better management of HNSCC population. Identification of molecular tumor markers in malignancy may not only categorize the high risk patients but it may also help to choose the patients who require more aggressive treatment to improve the survival [43]. p53 protein plays an essential role in regulation of pathways which are accountable for maintenance of the cellular integrity after DNA damage [31]. Several studies have proved that alterations in p53 expression occur in very early stage of the disease and can be detected in premalignant lesions [44]. The p53 expression can estimate the extension of disease better than TNM staging and may stratify patients according to risk of disease recurrence [45]. Although p53 is one of the most commonly studied molecular marker in HNSCC [30,46], still, acquaintance about the role of p53 protein in HNSCC has not yielded a satisfactory clinical outcome. In order to improve our knowledge about clinical and prognostic relevance of p53 protein expression in primary HNSCC, we investigated immunohistochemically a series of 100 surgically treated HNSCC patients and correlated the results with traditional clinicopathological parameters, probability of disease recurrence, disease free survival and overall survival. The IHC is simple, fast and inexpensive way to perform and evaluate the head and neck tumors. Although p53 protein expression by IHC has been widely used as a substitute for mutation analysis but p53 detection does not necessarily correspond with p53 mutation [47]. The application of molecular predictors of clinical outcome would be remarkably useful to allow rational selection of patients who are more likely to be benefited from treatment and to spare unnecessary toxicity to those with poor chance of response. p53 expression ranges from 25-90% cases of HNC [48]. p53 expression was observed in 28.5% cases by Etemad-Moghadam et al in Iraq [49], 31% cases by Dragomir et al [50], 57.7% cases by Gonzalez-Moles et al [51], 63.3% cases by Abrahao et al 2011 in Brazil [52], while 85.7% cases by Khan et al in Indian population [53]. In the current study, 70% of investigated HNSCC revealed positive nuclear p53 immunoexpression in Indian population based on 10% cut-off points. The ambiguity in results of p53 in HNSCC probably attributed to different methodology, variation in fixation procedures, interpretive error in IHC technique, applied antibodies, the arbitrary cut-off points used to define p53 expression, false positive and false negative results, difference in ethnicity and involved risk factors [54]. The existence of heterogeneity in selected patient population, stage and treatment also confines the HNSCC analysis.No significant association present between p53 expression and age groups in HNC patients in several studies [55-57]. Our results (p = 0.963) are also in agreement with these researcher as we did not find any correlation between age of HNSCC patients with p53 expression. On the other hand, De paula et al evaluated HNSCC in young (under 45 years) and old (46-92 years) patients group and reported a significantly higher expression of p53 in younger patients [58]. The histological grades of tumor showed strong association with p53 expression in HNSCC in various previous studies [48,59-62]. Where Warnakulasuriya et al 1992 reported no association between degree of differentiation and p53 expression [63]. Our findings are also in agreement with this result as we also could not find any association between tumor grades of differentiation and p53 expression in current study (p = 0.308).The probability of oncogenesis increases with the excessive consumption of tobacco and alcohol [64]. Heavy smoking and alcohol uses are believed to disrupt the two major pathways controlling cell proliferation that of the tumor suppressor protein p53 and of the retinoblastoma gene (pRb) [65]. The strong epidemiological association of p53 protein mutation and tobacco consumption in HNC patients reported in numerous studies [66,67]. On the contrary, few reports have shown no statistically significant association of p53 expression with tobacco and alcohol consumption [46,62,68]. In current study, association of p53 expression in HNSCC with tobacco and alcohol consumption were also not observed (p = 0.634 and p = 0.178 respectively). The divergence of results may be due to geographic distribution and difference in prevalence of risk factors. Peltonen et al found that patients with negative family history for cancers contained more p53 mutation than patients with positive family history [69]. Conversely, there was no association between p53 expression and family history for cancer in our observation (p = 0.615).Our study found no correlation between p53 expression and tumor site (p = 0.457). This result was in accordance with several similar studies showed no association [55-57,62]. Whereas, a significant association was noted between p53 immunoexpression and tumor site in HNSCC by few researchers [58,70].Yan et al reported no correlation between p53 expression and disease stage, node status, early local recurrence [59]. In present study, p53 immunoexpression was statistically significantly correlated with individual tumor stage (stage I, II, III and IV) (p = 0.010), early and advanced tumor stage (p = 0.004), Lymph node involvement (p = 0.028). However, no association was noticed between given treatment, disease recurrence and p53 expression in current study.The survival rate remains low in HNSCC than other malignancies perhaps due to detection of advanced stage disease [71]. Many immunohistochemical studies have failed to detect any correlation between p53 expression and clinical outcome [39,72-75]. However, a number of other studies have reported the association of p53 with clincopathological variables and reduced survival [36,46,65,76] while some observed it to be associated with prolonged survival [77]. We found the insignificant longer overall survival (p = 0.556) and disease free survival (p = 0.608) in p53 negative patients than p53 positive. The expression of p53 can serve a prognostic role for disease recurrence and disease specific mortality in HNSCC [78], whereas no association of p53 expression serve as a marker for poor prognosis [79]. Correlation between p53 overexpression and a very poor prognosis in 'end stage disease patients', indicating that p53 over expression has a very specific effect on tumor behaviour in the late stages of the disease [72]. Our findings of present study suggest that p53 expression serves as a marker for poor prognosis in HNSCC patients. However, we studied p53 expression in a limited number of cases; studies based on large population can provide more insight into possible biological and clinical relevance of p53 protein in HNSCC.
5. Conclusions
- Despite aggressive multidisciplinary treatment strategies, the clinical outcome of HNSCC remains dismal and has not changed significantly in the past few decades. Understanding of the global demography, potential prognostic molecular markers, current statistics and risk factors of HNSCC are crucial in order to accelerate further progress in the field of anticancer therapies, effective prognostic system and reduction of mortality rates. p53 mutations are considered to be an early event in carcinogenesis and play a diverse role in the development of HNSCC. Considering our findings, we conclude that p53 immunoexpression have no statistically significant association with aforementioned prognostic parameters except tumor stage and lymph node involvement. No correlation observed between p53 expression and disease recurrence, overall survival, disease free survival in our series of HNSCC patients. Thus, p53 in HNSCC is not recommended as a potential prognostic tumor marker. This study will considerably contribute in the field of oncology and raise awareness about the clinical and prognostic significance of p53 immunoexpression in HNSCC. The result suggest that further investigations on larger group of patients are still required to elucidate the clinical and prognostic potential of p53 in HNSCC as small sample size limits the conclusiveness of the current study. p53 expression in HNSCC may provide clinicians more accurate information to evaluate tumor aggressiveness and survival rates for better future management of the disease.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML